By Eric Pilat, CEA-INES, LMPV (Module Laboratory); Manuel Hidalgo, Senior Research Scientist, ARKEMA Sollia Laboratory, LMPV; Dominque Thil, ARKEMA Sollia Laboratory, LMPV; Marion Vite, CEA-INES, LMPV (Module Laboratory)
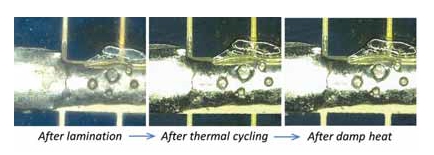
A major cause of failure in PV modules is related to the penetration of the module by moisture and its retention within. The presence of moisture results in corrosion of metallic contacts or accelerates the molecular degradation of the encapsulant, causing a loss of transparency and in some cases the development of yellowing. The moisture penetration may be intrinsic to the resin itself, but most often it will occur at the interfaces. As a consequence, the adhesion of the resin to glass, metallization, cell and backsheet surfaces may be affected. Engineers involved in the assembly of PV modules used to link adhesion degradation issues to poor conditions for storing polymeric materials, especially the encapsulation resin and the backsheet. In this paper another cause, which has not yet been studied by specialists, is discussed. It is shown that the welding of copper strips can induce residues which prevent the satisfactory adhesion of the resin, resulting in elamination. This phenomenon is identified by ‘spots’ along the busbars after lamination. The study highlights the possible consequences of these defects for a module’s performance, after consecutive thermal cycling, damp-heat and humidity-freeze testing. Recommendations are also given for choosing a suitable solder flux and optimizing the soldering process, in order to maintain satisfactory control over potential delamination problems.