The latest release of the ‘PV ModuleTech Bankability Ratings Quarterly’ report – covering the leading global solar PV module suppliers – reveals a Chinese sector on the verge of widespread company insolvencies, after three years of chronic overinvestment, ahead of a destructive industry shakeout in 2025.
Meanwhile, the top six Chinese PV module suppliers – comprised of JinkoSolar, JA Solar Technology, Trina Solar, LONGi Green Energy Technology, Tongwei and Canadian Solar – remain well placed financially to absorb short term losses during the current industry downturn, and are expected to resume manufacturing expansions in 2026.
Unlock unlimited access for 12 whole months of distinctive global analysis
Photovoltaics International is now included.
- Regular insight and analysis of the industry’s biggest developments
- In-depth interviews with the industry’s leading figures
- Unlimited digital access to the PV Tech Power journal catalogue
- Unlimited digital access to the Photovoltaics International journal catalogue
- Access to more than 1,000 technical papers
- Discounts on Solar Media’s portfolio of events, in-person and virtual
Excessive Chinese investments into new solar manufacturing facilities in the past three years has reached a tipping point. The last downturn ten years ago, caused also by excessive spending in China, resulted in Western companies going bankrupt, but this time the insolvencies will be widespread within China; not simply at the module part of the value chain but across wafer and cell producers also.
Chinese companies dominate the production of PV modules today, accounting for more than 90% of global shipments, with 40 suppliers in the gigawatt-plus category. Currently, one-third of China’s module suppliers are operating with severe liquidity and debt concerns, selling products where costs exceed sales by more than 50%.
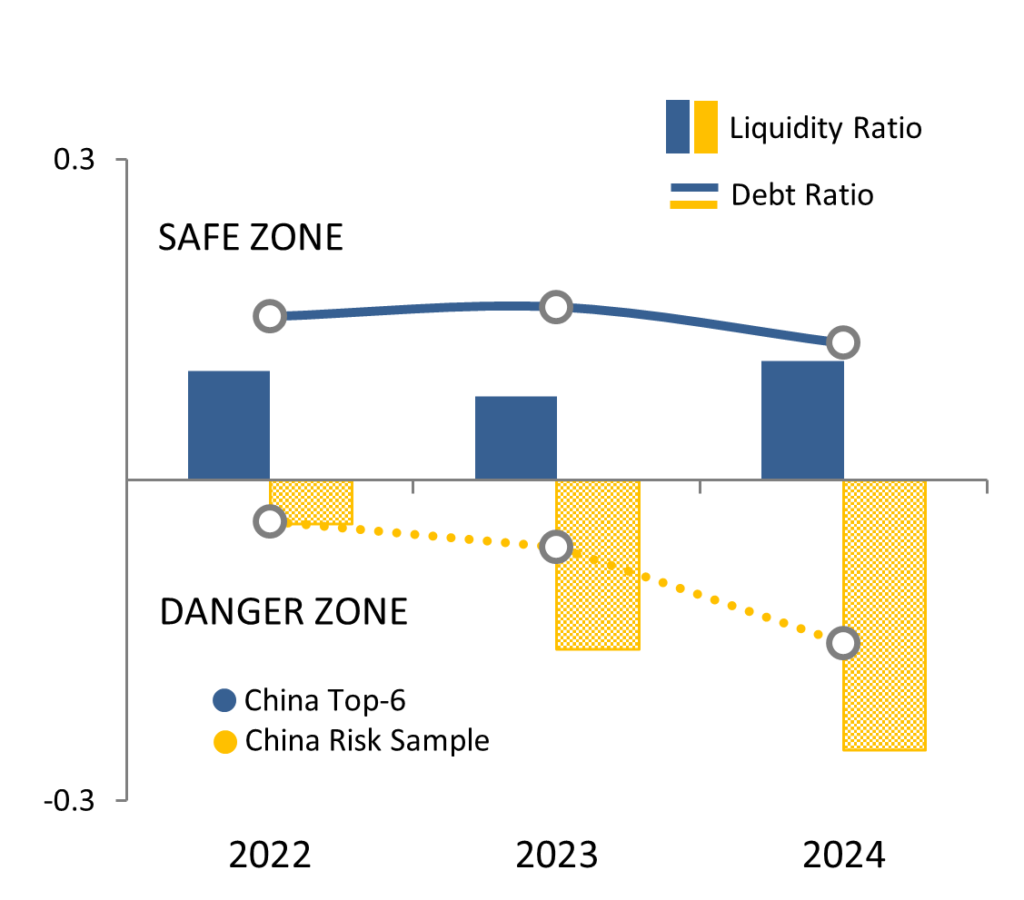
The leading six Chinese suppliers, which control 60% of the market, have reacted to the downturn, cutting capital expenditure commitments by 50% and implementing additional short-term cost cutting measures. These companies are now focused on reducing operating costs further, while introducing new products to reduce the dependency on module sales.
The leading solar module companies in China have accumulated sufficient cash reserves to weather the storm of 2025, and have long-term debt under control, while most other Chinese suppliers had liquidity problems before the downturn even started and are at risk of enforced insolvency proceedings next year.
Learn more about the ‘PV ModuleTech Bankability Ratings Quarterly’ report here.