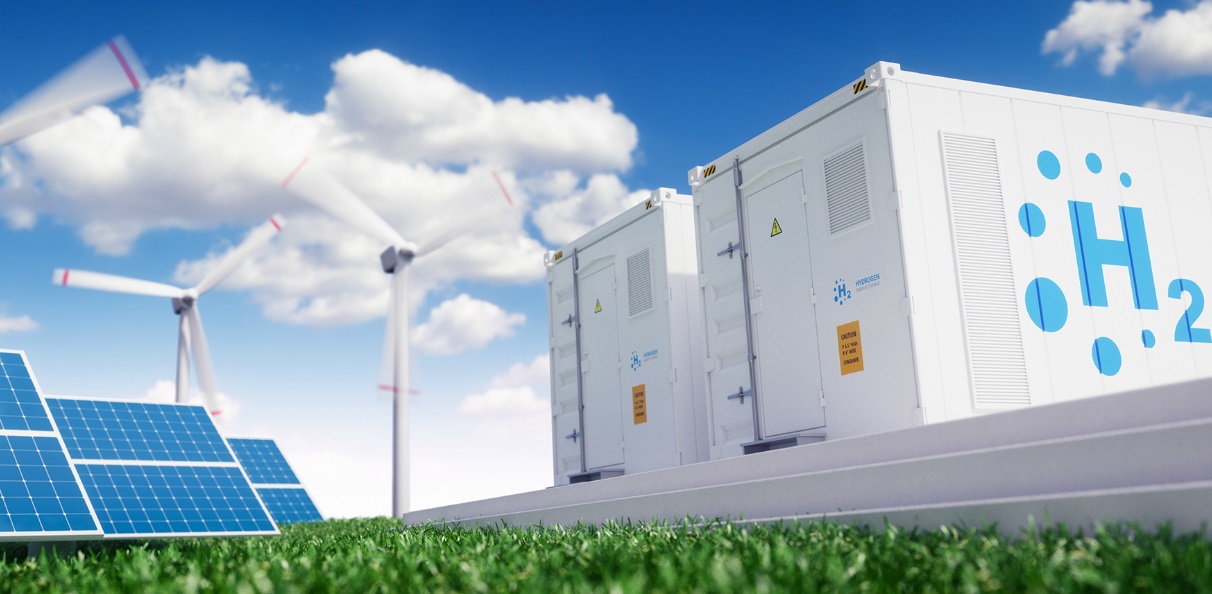
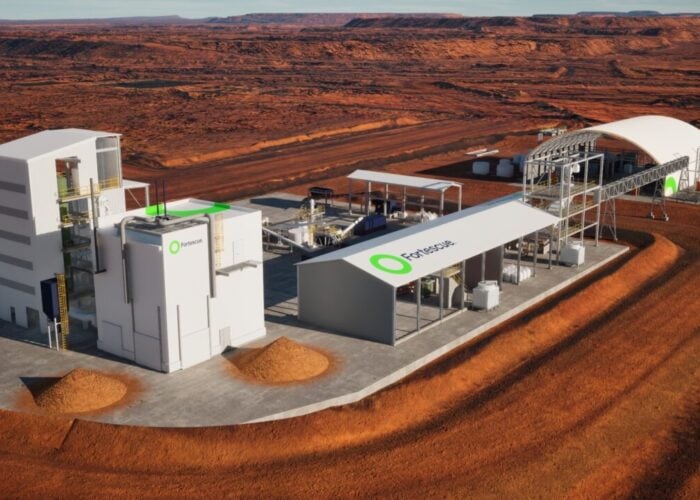
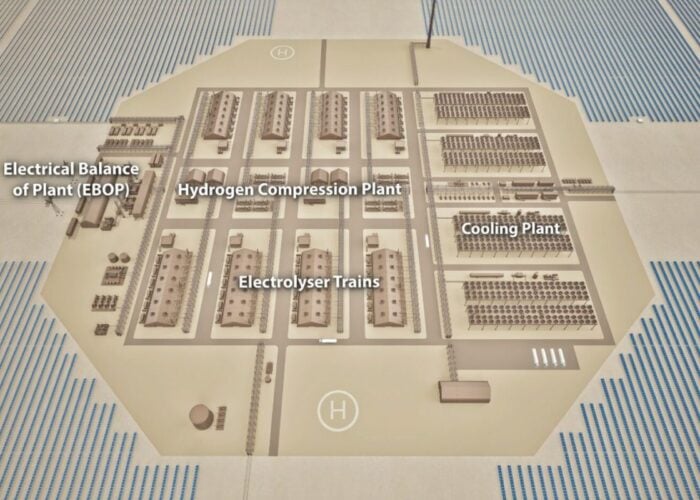
The cost of hydrogen produced with green energy could compete with those of fossil fuels by 2030, according to new research.
The International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA) claims that further investment in the technology from governments could reduce the cost of electrolysis by 40% within a decade, and by 80% by 2050.
Unlock unlimited access for 12 whole months of distinctive global analysis
Photovoltaics International is now included.
- Regular insight and analysis of the industry’s biggest developments
- In-depth interviews with the industry’s leading figures
- Unlimited digital access to the PV Tech Power journal catalogue
- Unlimited digital access to the Photovoltaics International journal catalogue
- Access to more than 1,000 technical papers
- Discounts on Solar Media’s portfolio of events, in-person and virtual
Francesco La Camera, IRENA’s director-general, said that implementation could be a “game-changer” as more governments have started to implement decarbonisation targets. The report noted that green hydrogen could be “critical” for sectors that are inherently harder to decarbonise such as steel, chemicals, long-haul transportation and shipping, but the higher cost of hydrogen produced from renewables compared to so-called blue hydrogen is a significant barrier to entry.
Some authorities have made green hydrogen a key component of their carbon reduction targets. The European Union’s green hydrogen strategy, published in July, called for at least 6GW of renewable hydrogen electrolysers to be installed by 2024.
“Levelling the playing field to close the cost gap between fossil fuels and green hydrogen is necessary,” Camera said, adding that cheaper green hydrogen would support the development of a “resilient energy system that thrives on modern technologies and embraces innovative solutions fit for the 21st century”.
Key to the sector’s growth in the coming years will be the standardisation of technologies and products, investing in electrolyser developers to enable them to scale up and benefit from spreading their fixed costs over greater production and reducing overheads within the supply chain, the report said.
However, it added that scale-up and deployment growth would need to be both “rapid” and “aggressive” for costs to come down on a par with that of hydrogen produced from fossil fuels.