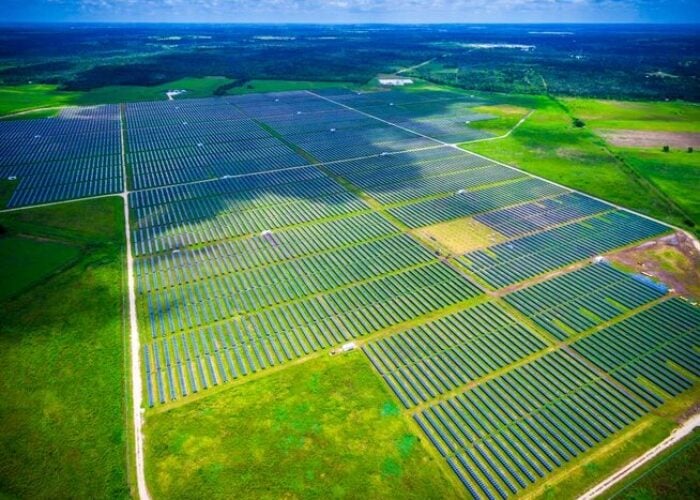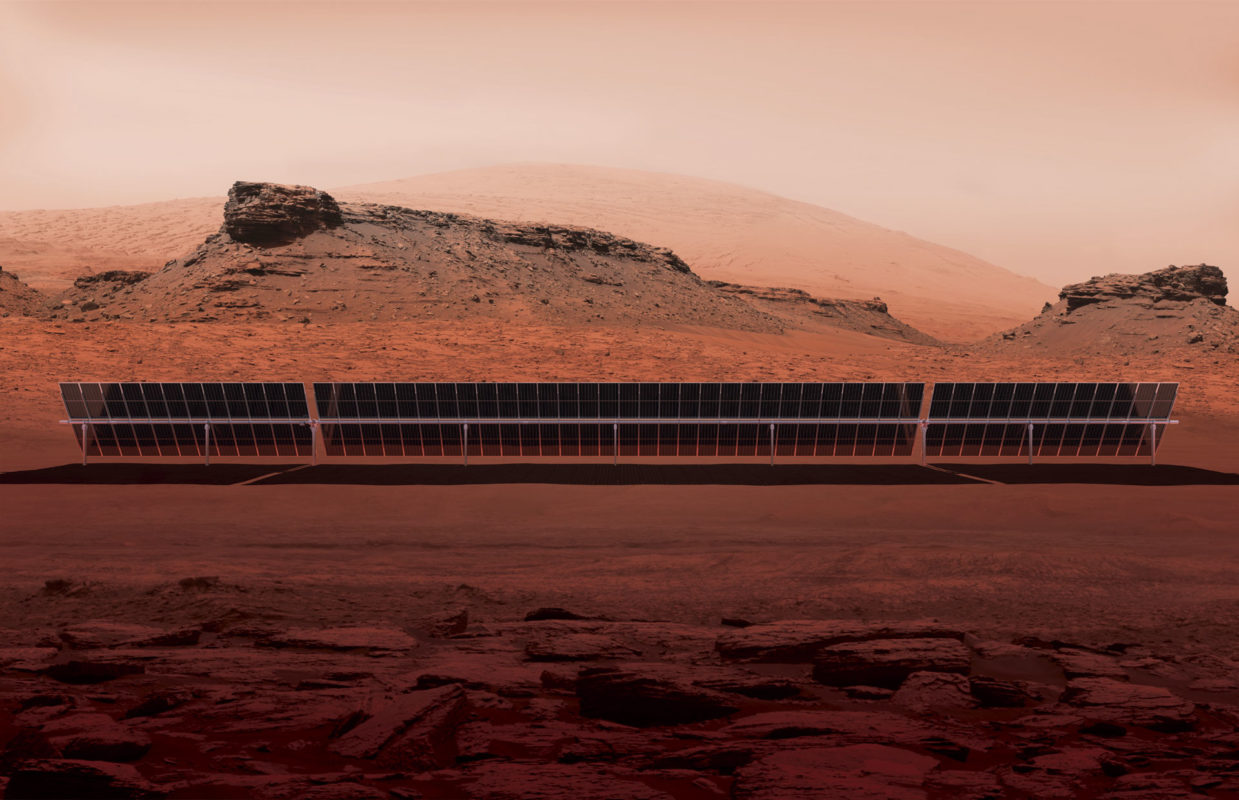
Soltec has launched its next-generation ‘SF8’ single-axis tracker system to meet the needs of utility-scale PV power plants adopting the new wave of large-area solar panels.
The SF8’s 4 to 6 strings, 2 x 60 minimum configuration is designed to reduce installation and maintenance costs, yield more energy and increase overall PV plant performance.
Try Premium for just $1
- Full premium access for the first month at only $1
- Converts to an annual rate after 30 days unless cancelled
- Cancel anytime during the trial period
Premium Benefits
- Expert industry analysis and interviews
- Digital access to PV Tech Power journal
- Exclusive event discounts
Or get the full Premium subscription right away
Or continue reading this article for free
Problem
The rapid transition in the upstream manufacturing solar sector to significantly larger modules to provide lower cost per-Watt means a new era for the industry in higher module performance and a leap in reducing PV power plants levelised cost of electricity (LCOE) in a rapidly changing downstream market that becomes subsidy free, bidding orientated and targeting grid parity and beyond. To cater for these developments single-axis tracker systems used in utility-scale PV power plants need to be redesigned, provide further yield gains and meet demanding safety needs for potential wind related issues.
Solution
The new SF8 tracker reinforces its structure to facilitate installation and favors high performance on any terrain. A reinforced torque tube with a new, improved geometry, together with an autonomous self-stow system, contribute to increased tracker resistance to adverse weather conditions. In addition, the SF8 tracker increases the rigidity of its structure by 22% more than the previous generation of Soltec trackers, the SF7.
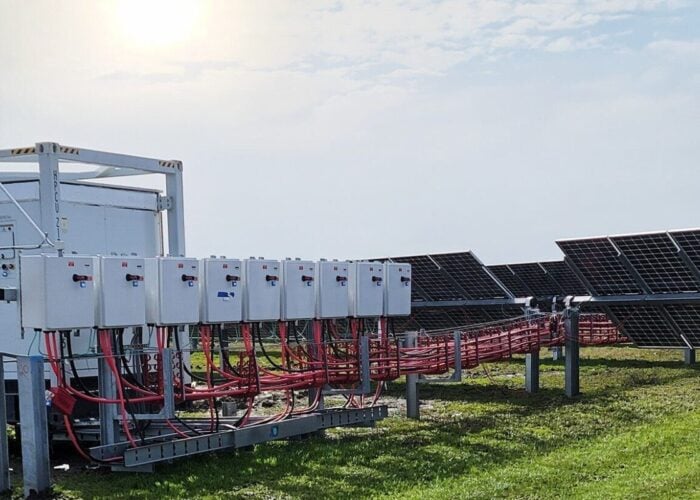
The SF8 has 5.16% fewer parts per module than the previous generation of Soltec trackers, thus reducing costs while improving installation efficiency. Each SF8 tracker is equipped with, at least, four strings, contributing to ease electrical module connections. Due to these innovations, the SF8 allows for easier and quicker installation, favoring enhanced return on investment and reduced installation and maintenance costs.
The SF8 tracker is claimed to allow up to 8.6% more power generation when bifacial modules are installed. With the ‘TeamTrack’ system, Soltec claims the SF8 is capable of enabling 6% more energy yield. The improved and adapted algorithm for bifacial modules, achieves an extra yield of up to 0.5%, according to the company. This extra bifacial gain adds to the 2.1% gain yielded in comparison to 1-in-portrait configuration trackers, according to the company.
Applications
The tracker system is specially designed for larger 72 and 78-cell modules (including bifacial modules) for utility-scale PV power plants.
Platform
The SF8’s 4 to 6 strings, 2 x 60 minimum configuration is designed to reduce installation and maintenance costs, yield more energy and increase overall PV plant performance. With a multidrive transmission system within the tracker structure and supersized torque-tube with improved geometry is designed to provide the highest resilience to wind conditions. There are two or more drives per tracker with better angle accuracy and wind reliability. 'Dy-WIND' design methodology is used comprehensively. Completely autonomous tracker electronics ensures the most secure position for given wind episodes. A new full-wireless system allows complete plant and inter-tracker connection. The ‘Open Thread’ system developed by Google contributes to improved plant protection and to preventing damages by accurately anticipating weather conditions.
Availability
September 2020, onwards.






