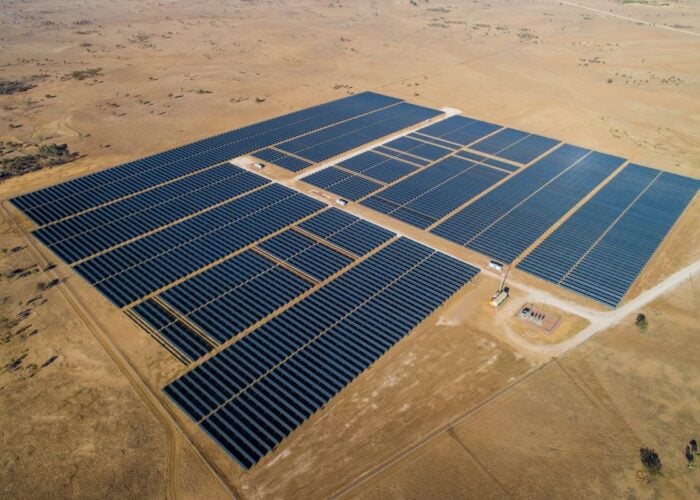
Australia has topped the international leaderboard in scaling electricity generation from low-emission and clean technologies, with growth between 2018 and 2023 at just over 100%.
According to the International Energy Agency’s (IEA) World Energy Outlook 2024 report, deployment of renewable energy generation technologies, such as solar PV, wind and hydro, all contributed to this growth, which led to generation outpacing demand growth for electricity across the country.
Try Premium for just $1
- Full premium access for the first month at only $1
- Converts to an annual rate after 30 days unless cancelled
- Cancel anytime during the trial period
Premium Benefits
- Expert industry analysis and interviews
- Digital access to PV Tech Power journal
- Exclusive event discounts
Or get the full Premium subscription right away
Or continue reading this article for free
Solar PV has been a stalwart technology in Australia’s energy transition, with the country boasting the highest installed solar per capita in the world, as of 2022, standing at 15%. This was according to the International Energy Agency and Photovoltaic Power Systems Program.
This rise in renewable energy generation has also affected Australia’s use of fossil fuels, citing a decrease in unabated fossil fuel emissions of around 20%. Below is a breakdown of the leading countries from the IEA report below.
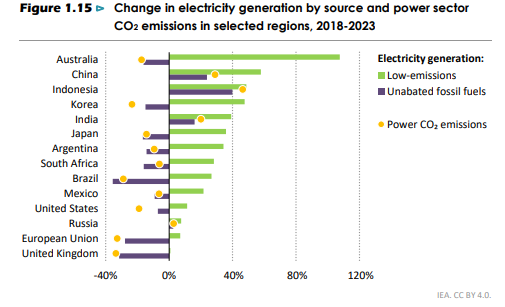
Alongside Australia, Korea, Japan, Argentina, South Africa, Brazil and Mexico all managed to outpace the rise in demand leading to unabated fossil fuel reductions.
It is also worth noting that low-emissions generation sources increased by around 10% or less in the EU, UK and US, but this was enough to outpace any demand growth and reduce the use of unabated fossil fuels in each case.
Australia’s solar PV prowess
One of the major contributors to Australia’s global leading generation surge is the use of solar PV. However, it’s worth mentioning that the country has been actively supporting the development of utility-scale and rooftop solar PV.
For instance, a recent The Race to the Top report by not-for-profit organisation the Climate Council, found that Queensland remains the leader in rooftop solar PV deployment, with around 50.2% of the state’s homes having solar PV installed on them, higher than any other region in Australia.
Equally, analysis by PV Tech revealed that, on the final day of winter 2024, South Australia ran on 100% renewable energy. Rooftop solar PV generated 21.1% of the 102.2% figure, around 56GWh generated over the week. On the other hand, utility-scale solar provided 3.9% of the overall mix, around 10.4GWh.
From a utility-scale perspective, Australia has 5,516MW of solar PV projects currently in financial commitment or under construction, with the majority of these based in Victoria in the second quarter of 2024, according to the Clean Energy Council (CEC).
Indonesia and Australia responsible for over half of global exports of coal in 2023
Although Australia has seen major growth and is committed to the energy transition and achieving net zero, the country still relies on coal for power generation for grid reliability and as a lucrative economic boost via exportation.
The IEA report highlighted that global coal exports reached historical levels in 2023, primarily due to increased demand in the Asia Pacific region, which accounts for 80% of total imports. Indonesia and Australia together were responsible for over half of the global exports, with Indonesia establishing itself as the largest exporting country.
Australia contributes 45% of the world’s coking coal exports, while Indonesia accounts for approximately 40% of steam coal exports. China is the largest single importer, purchasing about 30% of the global total, which satisfies 10% of its domestic demand. Additionally, India, Japan, and South Korea collectively make up around 35% of global imports.
The Australian Energy Market Operator (AEMO) detailed in a report released earlier this year that by 2038, the last coal-fired plant in Australia will have been withdrawn.
You can find PV Tech’s full analysis of the IEA’s World Energy Outlook 2024 report here.





