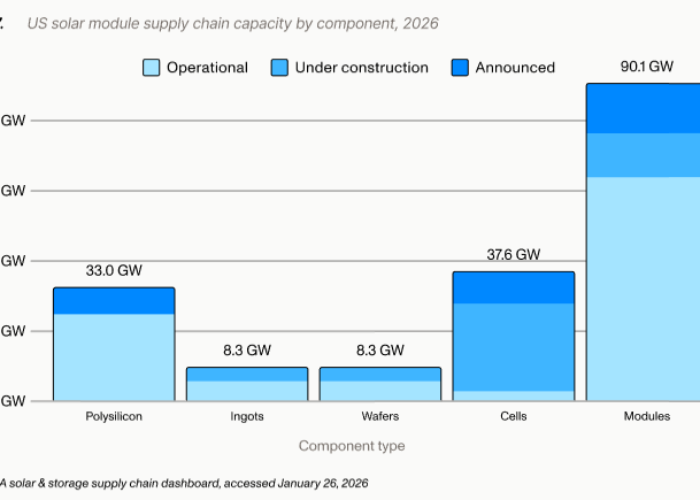
Domestic supply of solar cells in the US will be insufficient to keep pace with module manufacturing expansion plans announced since the 2022 Inflation Reduction Act was passed, according to advisory body, Clean Energy Associates (CEA).
Try Premium for just $1
- Full premium access for the first month at only $1
- Converts to an annual rate after 30 days unless cancelled
- Cancel anytime during the trial period
Premium Benefits
- Expert industry analysis and interviews
- Digital access to PV Tech Power journal
- Exclusive event discounts
Or get the full Premium subscription right away
Or continue reading this article for free
In a guest article published today on PV Tech, Martin Meyers, principal consultant, market intelligence at CEA wrote that the lower capacity additions from cells compared to modules means “many US module assembly facilities will depend on imported cells”.
With a large majority of global cell processing capacity located in Asia, procurement of cells will have similar constraints seen up until now with modules, limiting the available supply due to the Uyghur Forced Labor Prevention Act (UFLPA), which came into force in June 2022 or the anti-dumping/countervailing duty (AD/CVD) with tariffs suspended until July 2024, under US president Joe Biden’s two-year waiver.
Further up in the upstream manufacturing, the problem will also arise for ingots and wafers as domestic cell capacity additions far exceed US ingots/wafers capacity additions, wrote Meyers.
“Hence US cell-processing facilities will depend on wafer imports – and with ingot/wafer capacity even more concentrated in Asia than cell/module capacity, the constraints impacting module and cell imports will impact wafer imports as well. In short, notwithstanding the announcements of US PV manufacturing capacity additions, the US market will depend on imports of modules, cells and/or wafers for years to come.”
To read the full post, visit our Guest Blog section.