By Ingrid Romijn, Researcher, ECN Solar Energy; Bas van Aken, PV Modules and Application Group, ECN Solar Energy; John Anker, ECN Solar Energy; Ian Bennet, Member of the Module Technology and Application Group, ECN Solar Energy; Bart Geerligs, Coordinator of R&D, ECN Solar Energy; Nicolas Guillevin, Researcher, ECN Solar Energy; Astrid Gutjahr, Researcher, ECN Solar Energy; Martien Koppes, ECN Solar Energy; Eric Kossen, Senior Process Engineer, ECN Solar Energy; Kees Tool, ECN Solar Energy; Marten Renes, Tempress Systems BV; Peter Venema, Tempress Systems BV; Nico van Ommen, Eurotron BV; Jan Bak, Eurotron BV
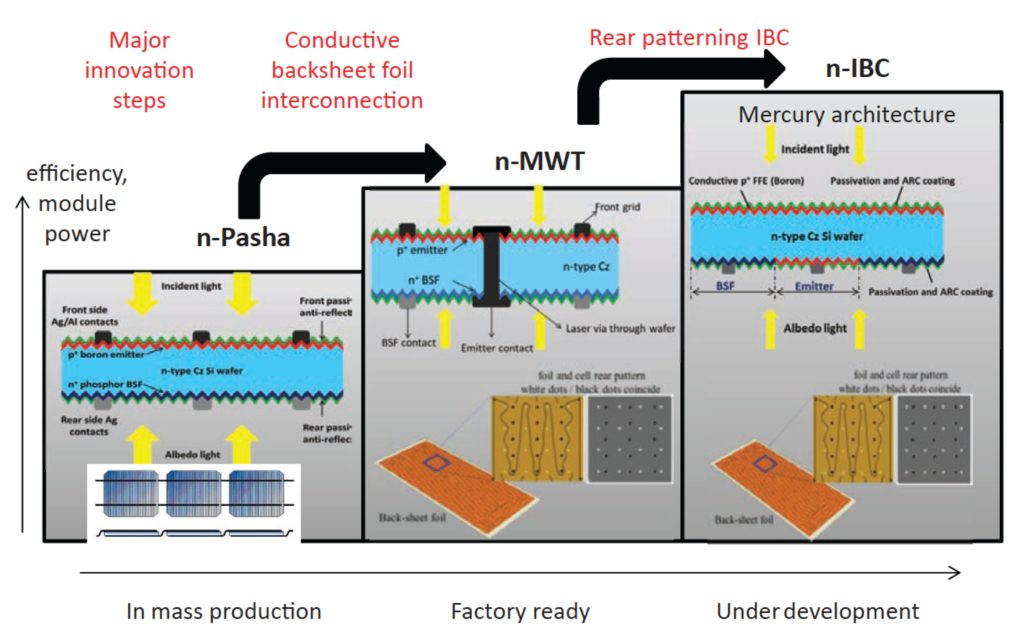
This paper reports on the progress of R&D in two n-type cell and module concepts: the n-Pasha solar cell and bifacial module, and the n-MWT (metal wrap-through) cell and module. Both are part of ECN's technology platform, acting as a roadmap for research in n-type Cz cells and modules. The technology platform also encompasses low-cost IBC solar cells. In the case of n-Pasha, recent developments involve improved stencilprinted metallization, resulting in an increased Isc and Voc and efficiencies of up to 20.5%. For the bifacial module aspect, research has been done on the effect of different albedo on the module output. A gain of 20%rel in module output power was obtained with an optimized background, increasing the module power from 314W to 376W. As regards n-MWT cells, the front-side metallization pattern has been changed significantly. The number of vias for conducting the emitter current to the rear has been increased from 16 to 36, resulting in reduced lengths of busbars and fingers and consequently an increase in FF. At the same time, the metal coverage on the front side has been reduced from 5% to 3% of the total area, leading to a gain in Isc and Voc and a significant reduction in Ag consumption. All these factors will result in a lower cost/Wp. For the improved n-MWT design, average efficiencies of 20.8% over a large batch (134) of cells have been obtained, with the highest recorded efficiencies being 21.0%.