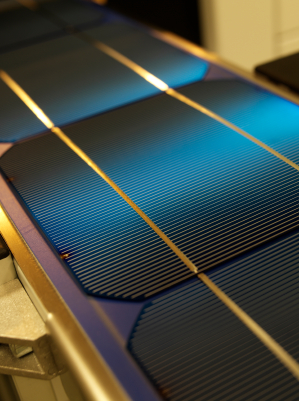
PV Nano Cell announced its plans to enter the US solar market with its ‘Sicrys’ silver and copper inks. The inks are expected to accelerate the adoption of solar photovoltaics (PV) by reducing the cost of silicon solar cell production, using an efficient process that produces sustainable inks without the use of hazardous wastes, and by increasing solar cell efficiencies at a mass production scale.
Problem
Try Premium for just $1
- Full premium access for the first month at only $1
- Converts to an annual rate after 30 days unless cancelled
- Cancel anytime during the trial period
Premium Benefits
- Expert industry analysis and interviews
- Digital access to PV Tech Power journal
- Exclusive event discounts
Or get the full Premium subscription right away
Or continue reading this article for free
With the solar industry under enormous pressure to speed acceleration by reducing costs while continuing an environmentally responsible production process, the search is underway for new printing technologies that reduce the costs of producing solar cells and increase solar cell efficiency, thus allowing more energy to be harvested from each cell.
Solution
PV Nano Cell’s Sicrys silver and copper inks are said to reduce costs because they can be used with innovative noncontact digital inkjet printing, instead of traditional screen printing. Because it does not involve contact with the cell, inkjet printing reduces the amount of cell breakage, reducing the wastage of costly silicon; in addition, it also enables the use of thinner wafers, which also saves on silicon costs. Silicon, the expensive semiconductor material used in solar cells, represents 75% of the cost of a solar cell. Implementing Sicrys silver nano-metric inkjet inks allows manufacturers to reduce the amount of silver needed in the cell. Depending on the cell set up, the level of silver consumption reduction can reach up to 70%, saving on the cost of silver, which is the most expensive material used in the production of solar cells.
Applications
Solar cell metallization of silver and copper.
Platform
The effect of PV Nano Cell’s conductive inks on efficiency is due to the fact that they allow for coverage of less of a solar cell’s surface area, thus producing a greater energy harvest, and because they are better conductors as a result of their nano-structural properties. PV Nano Cell’s inks increase solar cell efficiency by more than 0.2% absolute, which represents a substantial improvement over existing solar cell efficiencies, according to the company.
Availability
Currently available.





