DuPont Photovoltaic Solutions' annual 'Global Photovoltaic Reliability Report' for 2020 has identified a rapid increase of cracking in PVDF (Polyvinylidene Fluoride) backsheets after inspecting more than nine million PV panels.
Having conducted field inspections at more than 551 existing installations, DuPont said it had observed many examples of widespread backsheet material failures, notably the emerging trend of cracking in PVDF backsheets.
Unlock unlimited access for 12 whole months of distinctive global analysis
Photovoltaics International is now included.
- Regular insight and analysis of the industry’s biggest developments
- In-depth interviews with the industry’s leading figures
- Unlimited digital access to the PV Tech Power journal catalogue
- Unlimited digital access to the Photovoltaics International journal catalogue
- Access to more than 1,000 technical papers
- Discounts on Solar Media’s portfolio of events, in-person and virtual
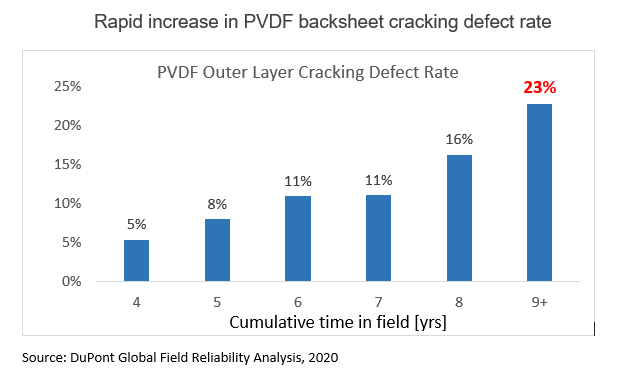
This was notable in the overall outer layer cracking rate of PVDF backsheets, which had increased four-fold (from 5 to 23%) in module arrays in the field for between four and nine years, according to DuPont. Overall, outer layer cracking rates for PVDF backsheets had increased by more than three times compared to previous studies.
The widespread problem of PVDF backsheet through-cracks was observed along busbar ribbons, which meant that with continued weathering could extend to cell gaps and other regions of the modules. Deeper backsheet cracks had also led to backsheet delamination issues.
Dr. Kaushik Roy Choudhury, senior scientist and global technology leader, DuPont Photovoltaic Solutions said, “Delamination and cracking were observed in multiple double glass module installations. Delamination appears to originate near edges of a module or at individual cells, while cracks likely originate at scratches or chips on glass surfaces and edges or at stress risers introduced by the racking system”.
Problems included arcing and shorts, which would often lead to localised burn-through and sometimes full module fires, noted DuPont. This would also be noted in reported inverter tripping and ground faults.
Exacerbating this issue was that DuPont had identified PVDF backsheet cracking in countries such as China, Europe, India, North America and the Mediterranean region, strongly indicating that there was not a clear correlation between cracking and climate conditions as cracking of these backsheets had been observed in hot-arid, cold-arid and temperate weather conditions.
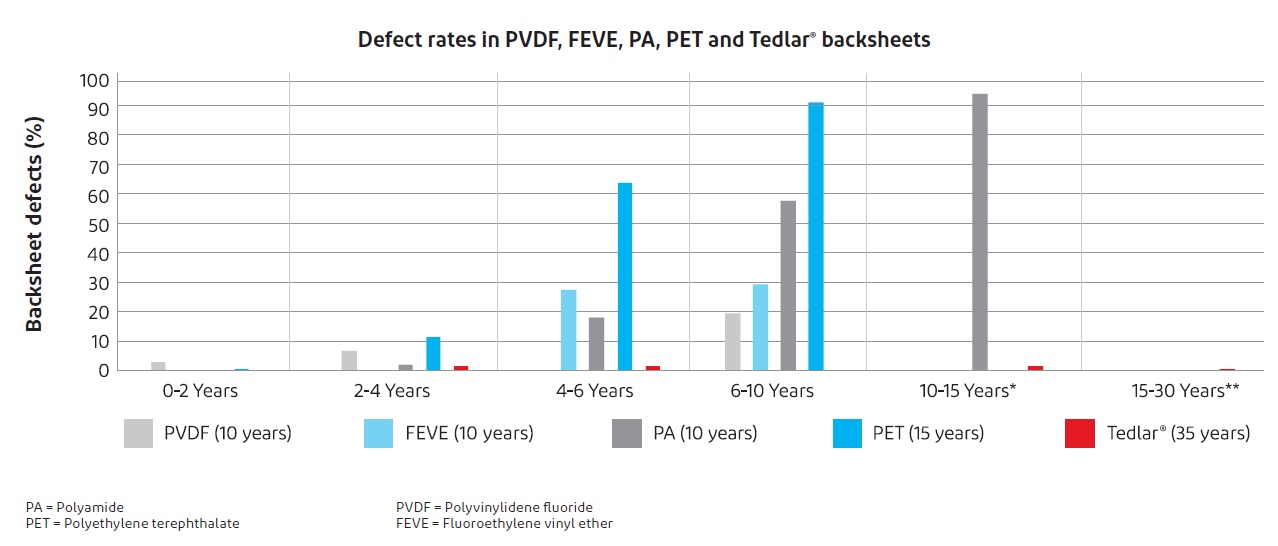
In general, DuPont has found that inner layer cracking has been found in fluoroethylene vinyl ether (FEVE) and polyethylene terephthalate (PET) backsheets. In last year’s report, DuPont noted higher backsheet failures when using PET and glass/glass modules.
The number of PV panels surveyed in the 2020 report increased from 6.5 million in 2029, to 9 million panels in the 2020 report. Site inspection also increased from 355 in 2019, to 551 in the latest report.







