A report published under the US Department of Energy’s (DOE) Path to SunShot series by the National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL) and Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (Berkeley Lab) has revealed solar power could deliver US$400 billion in environmental and public health benefits throughout the US by 2050.
“We find that a U.S. electric system in which solar plays a major role—supplying 14% of demand in 2030, and 27% in 2050—would result in enduring environmental and health benefits. Moreover, we find that the existing fleet of solar plants is already offering a down-payment towards those benefits, and that there are sizable regional differences in the benefits,” said Ryan Wiser of Berkeley Lab's Energy Technologies Area.
Try Premium for just $1
- Full premium access for the first month at only $1
- Converts to an annual rate after 30 days unless cancelled
- Cancel anytime during the trial period
Premium Benefits
- Expert industry analysis and interviews
- Digital access to PV Tech Power journal
- Exclusive event discounts
Or get the full Premium subscription right away
Or continue reading this article for free
“Moreover, we find that the existing fleet of solar plants is already offering a down-payment towards those benefits, and that there are sizable regional differences in the benefits.”
The report, The Environmental and Public Health Benefits of Achieving High Penetrations of Solar Energy in the United States, centres on the financial benefits of reduced greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions, air pollution-related diseases and water usage under high-penetration solar forecasts. The report is one of eight reports produced through a collaborative effort by DOE and researchers at four national laboratories: the National Renewable Energy Laboratory, Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory, Sandia National Laboratories and Argonne National Laboratory. They examine the lessons learned in the first five years of the Sunshot Initiative and the challenges and opportunities the industry faces in the final five.
The report is founded upon a scenario-based analysis in which SunShot’s cost targets (of achieving grid parity by 2020) that result in solar meeting roughly 14% of US electricity demand by 2030 and 27% by 2050 is compared with a ‘no new solar’ (NNS) baseline scenario in which no new solar is deployed after 2014. This framework is then used to assess the potential benefits of all incremental solar deployment.
Benefits of the existing fleet of solar projects
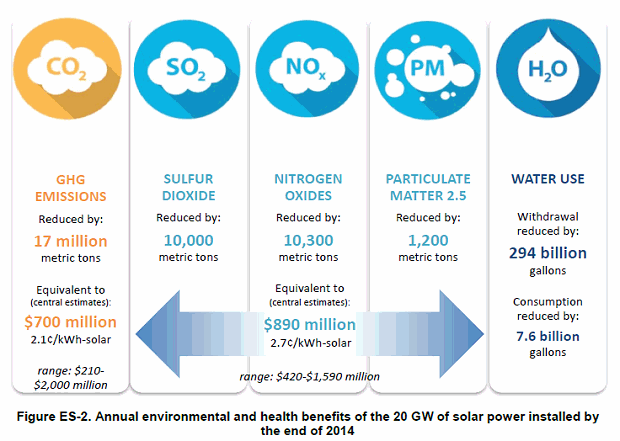
At the end of 2014, 20GW of solar capacity had been installed across the nation, which displaced GHG emissions by 17% million tonnes, with an annual benefit of approximately US$700 million if calculated according to an estimate of the ‘social cost of carbon’. More than 50% of these benefits come from emissions reductions in California.
The overall health and environmental benefits from the reduced air pollutants from power plants as a result of solar culminate into an estimated US$890 million from avoiding premature deaths and a host of other health ailments.
According to the ‘social cost of carbon’ estimate, the US existing fleet of solar installations and plants already saves more than US$1.5 billion per year.
Benefits from a high-penetration solar energy future

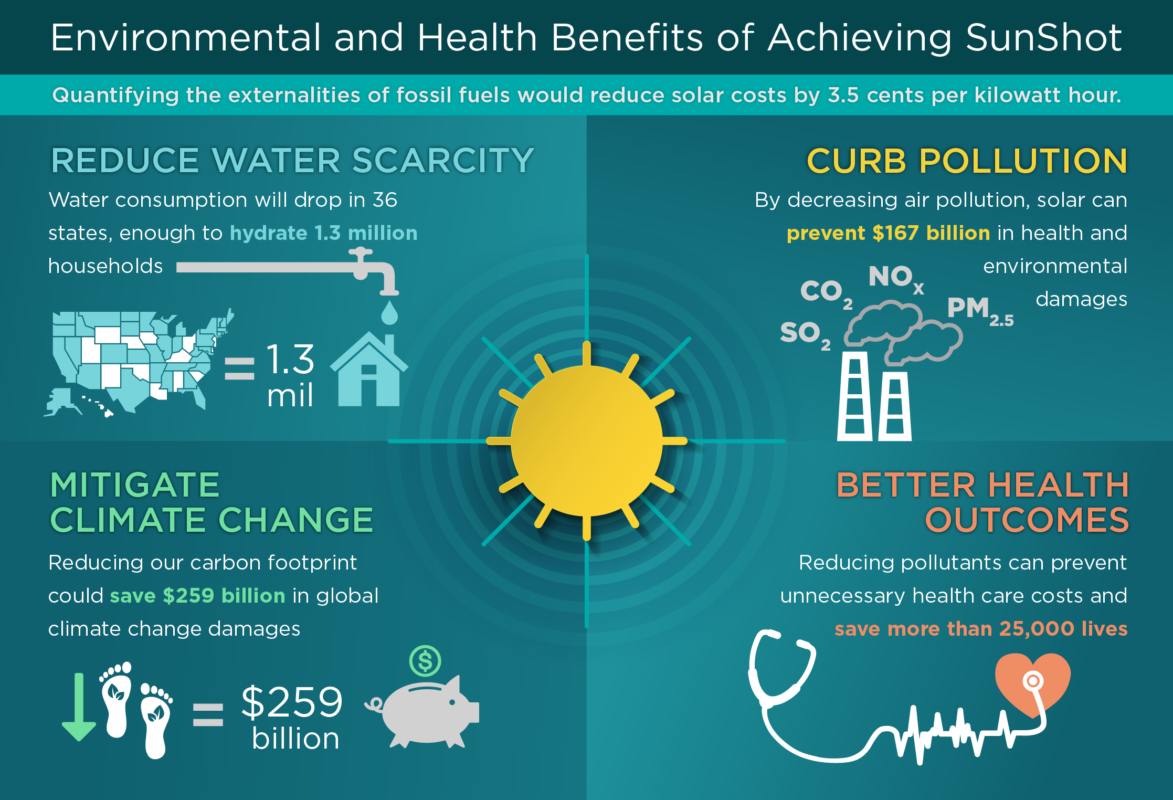
Compared to a scenario of no new solar, the study reveals that successfully reaching the SunShot target would result in a drop in annual GHGs of 13% in 2030 and 18% 2050 – reductions worth nearly US$260 billion in avoided climate damage, or ¢2.2/kWh.
The report also details how using solar reduces power-sector water withdrawals by 8% in 2030 and 5% in 2050, compared with the baseline scenario in which water consumption is reduced by 10% in 2030 and 16% in 2050.
The report concludes that quantifying the environmental and public health impacts of solar energy is essential to understanding the true costs and benefits of solar technologies. It is estimated that these benefits could add approximately ¢3.5/kWh to the value of solar energy.





