By Ulrich Eitner, Project Leader, Institute for Solar Energy Research Hamelin (ISFH); Sarah Kajari-Schröder, Scientist, PV Module Technology Group, Institute for Solar Energy Research Hamelin (ISFH)
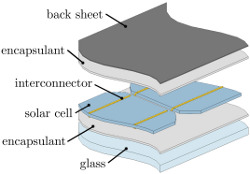
Since the 1980s, ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) has been the standard encapsulation material for crystalline photovoltaic modules. From a mechanical point of view, the encapsulant takes the function of a compliant buffer layer surrounding the solar cells. Therefore, understanding its complex mechanical properties is essential for a robust module design that withstands thermal and mechanical loads. In the cured state after lamination, its stiffness features a high sensitivity to temperature especially in the glass transition region around -35°C, and a dependence on time which becomes obvious in relaxation and creep behaviour. This paper outlines the viscoelastic properties of EVA and the corresponding standard experimental methods, as well as the impact on the accuracy of wind and snow load test procedures for PV modules.