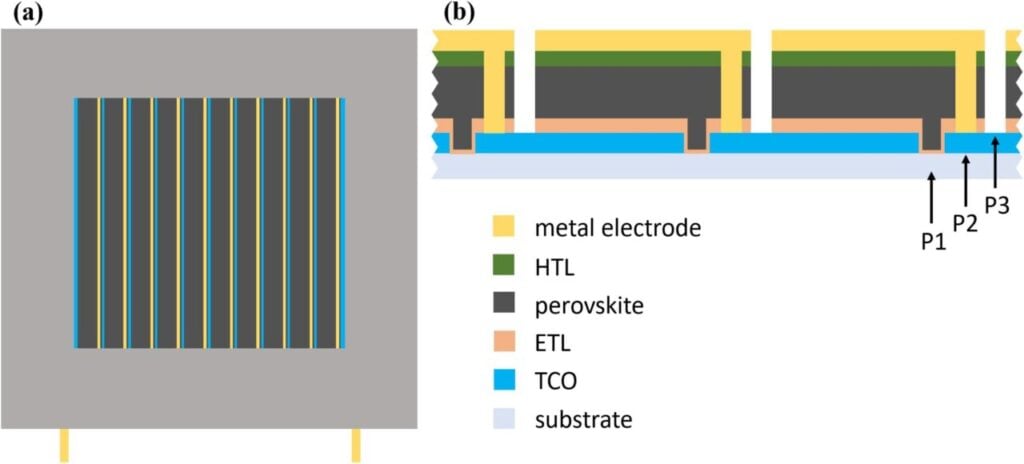
Researchers in Japan have undertaken a comprehensive study to test the degradation of perovskite solar cells in extreme heat and humidity.
The study has underlined the importance of barrier film quality in preventing the breakdown and reduction in operational efficiency of perovskite cells.
Unlock unlimited access for 12 whole months of distinctive global analysis
Photovoltaics International is now included.
- Regular insight and analysis of the industry’s biggest developments
- In-depth interviews with the industry’s leading figures
- Unlimited digital access to the PV Tech Power journal catalogue
- Unlimited digital access to the Photovoltaics International journal catalogue
- Access to more than 1,000 technical papers
- Discounts on Solar Media’s portfolio of events, in-person and virtual
Flexible perovskite solar cells’ versatility and high efficiency present a potentially significant leap forward for PV technology, but their commercial applications have thus far been hindered by their sensitivity to factors such as humidity and temperature.
To address this, a team of researchers led by Professor Takashi Minemoto of Ritsumeikan University, Japan, recently conducted research to investigate the durability of perovskite solar cells in harsh environmental conditions. The study was recently published in the journal Solar Energy.
“Perovskite solar cells stand out as particularly promising due to their low-temperature wet-coating process and compatibility with flexible substrates, offering unique opportunities for the solar industry. However, the stability of perovskite is weak compared with conventional material, which can be improved by fabrication processes such as encapsulation with barrier films,” Prof. Minemoto said.
The study tested perovskite modules made of methylammonium lead iodide (MAPbI₃) encapsulated with polyethylene terephthalate substrate with barrier films of varying water vapour transmission rates (WVTR).
The modules were then subjected to a damp heat test that exposed them to temperatures of 85°C and 85% relative humidity. After 2,000 hours of exposure, the modules’ photovoltaic performance was recorded, and their degradation was confirmed through characteristics of current voltage, spectral reflectance and electroluminescence.
The researchers found that high humidity led to the decomposition of the MAPbI₃ layer into lead iodide, leading to a significant reduction in the efficiency of the perovskite modules.
The findings also revealed that the quality of the barrier film played a critical role in the module’s stability. The module with the lowest WVTR barrier of 5.0 × 10⁻³ g/m²/day retained 84% of its power conversion efficiency, while the modules with higher WVTR experienced rapid degradation, ceasing to function after just 1,000 hours, according to the researchers.
The researchers said the study highlighted the importance of barrier film in maintaining the long-term durability of flexible perovskite modules, potentially helping pave the way for their wider commercial deployment.
“Our study is the first to report the durability of encapsulated flexible MAPbI₃-based PSC modules. When considering solar energy applications for walls and rooftops with weight limits or for mobile platforms, flexible PSCs are a great alternative to the traditional silicon panels. Insights from our study could help industries optimise these modules for highly stable and durable constructs,” concluded Prof. Minemoto.
Read more about the path to commercialisation for perovskite PV technology in the latest edition of our quarterly journal, PV Tech Power (subscription required).