By C.C Huang, R&D Division, Motech Industries; Y.T. Huang, Department of Photonics, National Chiao Tung University; Y.W. Tseng, Department of Photonics, National Chiao Tung University; W.H. Chen, Motech Industries; T. Fang, R&D Division, Motech Industries; C.C. Li, R&D Division, Motech Industries; C.C. Tsai, Professor, National Chiao Tung University
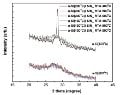
A hydrogenated amorphous Si (a-Si:H) film, combined with a silicon nitride (SiNx:H) capping layer and a post-deposition anneal, can hugely enhance the surface passivation on crystalline silicon wafers. In this work, the influence of various deposition temperatures of a-Si:H films on the thermal stability of a-Si:H/SiNx:H stacks and a possible mechanism are discussed. Both minority carrier lifetime measurement and grazing-angle XRD were employed to study the thermal stability of a-Si:H/SiNx:H stacks, and the results are interpreted in terms of dihydrides concentration and epitaxial crystallization. With an appropriate thermal treatment, the a-Si:H film deposited at 130°C and capped by SiNx:H showed better passivation performance than 200°C-deposited a-Si:H/SiNx:H stacks, but under an excessive thermal budget the former showed more severe degradation of carrier lifetime. The more dihydride-rich composition within 130°C-deposited a-Si:H/SiNx:H stacks could be regarded as providing more effective intermediates for hydrogen interchanges, but on the other hand, it is also more susceptible to epitaxial crystallization.