Plenty of uncertainty surrounds the potential effects of India’s forthcoming Goods and Services Tax (GST) Bill, but the cost of solar could go up by as much as INR4.5 million/MW (US$67,000), according to a new study from the Council on Energy, Environment and Water (CEEW).
Originally due to come into effect of the 1 April, but now touted by finance minister Arun Jaitley for a 1 July rollout, the GST sought to bring India under single tax rate. However, the GST Council recently decided to fix a four-tier GST tax structure.
Try Premium for just $1
- Full premium access for the first month at only $1
- Converts to an annual rate after 30 days unless cancelled
- Cancel anytime during the trial period
Premium Benefits
- Expert industry analysis and interviews
- Digital access to PV Tech Power journal
- Exclusive event discounts
Or get the full Premium subscription right away
Or continue reading this article for free
As a result, CEEW modelled various scenarios, focusing on the threat that GST poses to the existing tax benefits for PV and the ensuing headache for both developers and investors.
It found that if current tax exemptions are removed, grid-connected solar tariffs could rise by as much as 9.5% and the rollout of the second 20GW phase of solar parks would be hampered. In this scenario, O&M, solar panel and financing costs would all increase. Furthermore, states would be affected differently. For example Rajasthan, which has a VAT and Entry Tax exemption for solar equipment, would be hit harder than other states where the exemptions are not already provided, such as in Andhra Pradesh and Gujarat.
The following table shows the possible effects on solar tariffs. Scenario 1 assumes GST rates will be calculated based on the total applicable taxes without considering any tax exemptions. Scenario II assumes GST rates will be calculated based on current subsidised tax rates:
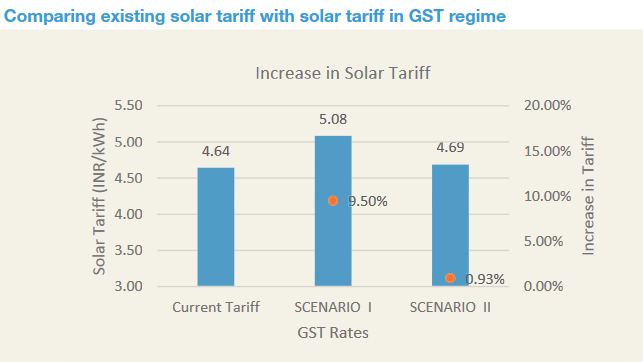
Such a hike in costs would certainly hinder the downward trend in Indian solar tariffs, seen most recently in the ‘transformational’ record lows of around INR2.97/kWh (US$0.044) from Acme, Mahindra and Solenergi for 750MW in Madhya Pradesh. CEEW said it would set back Indian PV cost-competitiveness by 18 months.
CEEW also modelled which particular costs would be most affected by removal of tax exemptions in scenario 1:
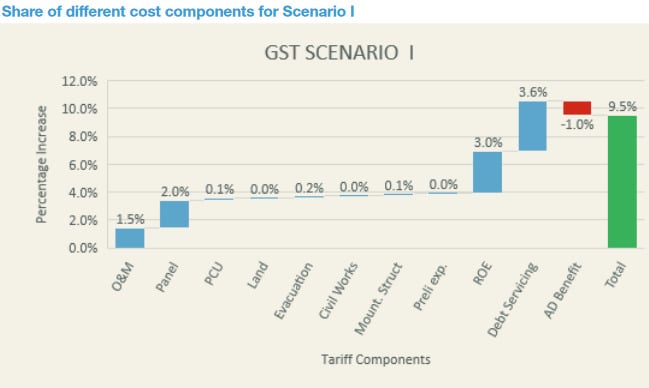
Even the Ministry of New and Renewable Energy (MNRE) had internal communications with officials requesting that solar benefits be exempt from the GST, but energy minister Piyush Goyal gave a strong suggestion that this would not be allowed last year. The result remains to be seen.
‘Make in India’ boost
On the flip side, CEEW found that such an environment would improve the competitiveness of Indian manufacturers of solar cells and modules, with the potential creation of another 37,000 jobs in the sector by 2022.
India’s latest budget benefitted domestic manufacturers by eliminating basic customs duty for tempered glass used in manufacturing solar cells and modules and the reduction of countervailing duty from 12.5% to 6% for parts used in the manufacture of tempered glass.
In the report, Arunabha Ghosh, chief executive, CEEW, said: “With the annual solar power capacity addition expected to be more than 12GW in 2017-18, it is vital that major hurdles for deployment, such as the potential impact of GST on the sector, be ironed out as early as possible.
“GST offers many long-term benefits, but MNRE, Solar Energy Corporation of India (SECI) and other related agencies must provide clear guidelines regarding the applicable GST slab for upcoming solar power projects and introduce government mechanisms to offset the short term negative impacts of GST.
“If current tax exemptions are curtailed, the impact of the increase in solar tariffs could be partially offset by policy instruments, such as Accelerated Depreciation benefits or Viability Gap Funding for projects incurring increased capital investments.”






