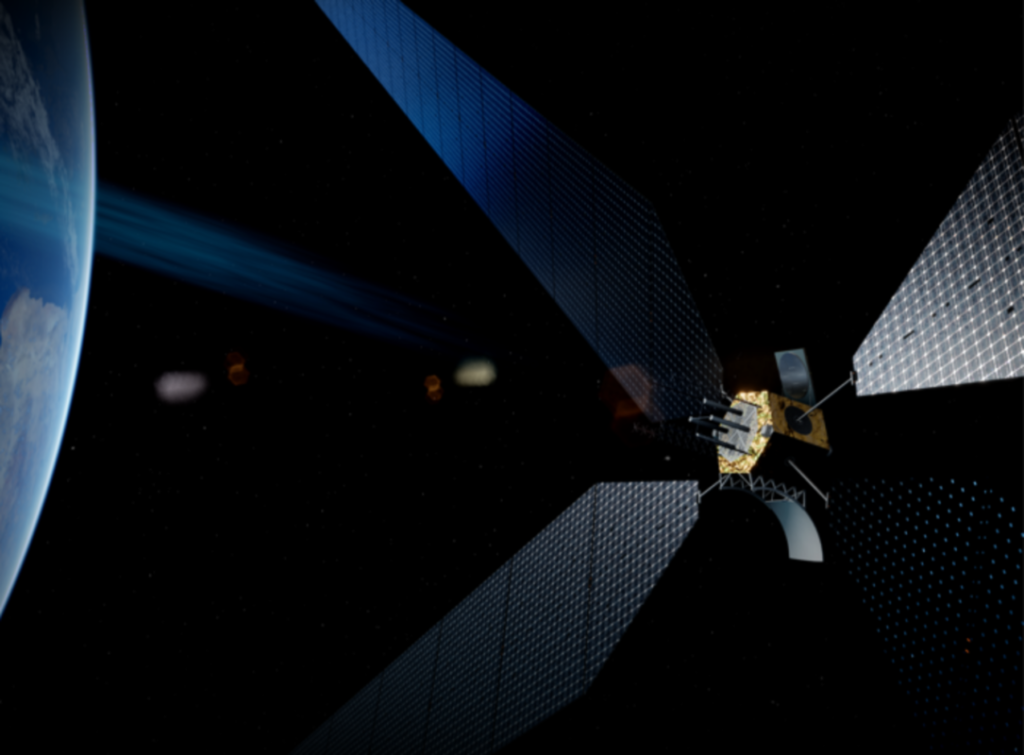
The European Space Agency (ESA) will present an initiative aiming to deliver space-based solar power at the International Conference on Energy from Space in London this week.
The initiative, dubbed SOLARIS, will see the ESA investigate the construction of large mirrors in space to reflect sunlight towards operating solar farms on Earth. The project builds on an earlier iteration of the initiative, launched in April 2023 alongside Thales Alania Space Italy and renewable power company ENEL, which proposed using radio waves to deliver energy to the Earth.
Try Premium for just $1
- Full premium access for the first month at only $1
- Converts to an annual rate after 30 days unless cancelled
- Cancel anytime during the trial period
Premium Benefits
- Expert industry analysis and interviews
- Digital access to PV Tech Power journal
- Exclusive event discounts
Or get the full Premium subscription right away
Or continue reading this article for free
The latest initiative, which involves the work of consultancy firm Arthur D Little and French energy major Engie, will aim to ensure solar farms remain productive, even during times of low sunlight, such as nighttime or periods when solar farms are subject to cloud cover. The work builds on research completed by Caltech in June 2023, where researchers successfully transmitted solar power from a satellite in low-Earth orbit to receivers on the roof of the university, demonstrating the feasibility of the technology.
“The physics behind this design is already implemented in telecommunications, where satellites beam small amounts of energy in the form of radio-frequency waves from orbit to a receiving ground station,” said Sanjay Vijendran, ESA’s lead for the SOLARIS initiative.
“The difference with space-based solar power is that the amount of energy transmitted and successfully collected would need to be far larger to make the venture viable,” Vijendran added. “This presents many technological hurdles to be overcome.”
While space-based solar will need to be scaled up to make the process financially viable, the sizable targets for the European solar sector could encourage more investment into technologies such as these. Earlier this year, a leaked report suggested that the EU is aiming to meet 90% of its electricity demand with renewables by 2040, with the majority set to come from solar and wind, while a number of EU governments have already dramatically expanded their targets for solar power generation until the end of the decade.






