By Thomas Weber, Project Manager, PI-Berlin; Juliane Berghold, Head of the PV Technology and R&D Services Business Unit, PI-Berlin
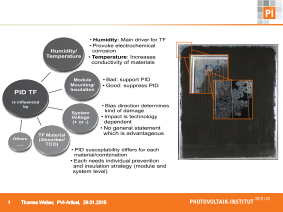
The current standards (IEC 61646 and IEC 61730-2, and IEC 62804 draft for c-Si only) are clearly insufficient to guarantee satisfactory long-term stability and energy yield for thin-film modules, given that reports from the field, as well as from laboratory test results (beyond IEC testing), in some cases show significant degradation of IEC-certified modules. Accordingly, thin-film modules can also exhibit degradation effects, such as TCO corrosion and power degradation, because of potential-induced degradation (PID). This paper presents the results obtained for thin-film modules subjected to bias and damp-heat (BDH) conditions in both indoor and outdoor tests. In order to assess module lifetimes for different thin-film technologies with respect to PID, indoor- and outdoor-determined leakage currents are compared and analysed, taking into account weather data and results from accelerated ageing tests. Finally, on the basis of simulations and investigations for different installation locations, module lifetimes are estimated and discussed.