Federal tax provisions set out by members of Congress one week before Christmas did not bring good tidings to the US solar industry.
While the wind industry wrangled an extra year of federal incentives in the tax package, the US$1.37 trillion budget omitted the extension of the solar investment tax credit (ITC) industry groups had lobbied for throughout the year.
Unlock unlimited access for 12 whole months of distinctive global analysis
Photovoltaics International is now included.
- Regular insight and analysis of the industry’s biggest developments
- In-depth interviews with the industry’s leading figures
- Unlimited digital access to the PV Tech Power journal catalogue
- Unlimited digital access to the Photovoltaics International journal catalogue
- Access to more than 1,000 technical papers
- Discounts on Solar Media’s portfolio of events, in-person and virtual
The only federal incentive for solar installations, the solar ITC (which extends to storage, when co-located and co-developed) started its decline on 1 January.
The incentive, signed into law by President George W Bush in 2005 and renewed three times since, allowed solar system owners to recoup 30% of a project’s total cost from their taxes. The subsidy dropped to 26% on 1 January of this year and will depreciate further next year to 22% before leveling at 10% for utility and commercial solar projects and expiring entirely for the residential market in 2022.
The Solar Energies Industries Association (SEIA), which has fronted the lobby to get the credit extended, has said that a 10-year extension of the full credit until 2030 would spur more than US$87 billion in investment and generate 81.8GW of deployment above the baseline.
Developers and analysts approached by PV Tech Power agreed that while an extension would turbocharge growth and level a federal tax code many believe to be biased towards fossil fuels, the utility-scale segment of the industry will weather any subsequent dip in growth. This is largely due to ever-declining materials costs, improving technology efficiencies and the maturity of financing models. The depreciation of the credit may have a bigger impact in the smaller-scale solar segments, where system costs are higher, and in the storage industry, where the technology is greener and the economic case for a subsidy is stronger.
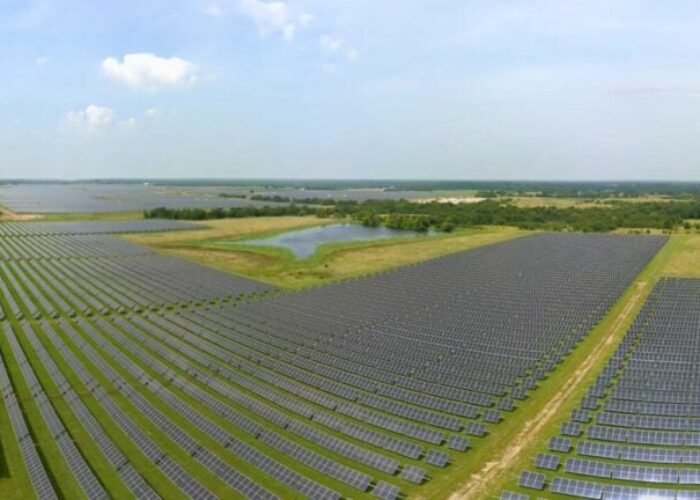
Annual capacity is set to steadily increase in the US between 2020 and 2022 in the utility-scale, residential and commercial segments, BloombergNEF figures show. The firm estimates that new solar additions will leap from 11.1GWDC at the end of 2019 to 14.9GWDC in 2020, 16.1GWDC in 2021 and nearly 18GWDC in 2022.
The rush to safe harbour
In 2020, the capacity of new installations is set to eclipse the 12-month record set in 2016 when 14.1GWDC was installed, or double the 7.3GWDC the year prior. The boom was due to the scheduled step-down of the solar ITC from 30% to 10% (a plan that was ultimately nixed) in 2016.
A similar phenomenon is at work once again, with a rush of project developments announced at the tail end of 2019 as developers met the conditions needed to qualify them for the full 30% credit before it started depreciating. In December 2019, analyst Wood Mackenzie noted that 21.3GW of new utility PV projects were announced from Q1 to the end of Q3 of 2019, bringing the contracted utility PV pipeline to a record high of 45.5GWDC.
US Internal Revenue Service deems a project’s construction to have officially “begun” when either “physical work of a significant nature” has started, or 5% of a project’s total cost has been spent. Purchasing – or safe harbouring – inverters and panels is one of the simplest ways developers can meet that benchmark and qualify their project for the existing ITC rate.
In December, residential and commercial developer Sunnova secured US$150 million of financing to purchase safe-harbour equipment, following in the footsteps of SunPower who purchased 200MW of safe-harboured panels, or enough to satisfy its residential lease customers and commercial PPAs through to 2022. Texas utility-scale developer 7X Energy revealed that it had purchased 2GWAC-worth of inverters.
“It’s a call to action from a selling perspective,” says Daniel Marino, chief commercial officer at BayWa r.e. Solar Systems LLC, the firm’s distribution, residential and commercial and industrial business. The step-down “is helping solar companies sell more solar in the short-term because of the threat of an impending charge”.
This is an extract of an article first published in Volume 22 of PV Tech Power. The full article can be read here, or in the full digital copy of PV Tech Power 22, which can be downloaded for free here.