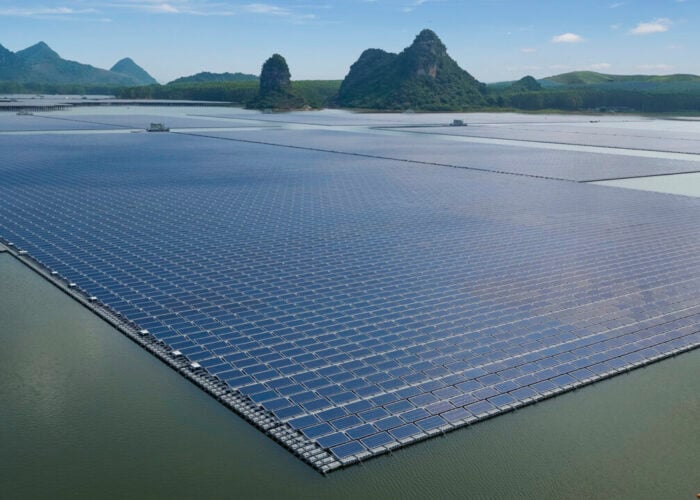
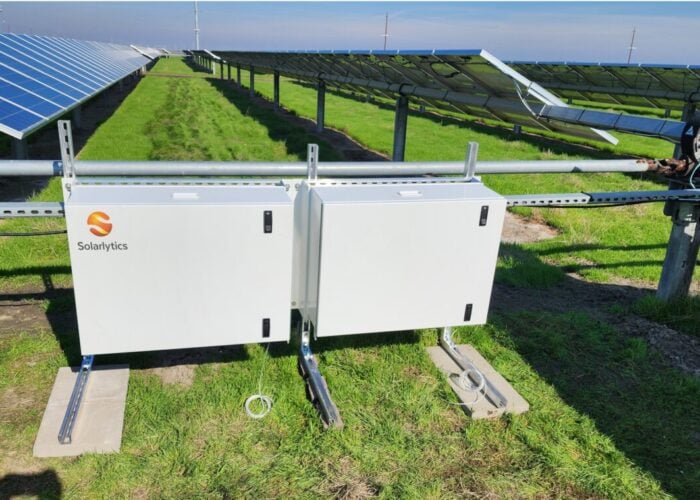
A recent report from the European trade association SolarPower Europe (SPE) has highlighted the use of data-driven techniques, industry 4.0 solutions and robotics as some of the key trends in operations and maintenance (O&M) for the solar industry.
On top of the latest innovations and trends in O&M, the sixth edition of SPE’s O&M Best Practice Guidelines also includes revised guidance on solar PV plant maintenance and data management and new chapters on electrical safety and common tests and inspections.
Unlock unlimited access for 12 whole months of distinctive global analysis
Photovoltaics International is now included.
- Regular insight and analysis of the industry’s biggest developments
- In-depth interviews with the industry’s leading figures
- Unlimited digital access to the PV Tech Power journal catalogue
- Unlimited digital access to the Photovoltaics International journal catalogue
- Access to more than 1,000 technical papers
- Discounts on Solar Media’s portfolio of events, in-person and virtual
The report highlights several trends, including the use of data-driven and industry 4.0 techniques, which aim to reduce the number of human interventions while embracing digitisation.
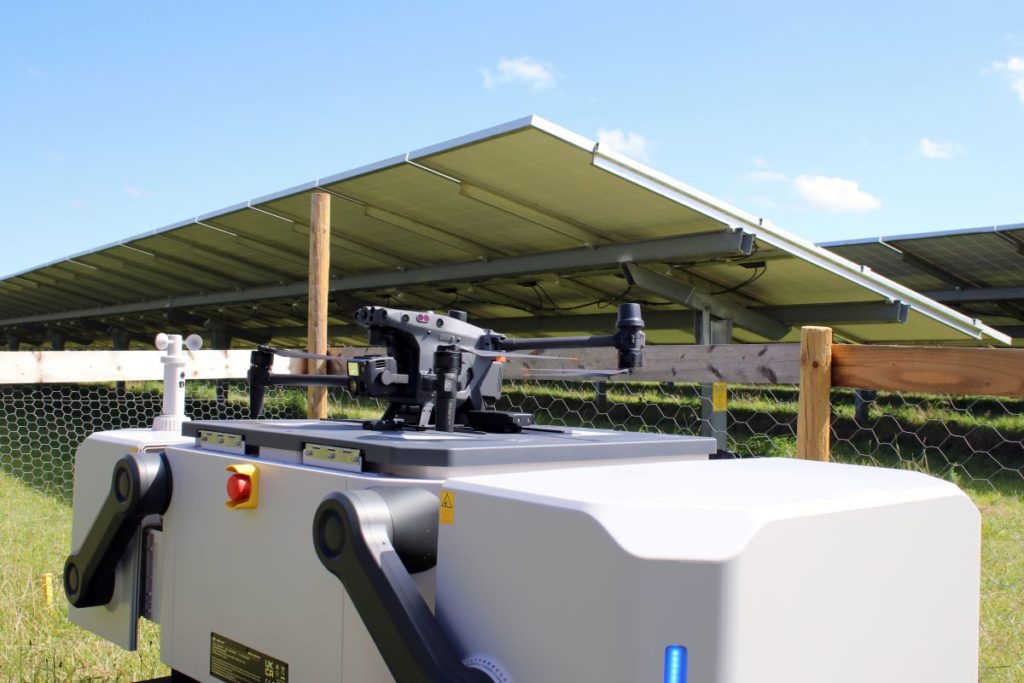
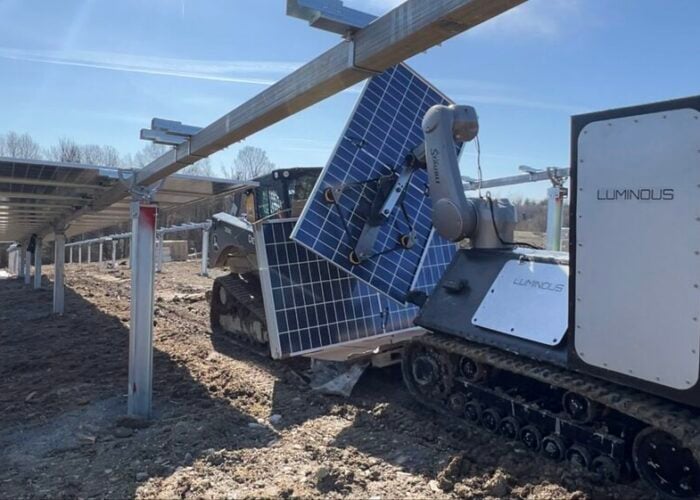
One of the solutions that continues to grow for O&M is the use of robotic solutions to carry out work, especially through drones. Dubbed “drone in a box” systems, these are designed for automated deployment, operation and data collection in order to carry out automated inspections and monitoring of a solar PV plant.
Despite a high initial cost, their potential for return on investment (ROI) through operational efficiency makes them a “promising” technology for the solar industry, according to the report.
In the past few years, the increased popularity of artificial intelligence (AI) through its use in large-language models (LLM), such as ChatGPT and others, has not escaped the solar industry. SPE’s report expects the use of generative AI in workflow automatisation to “reshape engineering software” for renewable energy asset operations and will become indispensable tools.
These models will be able to significantly save time by expediting data queries and contextual data visualisation.
Stelios Antellis, chair of the SolarPower Europe Lifecycle Quality workstream, and head of global strategic operation at Chinese solar manufacturer Astronergy, said: “The future of solar power relies on lasting quality, durability, and well-maintained systems that meet performance expectations.
“With the sixth version of these guidelines, we keep integrating and refining best practices which highlight the critical importance of proper O&M, and ensure that our solar PV power plants generate value for investors and communities for generations to come.”
In addition to these trends, the report highlighted the importance of high-quality O&M services in mitigating potential risks, improving the levelised cost of electricity (LCOE) and power purchase agreement (PPA) prices, and positively impacting the ROI.
Walburga Hemetsberger, CEO of SolarPower Europe, said: “A thriving solar industry with quality solar installations is the cornerstone of a successful energy transition. These guidelines will ensure that the sector installs solar systems that foster growth, strengthen trust, and accelerate the solar revolution across Europe.”
The first version of this O&M guideline report was published in 2016. The sixth edition comprises over 30 experts of SPE’s Lifecycle Quality workstream writing with background on O&M, recycling and circularity, utility-scale solar PV and manufacturing.
SPE’s sixth edition of its O&M guideline report can be accessed here.