A new technical report carried out by Energy and Environmental Economics, Inc. (E3) and sponsored by leading CdTe thin-film manufacturer First Solar, entitled “Investigating the Economic Value of Flexible Solar Power Plant Operation” attempts to dispel the assumption that high levels of solar and wind electricity on electricity grids cause grid instability.
The report, (which is available for free download here) uses the PLEXOS Integrated Energy Model to simulate generator unit commitment and dispatch of an actual Florida utility system.
Try Premium for just $1
- Full premium access for the first month at only $1
- Converts to an annual rate after 30 days unless cancelled
- Cancel anytime during the trial period
Premium Benefits
- Expert industry analysis and interviews
- Digital access to PV Tech Power journal
- Exclusive event discounts
Or get the full Premium subscription right away
Or continue reading this article for free
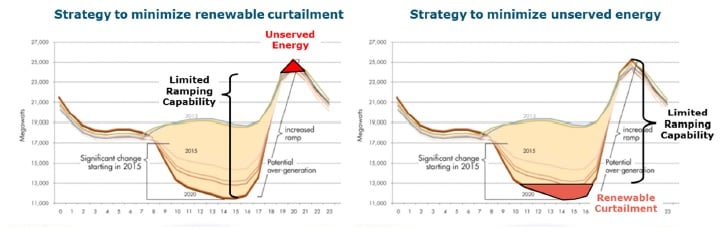
Importantly, the modelling takes utility-scale solar deployment levels up to 28% annual solar energy penetration of a grid system, while the E3 study also calculated operating cost savings of adding solar generation to the electricity system under four different solar operating modes, which represented different levels of flexible grid response.
The study finds that operating solar ‘flexibly’ provides additional value compared to other operating modes.
Primarily, incorporating solar into a utility’s real-time dispatch decision making as well as relying on solar energy to provide essential grid reliability services as solar can respond much faster than conventional resources to instructions from the grid operator
The increased value of using solar in a flexible mode stems from expected reduced fuel and maintenance costs for conventional generators, reduced curtailment of solar output, and reduced air emissions.
“The study confirms our intuition that solar can provide the most value to the system if grid operators fully utilize the flexible dispatch capabilities of solar power plants, especially under increased solar penetration levels,” said Arne Olson, Senior Partner at E3. “Utilities and grid operators should stop thinking of solar as a problem to be managed, and start thinking of it as an asset to be maximized.”
Importantly, the benefits of operating solar in a flexible mode increases as the level of solar penetration increases, according to the report.
“By leveraging the full suite of operational capabilities that all First Solar resources are already equipped to provide, solar can become an important tool to help operators meet flexibility and reliability needs of the grid,” said Mahesh Morjaria, Vice President of Systems Development at First Solar. “Such capability makes it possible for solar to go beyond a simple energy source and instead contribute to important system requirements the way conventional resources do.”
Link to the study here.






