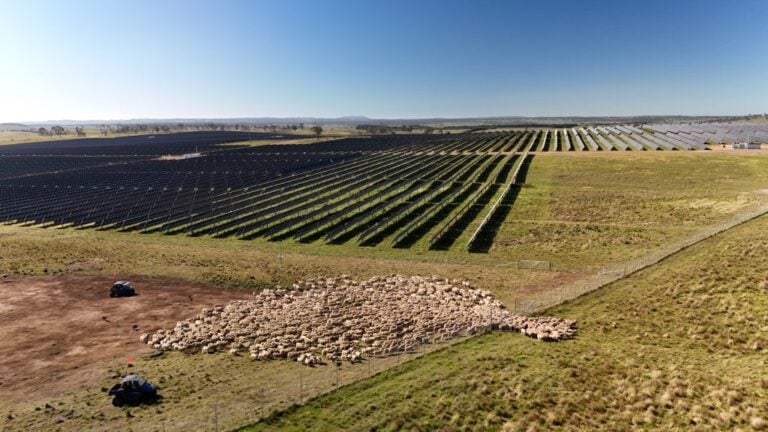
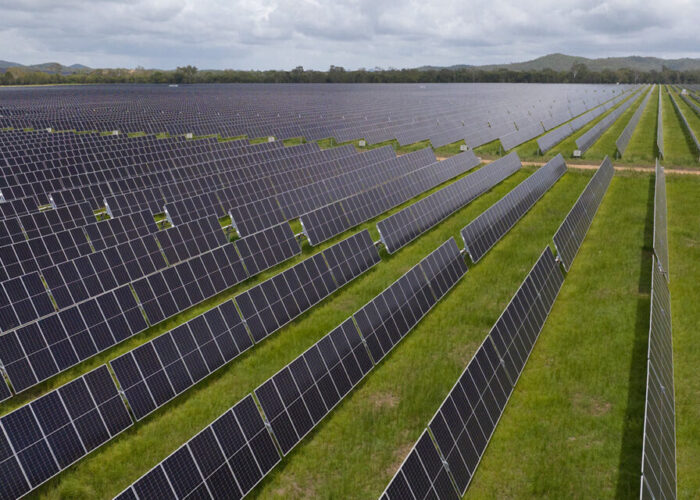
Renewable energy developer Acen Australia is seeking Federal government approval for a 320MW solar-plus-storage site in New South Wales, Australia, under the Environment Protection and Biodiversity Conservation (EPBC) Act.
The proposed Deeargee solar PV power plant will be located 12km southeast of the township of Uralla and developed inside the New England Renewable Energy Zone (REZ). It will feature a battery energy storage system (BESS) with ‘a capacity of up to 1,400MWac two-hour energy storage, which may be configured as 700 MW four‑hour energy storage,’ Acen wrote in its application.
Unlock unlimited access for 12 whole months of distinctive global analysis
Photovoltaics International is now included.
- Regular insight and analysis of the industry’s biggest developments
- In-depth interviews with the industry’s leading figures
- Unlimited digital access to the PV Tech Power journal catalogue
- Unlimited digital access to the Photovoltaics International journal catalogue
- Access to more than 1,000 technical papers
- Discounts on Solar Media’s portfolio of events, in-person and virtual
Acen noted that the Deeargee PV plant will be located around 5km south of its existing and operational 521MWdc stage one of its New England Solar plant. The second stage will increase this generation capacity to 936MWdc. This project supplies energy to Japanese-owned drinks company Asahi Beverages and not-for-profit care company BaptistCare via a power purchase agreement inked in July 2024.
The proposed project will cover 1,544 hectares of land currently categorised as predominantly freehold. Acen confirmed it has entered into agreements with the landholders for the site. You can find the proposed site outline below.
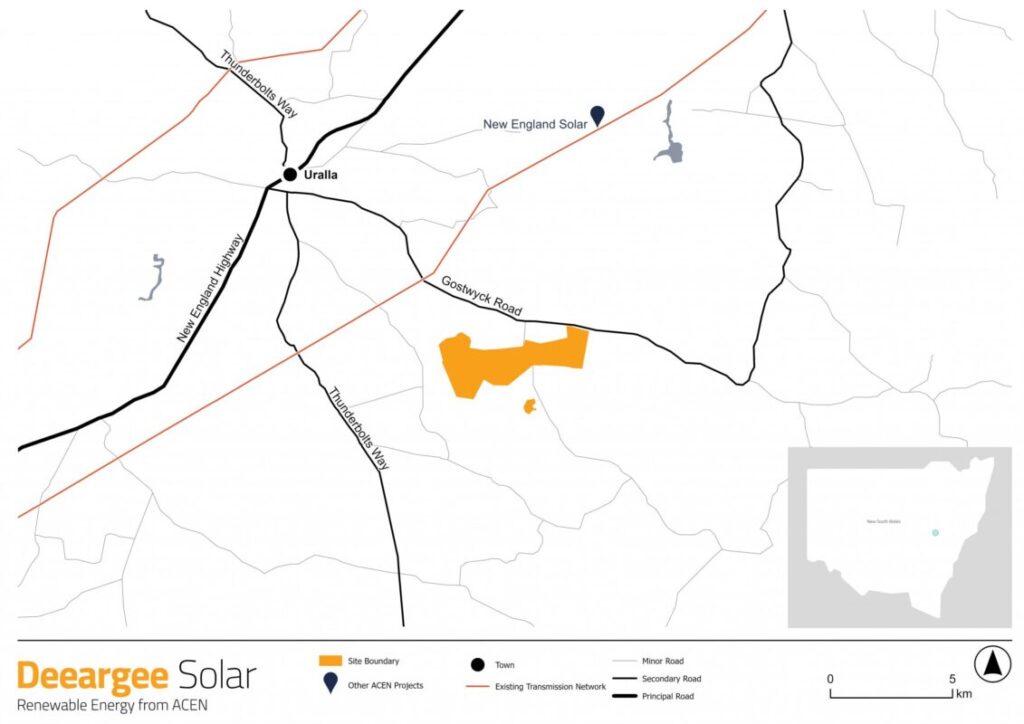
Planning documents submitted to the Australian government’s EPBC Act outline that the project will utilise around 750,000 solar PV modules. An on-site substation will be constructed and connected to the BESS and the solar PV power plant. A new transmission line will connect the project to either the infrastructure proposed as part of the New England REZ or the existing 330kV line located around 8km north of the solar array.
Acen said the project’s construction phase will last around 24 months and require 400 workers to complete. Once operational, the solar-plus-storage site will last for 30 years, with the potential to be repowered at the end of the PV modules’ technical life. Should this occur, the project’s lifespan could extend up to 50 years.
Acen Australia’s solar PV portfolio
Acen Australia has several solar PV power plants currently under development across the country, several of which include a co-located BESS to optimise its performance.
One such project is the 100MW Cooma solar-plus-storage project in New South Wales, which was submitted to the EPBC Act earlier this month. The site includes a 180MW/360MWh 2-hour duration BESS, with units around 3.5m high and featuring an active gas-fired fire protection system.
The project’s operational lifespan is 30 years, with the potential for upgrades, including repowering the plant. The project area stands at 290 hectares. A scoping report for the project was submitted in July 2024.
Acen Australia is also pursuing the 600MW Birriwa solar-plus-storage project in New South Wales having secured Federal approval in September 2024. The project will include a centralised BESS with a capacity of up to 600MW/1,200MWh and a duration of 2-hours. This setup will allow the excess electricity generated by the 600MW solar PV component of the project to be stored and released during peak demand periods.
Acen Australia had been granted approval for the project by the New South Wales Independent Planning Commission (IPC) in August.







