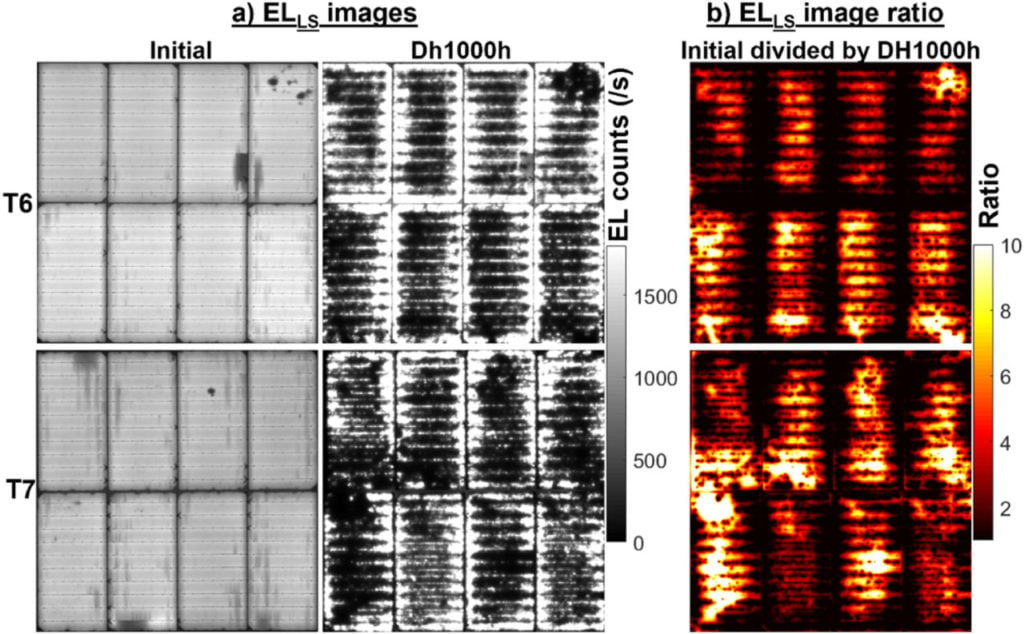
Scientists from the University of New South Wales have published a report into passivated emitter and rear contact (PERC) and tunnel oxide passivated contact (TOPCon) solar modules, finding that the latter has endured “significant degradation” in damp heat testing.
The results of the study were published in the report, ’Buyer aware: Three new failure modules in TOPCon modules absent from PERC technology’. The researchers tested a range of both TOPCon and PERC modules, with varying components, such as polyolefin elastomer and ethyl-vinyl acetate, to determine how exposure to damp heat environments could affect the modules’ performance.
Try Premium for just $1
- Full premium access for the first month at only $1
- Converts to an annual rate after 30 days unless cancelled
- Cancel anytime during the trial period
Premium Benefits
- Expert industry analysis and interviews
- Digital access to PV Tech Power journal
- Exclusive event discounts
Or get the full Premium subscription right away
Or continue reading this article for free
They found that variations in components made little difference to the performance of the modules in this environment, but that the use of TOPCon versus PERC technology made a significant difference. Over 1,000 hours of testing in damp heat environments, PERC modules endured a maximum power loss of just 1-2% relative, compared to a much higher, and wider-ranging, power loss of 4-65% relative in TOPCon modules.
The team suggested that “electrochemical reactions involving moisture” were likely to blame for the poor performance among TOPCon modules, with three types of failures observed among TOPCon modules: point-localised failure, failure at the connection point of ribbons and busbars and failure throughout “the whole area of cells [and] modules”.
While the researchers noted that the specific contaminant responsible for this decline in output is “unclear at present”, they speculated that the presence of sodium and chlorine on solar modules, transmitted from human fingertips during assembly and transportation, could have an effect on TOPCon cell, which were “found to be particularly vulnerable”.
This could be a significant development as TOPCon modules are expected to become more commonplace in the global solar sector. Vitor Rodrigues, technical director of Iberia and Latin America at GCL SI, spoke at Large Scale Solar Europe summit in London this week, and announced that “PERC will start to disappear” in 2024 as developers shift their focus from PERC to other technologies, such as TOPCon.
“Urgent and extensive research efforts are crucial to substantially increase our comprehension and fortify the reliability of TOPCon cells against the pernicious effects of moisture and other contaminants,” wrote the researchers in the report, highlighting the importance of further research into the performance of TOPCon modules in humid environments.






