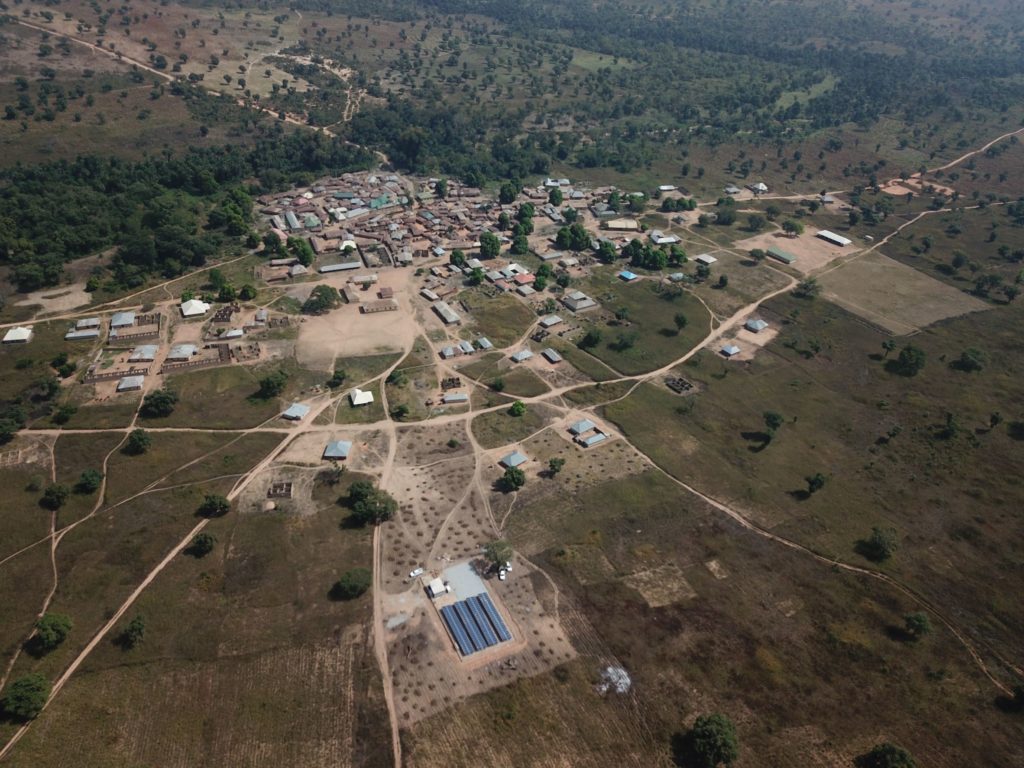
Canada-based greenhouse gas emissions reduction company CarbonAI has signed a memorandum of understanding (MOU) with the Rural Electrification Agency (REA) of Nigeria to develop small-scale rural solar projects across the country.
CarbonAI said that the solar mini-grid installations will be funded by carbon credits generated by its gas flare capture projects, which it has deployed across Nigeria.
Unlock unlimited access for 12 whole months of distinctive global analysis
Photovoltaics International is now included.
- Regular insight and analysis of the industry’s biggest developments
- In-depth interviews with the industry’s leading figures
- Unlimited digital access to the PV Tech Power journal catalogue
- Unlimited digital access to the Photovoltaics International journal catalogue
- Access to more than 1,000 technical papers
- Discounts on Solar Media’s portfolio of events, in-person and virtual
The projects will target underserved communities in areas affected by gas flares in proximity to CarbonAI’s technology. The REA will identify potential project locations and liaise with communities, while CarbonAI will take on financing, designing and construction.
”We are strong believers in win-win outcomes,” said CarbonAI chief carbon officer, Yvan Champagne. “We believe our climate dividend programme captures the spirit of the energy transition by leveraging immediate reductions in today’s energy system to build the energy system of tomorrow in Nigeria.”
Nigeria has pledged to eliminate gas flaring by 2025, and CarbonAI said that this MOU will contribute to reducing greenhouse gas emissions in communities near to gas and oil plants as well as providing a stable and secure energy supply to these areas.
The REA is an implementation agency of the government of Nigeria, primarily tasked with increasing access to electricity in unserved and underserved rural areas.
Managing director and CEO of the REA, Ahmad Salihijo Ahmad said: “The off-grid space in Nigeria is undergoing commendable growth. With the resultant opportunities, key stakeholders must take the responsibility to leverage these opportunities to accelerate sustainable impact, nationwide. This is another strategic and innovative way to finance climate-resilient infrastructure in Nigeria while alleviating energy poverty.”
In September, Crossboundary Energy Access and Engie Energy Access partnered to build US$60 million worth of mini-grids across Nigeria. The same month, the Nigerian government signed an MOU with India-headquartered Sterling & Wilson for 961MWp of solar PV installations.