PV InfoLink has updated its analysis of product market share based on different sizes of silicon wafers, indicating that, with M10 modules having a share exceeding 60% in the first half of the year, the overall figure for the format in 2022 has increased to 58%. With the analysts estimating the market share of 210 modules at just over 20% for the same period and, with some major players choosing to base investment in new technology cells on M10, the trend would suggest its continued growth to achieve mainstream status.
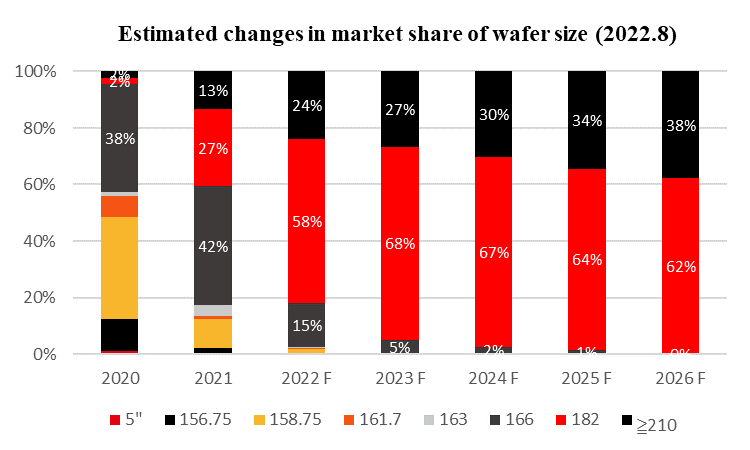
Market share expectations for M10 products have increased several times since the launch of M10 and G12 modules in 2020. Initial analysis suggested that use of M10 products made upstream and downstream matching easier to achieve, leading to a slight advantage in early comparisons. ≥ G12 products have a large-scale cell capacity layout which, over time, may result in the format being able to take advantage of equipment capability to win greater market share, although such a prediction only considers manufacturing capacity rather than an analysis of the technology and application of the product.
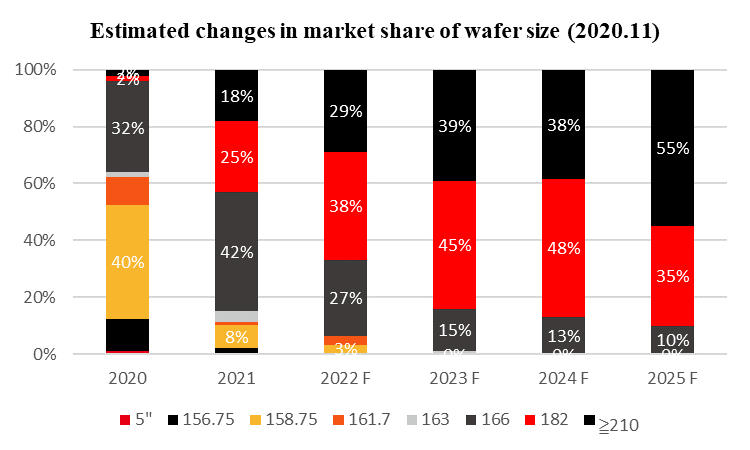
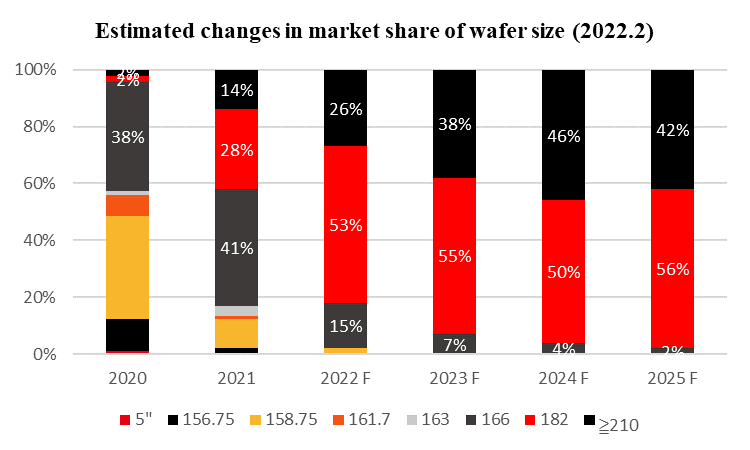
Some leading industry players, represented by LONGi, Jinko and JA Solar, believe M10 products have clear advantages in terms of reliability, manufacturing, packaging, installation, system design and electrical safety, citing application in numerous projects during the past two years as the basis for this view:
- The M10 format has maintained an advantage not only in silicon wafer yield, but also in efficiency and yield of PERC cells. In the case of TOPCon cells, the gap between the manufacturing yield of G12 and M10 has been further widened.
- Portrait packaging is considered to be inconvenient at a project site, particularly for the secondary transfer of modules, with the advantages of the landscape packaging enabled by M10 modules recognized by many.
- In terms of manual installation, workers generally feel 1.3-meter-wide modules to be too wide and heavy, resulting in fatigue and a reduction in installation efficiency. Statistical results also indicate higher breakage rates for larger modules.
LONGi believes that the M10 format can also reduce costs during the manufacturing process. Larger modules based on a G12 wafer do not necessarily reduce costs at module level due to higher expenditure on the wafer and module bill of materials (BOM). At the system level, the M10 module can achieve lower total costs compared with its larger size equivalent when considering cabling and tracker related expenditure.
- For cabling, the total cost is at its lowest when module current is between 14 and 15A, which is the working current of the large-size bifacial module. Cabling costs decrease as the module’s maximum working current increases, but resistive costs increase on a linear basis under this scenario.
- In the case of trackers, the limitation is tracker length. With a 1P tracker, larger sized modules will reduce the number of strings from three to two, meaning the total power carried by a single tracker is lower and the cost per watt is higher. With a 2P tracker, larger modules will eliminate one string of modules. The total power carried by the tracker will be equivalent to that of a large-size module, but there will now be a string of modules arranged on separate sides of the main axis, leading to power loss due to mismatch.
- When cost savings are combined with an M10 module’s full life cycle reliability guarantee, it is clear that initial cost efficiency and long-term return on investment can be improved.
As can be seen from module application in numerous projects, power station investors and EPC companies have been faced with a choice between high power and rational consideration of value and risk, with a resultant pause in the trend towards increasing the size of cells and modules witnessed for several years. As the respective market share of M10 and G12 products evolves, the PV industry may return to standardization, with the objective of technological innovation once again focused on the critical metric of conversion efficiency improvement.

