
A new technical study that is more detailed and extensive than previously achieved, the US Energy Department's National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL) has significantly increased the potential for US building rooftops to generate electricity from solar PV (photovoltaics) systems.
The analysis within the report entitled “Rooftop Solar Photovoltaic Technical Potential in the United States: A Detailed Assessment,” used detailed light detection and ranging (LiDAR) data for 128 US cities across the country, along with improved data analysis methods and simulation tools, to update and make more accurate estimates of technical potential of PV on rooftops at the national, state, and zip code level.
Unlock unlimited access for 12 whole months of distinctive global analysis
Photovoltaics International is now included.
- Regular insight and analysis of the industry’s biggest developments
- In-depth interviews with the industry’s leading figures
- Unlimited digital access to the PV Tech Power journal catalogue
- Unlimited digital access to the Photovoltaics International journal catalogue
- Access to more than 1,000 technical papers
- Discounts on Solar Media’s portfolio of events, in-person and virtual
Or continue reading this article for free
The report stated that the technical potential of 1,118GW of capacity and 1,432TWh of annual energy generation was possible, equivalent to 39% of current US electricity sales. This is almost double (664GW – 800 TWh) the previous analysis undertaken and reported in 2008.
The significant difference was said to be attributed to increases in PV module power density, improved estimation of building suitability, higher estimates of the total number of buildings, and improvements in PV performance simulation tools that previously tended to underestimated production.
NREL indicated that the latest total technical potential capacity analysis assumed a module efficiency of 16% to represent a mixture of various technology types. If a module efficiency of 20% were assumed instead, which corresponds to current premium systems, each of the technical potential estimates would increase by about 25% above the values stated in this report
“An accurate estimate of PV's technical potential is a critical input in the development of regional deployment plans,” said Pieter Gagnon, an engineering analyst of solar policy and technoeconomics at NREL and lead author of the report. “Armed with this new data, municipalities, utilities, solar energy researchers, and other stakeholders will have a much-improved starting point for PV research and policymaking, both regionally and nationwide.”
Robert Margolis, NREL senior energy analyst and co-author of the report added, “It is important to note that this report only estimates the potential from existing, suitable rooftops, and does not consider the immense potential of ground-mounted PV. Actual generation from PV in urban areas could exceed these estimates by installing systems on less suitable roof space, by mounting PV on canopies over open spaces such as parking lots, or by integrating PV into building facades. Further, the results are sensitive to assumptions about module performance, which are expected to continue improving over time.”
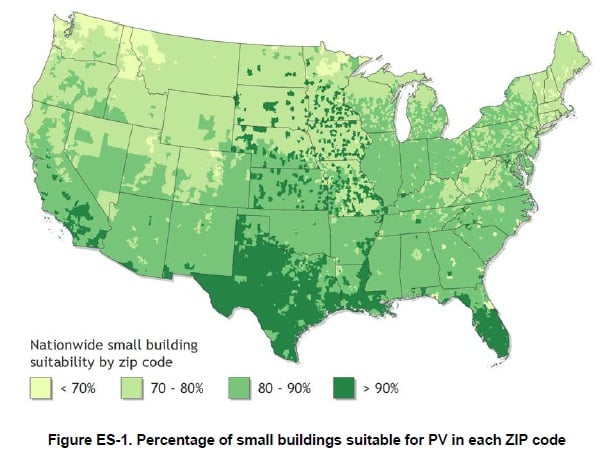
The new report noted that although only 26% of the total rooftop area on small buildings (5,000 ft2 or smaller) was suitable for PV deployment, the significant number of buildings in this classification meant that small buildings actually had the greatest technical potential.
Therefore, NREL noted that small building rooftops could accommodate 731GW of PV capacity and generate 926 TWh/year of PV energy, which represented approximately 65% of rooftop PV’s total technical potential.
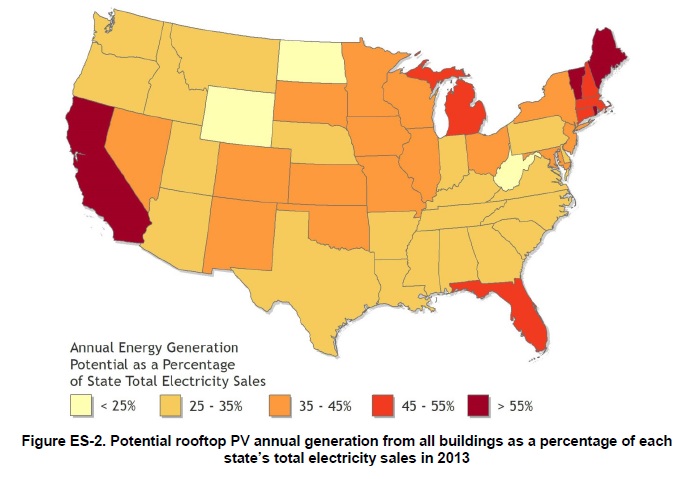
With regards to medium and large building rooftop classifications, total installed capacity potential of 386GW and energy generation potential of 506 TWh/year was calculated, which represented approximately 35% of the total technical potential of rooftop PV.
