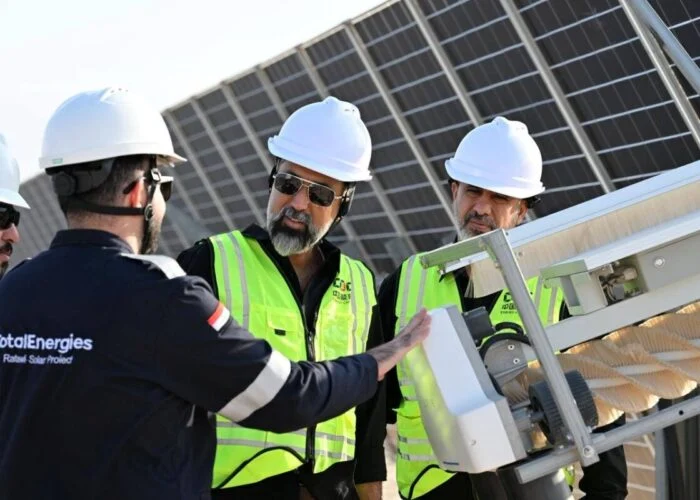
Last month, Maryland achieved a clean energy victory when the legislature voted to override governor Larry Hogan’s veto of the Clean Energy Jobs Act in a 32-13 vote.
The new Act not only raises the state’s renewable portfolio standard (RPS) to 25% by 2020, but also elevates the solar carve-out to 2.5% by 2020 and creates incentives for around 1.3GW of new clean energy capacity.
Try Premium for just $1
- Full premium access for the first month at only $1
- Converts to an annual rate after 30 days unless cancelled
- Cancel anytime during the trial period
Premium Benefits
- Expert industry analysis and interviews
- Digital access to PV Tech Power journal
- Exclusive event discounts
Or get the full Premium subscription right away
Or continue reading this article for free
The US Department of Energy (DOE) forecasts this 2.5% solar set aside to result in the development of more than 1,250MW of solar capacity by 2020.
The legislation is also expected to create 1,000 clean energy jobs annually through 2020.
The RPS breakdown
Maryland’s new increased RPS is divided into two tiers. Tier 1 includes electricity generation from solar, wind, biomass, geothermal, hydro and other renewable technologies. It also includes the technology specific targets, setting aside 2.5% of solar sales by 2020, as mentioned, up from 1.15%, and an offshore wind target that has not yet been determined.
Tier 2 renewables include hydroelectric power other than pump-storage generation. Tier 2 requirements will sunset, dropping to 0% in 2019 and beyond.
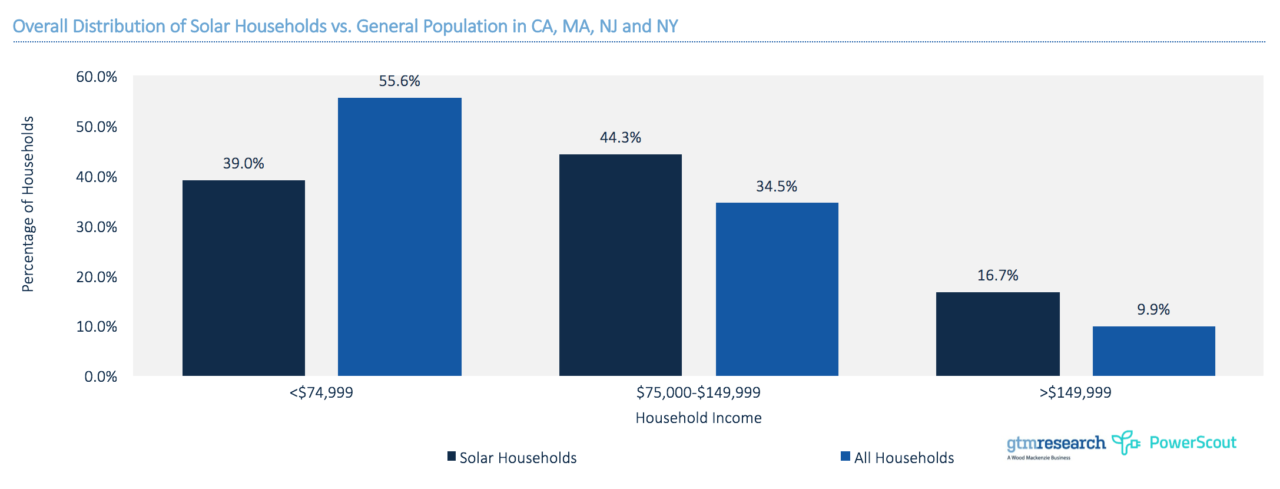
According to data from the Energy Information Administration (EIA) solar makes up only a small part of the state Renewable Energy Credits (RECs) used for compliance, but a relatively larger share of the cost of compliance. For example, of the RECs used for compliance in 2015, only 4% were from solar, but solar made up 31% of the cost of compliance.
The recent increase of in-state solar has meant that the cost of solar RECs has declined significantly. Conversely, tier 1 non-solar REC prices increased from just under US$1 per REC in 2008 to almost US$14 per REC in 2015, according to the EIA.