Background
Residential PV systems are generally installed on the rooftop of residential buildings, with a large metal surface area, higher distance from the ground and an exposed location. Such PV systems are therefore potential lightning targets during thunderstorms. If a power station does not have good lightning protection and grounding, the probability of being struck by lightning is extremely high and this could cause fire, electricity safety issues and property losses.
The PV industry has matured and system design and construction have become more standardized. However, there are still doubts about requirements for lightning protection: The whole design and construction of the system in this paper meets the requirements from the point of view of components, brackets, inverters, electricity distribution boxes and grounding cables.
Why is lightning damage still a common occurrence? In order to answer this, we will share with you problems that are easily overlooked during installation and ways to make system protection more effective.
PART 1: General Lightning Protection Solution
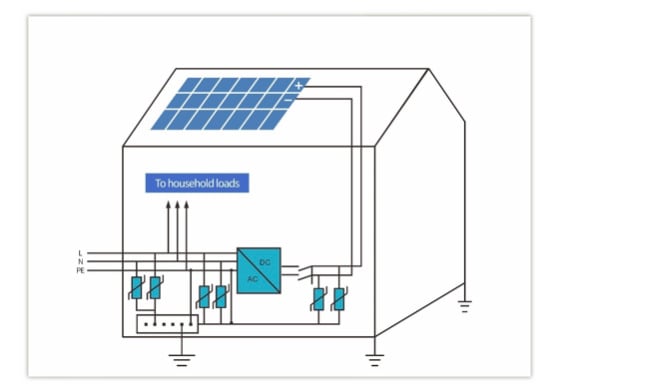
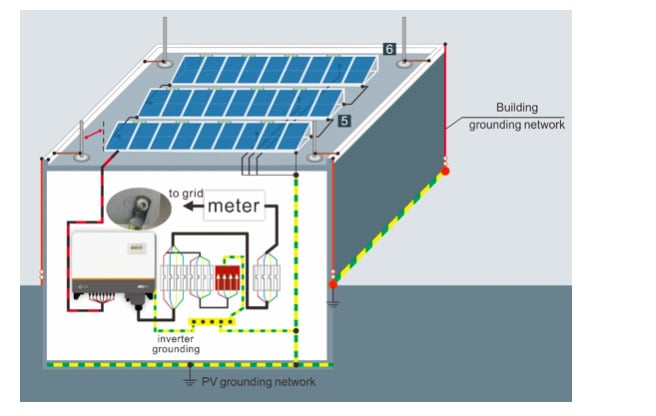
For areas with relatively less lightning frequency, grounding methods shown in Diagram 1 are commonly used without installation of additional lightning rods. If a system is installed on a flat roof, it tends to ground via the inverter cover or connect to the building’s existing lightning protection system. Such lightning protection is potentially inadequate for areas with high lightning probability.
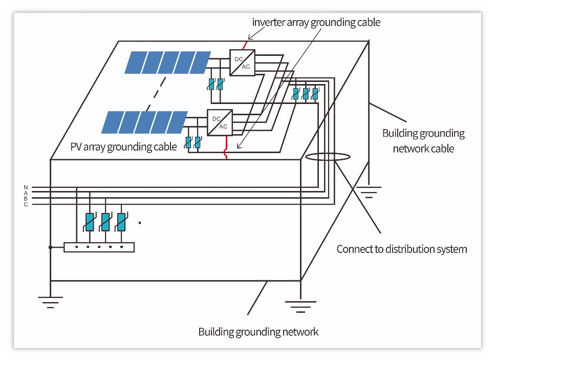
PART 2: Enhanced Lightning Protection Solution
Before considering the effective lightning protection of a PV system, we first need to understand the common types of lightning strikes.
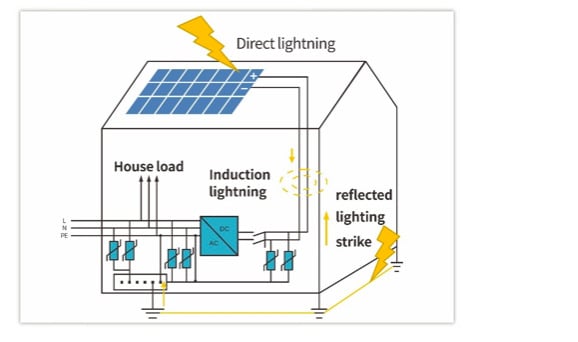
For residential PV systems, type one and type two lightning strikes are the most common: direct lightning and induced lightning strikes. If the property is in a lightning-prone area or there are other high metal objects on the rooftop, e.g. solar thermal heaters, water tanks or satellite antennae, the probability of these two strike types will be higher. It is therefore necessary to enhance and strengthen lightning protection during the design stage.


To enhance the effectiveness of lightning protection for residential systems, in addition to normal lightning protection measures, the following points should be considered:
1) If the system has a large capacity or is located in an area with high lightning strikes, it is necessary to install a lightning rod beside the solar array;
2) If there are other metal facilities on the roof, the DC side of the PV system should be kept as far from these structures as possible. Make sure the PV mounting system does not come into contact with these structures. It is also recommended to install a lightning rod on the roof.
3) Reduce the general PV system cabling cross-area to decrease the strength of an induced lightning strike.
4) It is recommended to implement a separate lightning protection solution for the PV system and avoid simply connecting to the building’s original lightning protection system.
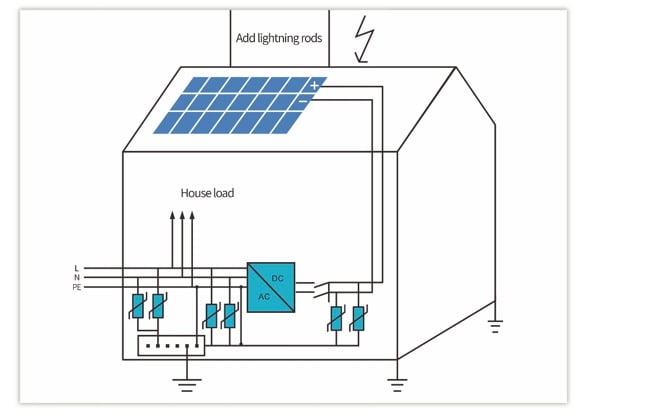
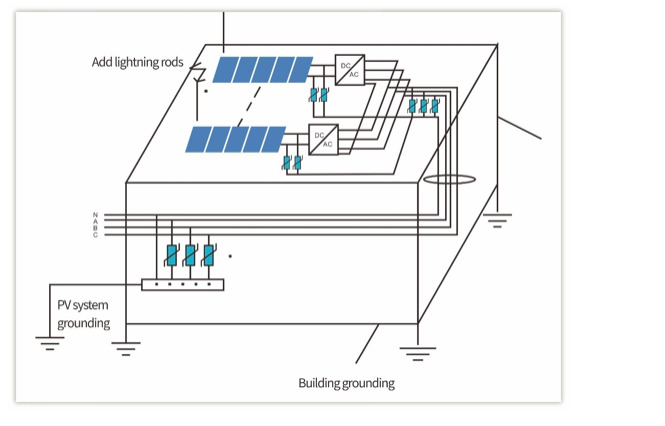
PART 3: Case Study
This project is in Fenghua, China. According to statistics, the area’s annual average lightning days of more than 75 define it as lightning-prone. The on-site residential buildings have a large flat roof area and the total installed capacity is 28kW, with a GCI-25K-5G inverter, so the lightning protection system scheme shown in the figure below is what was implemented.
In addition to the building lightning protection for the solar modules, brackets, inverters, and electricity distribution boxes, the lightning protection system for the project adds the following safety features based on the plan above:
For the most vulnerable parts of the system e.g. the inverter, make sure both the electrical (internal) grounding and cover (external) grounding are effectively connected.

1) Added four 1.5m length and Φ10mm round steel lightning rods at the four corners of the array and welded onto the building’s own lightning belt to reduce a direct lightning strike’s impact on the system.
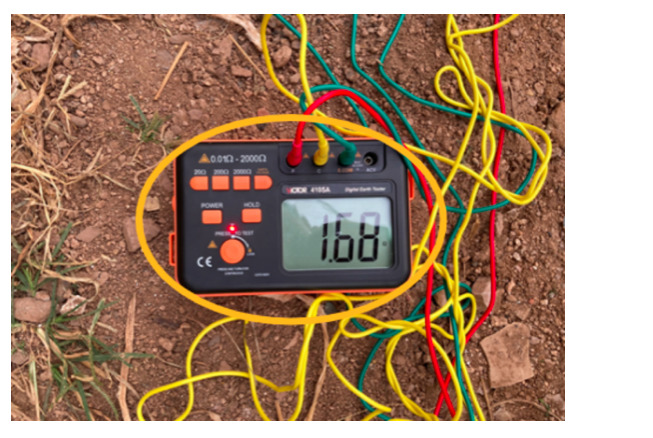
2) Separated grounding of residential PV system: Choose a location where the ground is thick and humid enough and dig a 1.5m-deep hole, then use Φ8 round steel (40*4mm flat steel can also be used or Φ10 round steel) to make the separated grounding. The grounding resistor is 1.68Ω and meets the requirement of less than 2Ω.

PART 4: Summary
The lightning protection and grounding of residential PV systems cannot be ignored. Therefore, in the system installation process, we must not only consider the scientific lightning protection and grounding technology, but also strengthen the system's lightning protection according to site conditions. In short, spend time considering your PV system lightning protection, because meticulous care and attention in the design and installation stage can avoid many problems later. A safe and stable lightning protection and grounding construction can avoid system damage and even personal and property losses.
