Concerns over the performance of TOPCon cells following UV exposure may be exaggerated, according to research by Germany’s Fraunhofer Institute for Solar Energy Systems (ISE).
Fraunhofer’s researchers investigated the common methods used to test for UV degradation and found that they can overstate the extent of the issue compared to what is experienced in the field.
Try Premium for just $1
- Full premium access for the first month at only $1
- Converts to an annual rate after 30 days unless cancelled
- Cancel anytime during the trial period
Premium Benefits
- Expert industry analysis and interviews
- Digital access to PV Tech Power journal
- Exclusive event discounts
Or get the full Premium subscription right away
Or continue reading this article for free
The rapid ascent of TOPCon market dominance has been overshadowed by mounting evidence suggesting the cell technology displays certain key vulnerabilities, notably to UV exposure and light- and temperature-induced degradation. As Fraunhofer noted, this has caused concern among PV developers, operators and investors given the high market penetration TOPCon now enjoys.
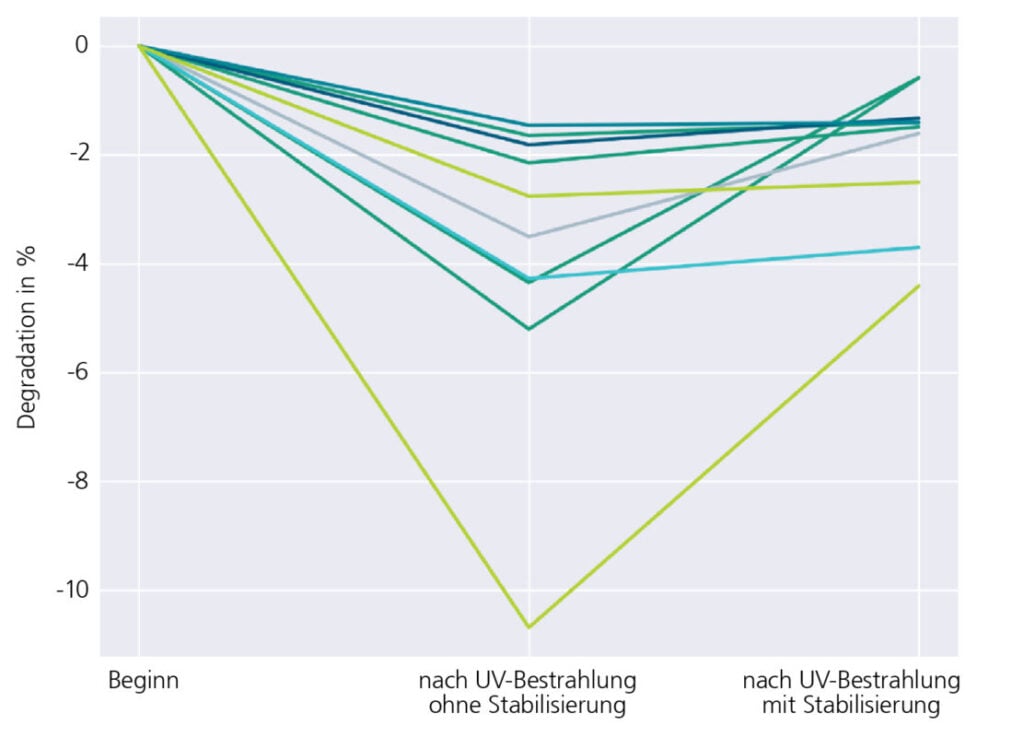
However, the institute said the current standard UV test painted an inaccurate picture of the real-world degradation a TOPCon module might sustain from UV exposure.
Notably, Fraunhofer’s research found that to achieve results that more accurately reflect field degradation, the PV modules must be stabilised after testing in order to distinguish UV-sensitive from less sensitive module types and evaluate them comparably.
The research indicated that UV degradation during testing destabilises modules to such an extent that they significantly lose efficiency during dark storage after UV exposure. Subsequent exposure to sunlight, however, leads to significant recovery, yielding degradation measurements closer to the values actually measured in practice.
Fraunhofer said some PV modules showed hardly any degradation after UV testing at 60kWh per square meter, roughly equivalent to one year’s UV exposure in Germany, and subsequent stabilisation under sunlight. Other modules still showed significant performance declines of up to 5% even after stabilisation. Overall, the researchers concluded that the degradation appears to be significantly less drastic than the standard UV tests suggest.
“Unfortunately, many module types of the current generation of commercial TOPCon PV modules react sensitively to UV irradiation. ‘Field returns’ and comparisons between laboratory-aged and field-aged modules also confirm this. However, the degradation rate does not appear to be as drastic as previously assumed,” said Daniel Philipp, Head of the Module Characterisation and Reliability Department at Fraunhofer ISE. “We recommend that users test PV modules according to the latest findings. Researchers need to further analyse this phenomenon in order to more accurately predict the long-term effects of solar radiation on module yield.”
Fraunhofer said UV tests in the laboratory simulate the natural UV radiation to which PV modules are exposed in real-world conditions, but significantly increase the irradiation intensity to accelerate ageing and enable predictions about long-term performance losses.






