Scientists at the University of Oxford last week (9 August) revealed a breakthrough in solar PV technology via an ultra-thin material that can be applied to “almost any building” and deliver over 27% conversion efficiency.
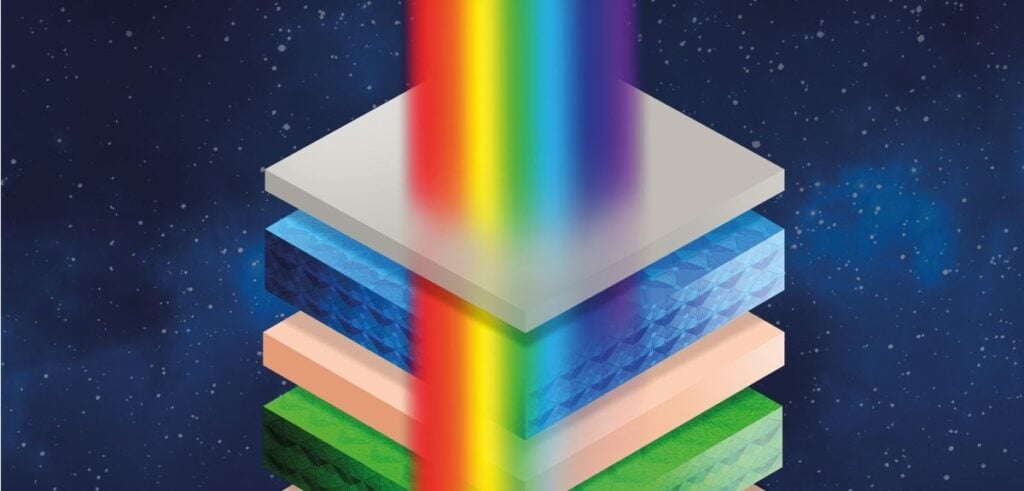
The Oxford scientists have described the new thin-film perovskite material, which uses a multi-junction approach, as a means to generate increasing amounts of solar electricity without the need for silicon-based solar modules.
Try Premium for just $1
- Full premium access for the first month at only $1
- Converts to an annual rate after 30 days unless cancelled
- Cancel anytime during the trial period
Premium Benefits
- Expert industry analysis and interviews
- Digital access to PV Tech Power journal
- Exclusive event discounts
Or get the full Premium subscription right away
Or continue reading this article for free
“During just five years experimenting with our stacking or multi-junction approach, we have raised power conversion efficiency from around 6% to over 27%, close to the limits of what single-layer photovoltaics can achieve today,’ said Dr Shuaifeng Hu, post-doctoral fellow at Oxford University Physics.

“We believe that, over time, this approach could enable the photovoltaic devices to achieve far greater efficiencies, exceeding 45%.”
The technology stacks multiple light-absorbing layers into one solar cell, harnessing a more comprehensive range of the light spectrum and allowing more power to be generated from the same amount of sunlight.
Oxford University said that contemporary solar modules’ energy efficiency levels stand at around 22%. Thus, with greater time and resources allocated to the new technology, it could contribute to the global energy transition as it grows more efficient.
The technology brings a new level of innovation with its thinness. At just over one micron thick, it is nearly 150 times thinner than a silicon wafer.
Unlike current photovoltaics, which are typically applied to silicon panels, this technology can be used on almost any surface. The scientists believe that this approach will further reduce the cost of solar energy and help establish it as the most sustainable form of renewable energy.
Japan’s National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology (AIST) gave its certification before publication of the researchers’ scientific study later this year.
‘By using new materials that can be applied as a coating, we’ve shown that we can replicate and outperform silicon while also gaining flexibility. This is important because it promises more solar power without the need for so many silicon-based panels or specially-built solar farms,’ said Dr Junke Wang, postdoc fellow at Oxford University Physics.
The scientists added that further breakthroughs promise additional cost savings as new materials, like thin-film perovskite, reduce the need for silicon panels and purpose-built solar farms.
This article first appeared on our sister site Solar Power Portal.






