Ground-mounted PV is the most cost-effective power generation technology available in Germany, according to the latest report from German research organisation Fraunhofer ISE.
The study, Electricity Production Costs of Renewable Energies, found that the levelised cost of electricity (LCOE) for ground-mounted solar projects could be as low as €0.041/kWh (US$0.045/kWh), the lowest among all power-generation technologies.
Try Premium for just $1
- Full premium access for the first month at only $1
- Converts to an annual rate after 30 days unless cancelled
- Cancel anytime during the trial period
Premium Benefits
- Expert industry analysis and interviews
- Digital access to PV Tech Power journal
- Exclusive event discounts
Or get the full Premium subscription right away
Or continue reading this article for free
Wind, both onshore and offshore, was also among the cheapest, around 5-10 Euro cents per kWh, with a number of other solar deployments, including small rooftop solar (no higher than €0.15/kWh) and ground-mounted solar with batteries (no higher than €0.11/kWh) among the cheapest in the country.
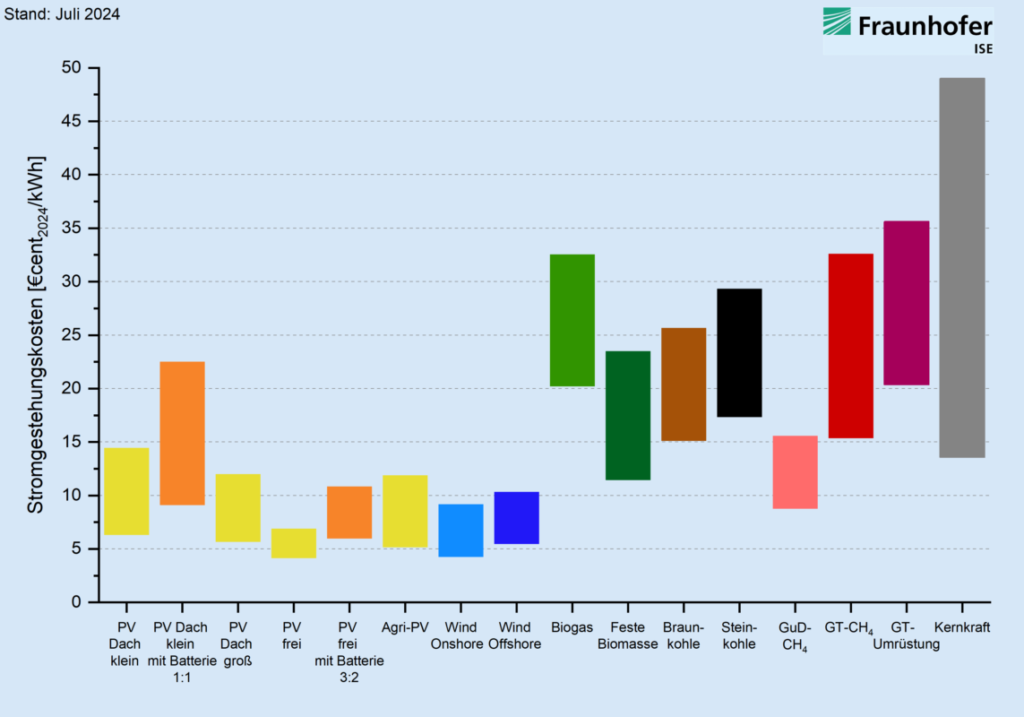
The graph above demonstrates how renewable power technologies are, across the board, cheaper than fossil fuel or other equivalents. The most expensive form of technology is nuclear, which boasts an LCOE as high as €0.5/kWh, but also shows the greatest range in LCOE of any technology. Renewable technologies, meanwhile, are both low-cost and, for the most part, demonstrate a very narrow range of LCOE.
“These calculations show that the large-scale projects currently underway in Germany, which combine open-space PV systems, wind farms and stationary battery storage systems, are good investments,” said Dr Christoph Kost, head of the Energy System Analysis Department at Fraunhofer ISE and lead author of the study. “The combination enables grid capacities to be better utilised, for example.”
The main exception to this trend is the LCOE of small-scale rooftop solar with co-located battery energy storage systems (BESS), which can be as high as €0.225/kWh, the highest among renewable technologies. This type of power generation also boasts the largest range in LCOE figures among clean energy types, which the Fraunhofer researchers attributed to the wide range in costs of battery systems, which can exacerbate cost variations inherent to solar systems, which are caused by differing levels of solar radiation.
However, the long-term outlook is encouraging for the renewable power sector. The study’s authors expect the LCOE of renewable technologies to fall even further in the coming years, expecting the LCOE of small-scale rooftop PV systems to fall as low as €0.049/kWh, while the LCOE of ground-mount solar could be as low as €0.031/kWh, by 2045.
Kost also notes that “small” PV battery systems could see LCOE fall as low as €0.19/kWh, an encouraging development for the storage sector alongside the renewable power generation industry.
The falling LCOE of solar power is nothing new, with figures from US analyst Lazard noting that solar is also one of the cheapest power-generation sources in the US. Similar figures from DNV suggest that the LCOE of solar could halve by 2050, and the continued fall in the cost of electricity will be a key component of the renewable energy transition.






