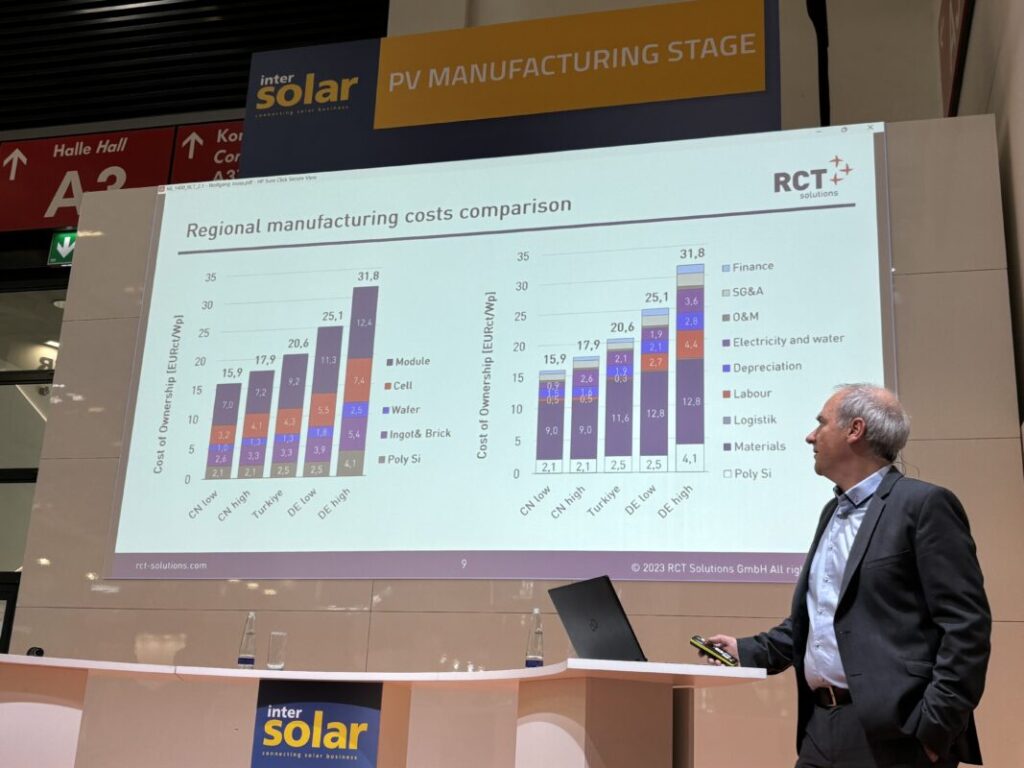
A study exploring the feasibility of resurrecting PV manufacturing in Germany and Europe more widely has identified an eight-cent-per-watt cost gap between modules produced in China and those produced locally.
The Libertas PV feasibility study was launched last year with funding from the German government to scope out the re-establishment of Europe’s PV manufacturing supply chain. The study has been jointly led by PV factory developer RCT Solutions, the German trade body VDMA, and research institutes ISC Konstanz, Fraunhofer ISE, ISFH and HZB.
Try Premium for just $1
- Full premium access for the first month at only $1
- Converts to an annual rate after 30 days unless cancelled
- Cancel anytime during the trial period
Premium Benefits
- Expert industry analysis and interviews
- Digital access to PV Tech Power journal
- Exclusive event discounts
Or get the full Premium subscription right away
Or continue reading this article for free
In a presentation yesterday at Intersolar Europe 2024, RCT Solutions chief technology officer Wolfgang Jooss revealed some of the study’s findings, including the headline cost gap between Chinese and Germany-manufactured modules.
The study compared the relative cost of producing modules in various parts of the world, based on analysis of key areas of the supply chain, including raw materials, labour, finance and energy costs.
Jooss said the cost of producing modules in Europe compared to China was around eight cents per watt higher than in China, due primarily to higher materials and labour costs, which each account for around 50% of the cost gap.
On labour, Jooss said the higher costs were not just down to the relatively higher personnel costs in Europe versus China, but also due to the fact that more people are required to work at any one time according to typical shift patterns in Germany.
“Usually in China, you need three operators. But in Germany, due to the shift systems and the hours you are working, you need five people. So…in addition to higher personnel costs, you also need more people to operate [production lines],” Jooss said.
Jooss said various measures, such as higher automation and economies of scale, could reduce the cost gap to around three or four cents, but this would require “hundreds of gigawatts” of manufacturing capacity to achieve.
To stimulate the growth of a European manufacturing ecosystem, Jooss said the report makes a number of recommendations.
These include a “resilience bonus” that would award projects using locally produced components a higher tariff. Such an idea is already under consideration in Germany and at an EU level and is seen in policy circles as a useful measure for boosting local production by giving manufacturers a visible end market for their products.
Another recommendation in the study is the establishment of a pilot production line or innovation centre, which Jooss said would serve a number of purposes:
“First of all, you have accelerated development of production expertise, which is not there. You can also test new equipment… also implementation of new technologies, test production and certification. So that helps the manufacturers… and also the research institutes to put their innovation into industrial manufacturing.”
Jooss said RCT Solutions along with partners including ISC Konstanz and Fraunhofer ISFH were already preparing to undertake a follow-up study looking at how such a pilot production would work.
The initial report from the Libertas project is being finalised and will be published in the coming weeks, Jooss added.
This article has been amended to correct the name of the partner organisations.






