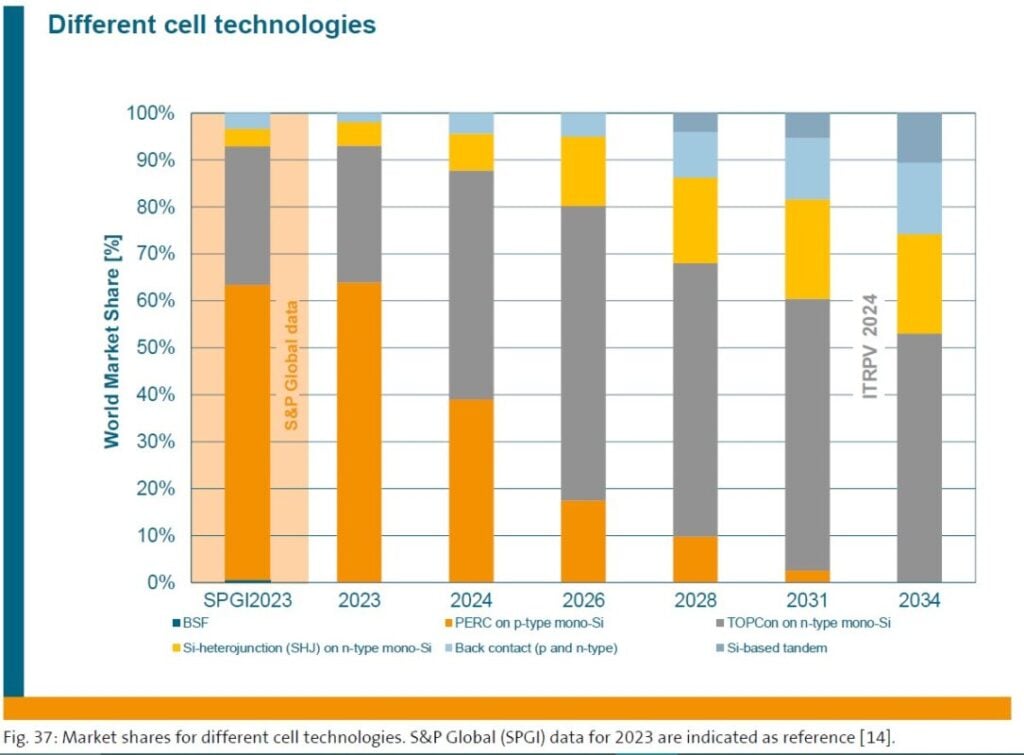
Silicon-based tandem solar cells and modules are expected to enter commercial production in 2027 with a module efficiency of 27%, according to the latest International Technology Roadmap for Photovoltaic (ITRPV) published by German engineering association VDMA.
This is the 15th edition of the ITRPV, which was jointly prepared by 50 global polysilicon producers, wafer suppliers, crystalline silicon (c-Si) solar cell manufacturers, module manufacturers, PV equipment suppliers, production material providers, and also research institutes and consultants.
Try Premium for just $1
- Full premium access for the first month at only $1
- Converts to an annual rate after 30 days unless cancelled
- Cancel anytime during the trial period
Premium Benefits
- Expert industry analysis and interviews
- Digital access to PV Tech Power journal
- Exclusive event discounts
Or get the full Premium subscription right away
Or continue reading this article for free
Tunnel oxide passivated contact (TOPCon) solar cells are expected to become – and retain – market leadership in 2024 and see their market share grow to over 50% by 2034, as shown in the chart above. PERC is not expected to feature at all after 2028.
Heterojunction cell technology is expected to increase its market share from 5% in 2023 to 19% within the next ten years.
P-type passivated emitter and rear cell (PERC) modules have reached efficiencies of 21.4%, while n-type heterojunction modules have shown efficiencies of 21.4% which are expected to increase up to 24% within the next decade.
Optimisation of manufacturing costs, combined with increased cell and module performance will further help to the cost reductions of PV systems, says the report.
Module price drop 50% in 2023
Premium prices for higher power, bifacial and n-type modules are no longer existent due to the price drops seen in 2023, the report said. Overall, solar module prices in 2023 dropped by 50% compared to 2022.
Shipment volumes reached a record 502GW last year, the report found. The shift from C-Si to mono-Si continues, including the rise of M10 (182mm) and G12 (210mm) wafer formats, along with bifacial modules.
The report estimates the global crystalline silicon and PV module annual production capacity to have surpassed 1TW at the end of 2023.
Looking ahead, the report identified reductions in the use of silver in solar cells as a key area for further cost reduction as silver remains one of the most expensive materials in cell production and has a relatively higher consumption rate in n-type cells than p-type PERC variants.
“Because silver will remain cost critical due to the world market dependency, it is extremely important to continue all efforts to lower silver consumption as a means of achieving further cost reductions,” the report said.
At a system level, the report said annual system degradation is expected to improve over the next ten years, while, at 40 years, the technical lifetime of modules is expected to be on average above the warranty period.
“Classical” PV power plants are expected to maintain a dominant 53% market share of different system end uses between now and 2034, but agriPV, building-integrated PV and floating solar systems are expected to grow in popularity.






