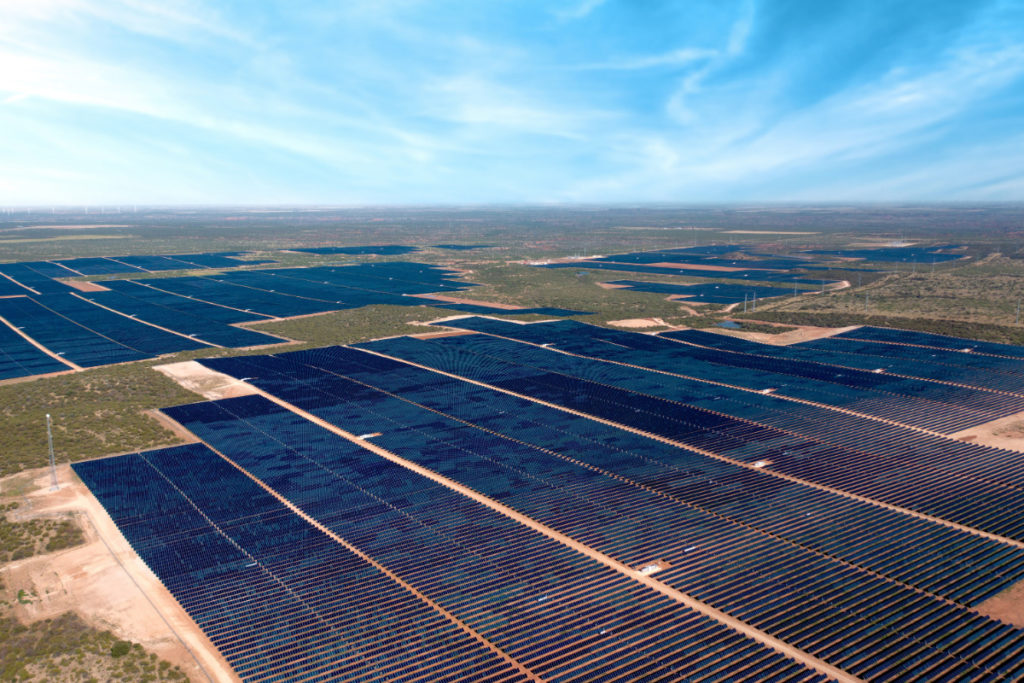
The US added 4,557MW of solar capacity in the first quarter of 2024, bringing the total installed capacity to over 100GW, according to the American Clean Power Association (ACP).
In its quarterly report for the US market, the ACP said project developers in the US commissioned 111 utility-scale solar, battery energy storage system (BESS) and wind projects in Q1, adding 5,585MW of clean power capacity to the grid. This represented a 28% increased compared to the same quarter in 2023.
Unlock unlimited access for 12 whole months of distinctive global analysis
Photovoltaics International is now included.
- Regular insight and analysis of the industry’s biggest developments
- In-depth interviews with the industry’s leading figures
- Unlimited digital access to the PV Tech Power journal catalogue
- Unlimited digital access to the Photovoltaics International journal catalogue
- Access to more than 1,000 technical papers
- Discounts on Solar Media’s portfolio of events, in-person and virtual
Of the new renewables additions, solar (4,557MW) accounted for 81.6% in Q1, followed by onshore wind (449MW), BESS (447MW) and offshore wind projects (132MW). Solar additions in Q1 increased by 83% compared to Q1 2023, but dropped by 63% quarter-on-quarter.
The largest project that came online during Q1 was the 828MWp/640MWac Lumina project in Texas, developed by US renewables company Intersect Power.
Cumulatively, the US had 269.9GW of renewables capacity as of the end of Q1 2024. Wind accounted for 56.1% of the total capacity (151.3GW), while the solar sector (11.5GW) made up 37.3%. BESS accounted for only 6.6% (17.8GW/47,543MWh) of the operating renewables capacity.
A growing renewables pipeline
In Q1 2024, renewables pipeline in the US increased to 174GW, up from 171GW in Q4 2023. On a year-over-year basis, the pipeline is now 26% larger than Q1 2023 (139GW). The ACP said the expansion of the pipeline can be attributed to BESS and solar, which have grown at an average rate of 11% and 4% per quarter, respectively, since Q2 2022.
The pipeline in Texas was 28.3GW, the highest among all states in the US, followed by California (17.7GW), New York (14.3GW), Arizona (8.7GW) and Virginia (7.9GW). The ACP said that Kentucky boasted only 81MW of operating renewables capacity, but it had more than 2.5GW of projects in its pipeline.
As of the end of Q1 2024, the US’ utility-scale solar pipeline reached 94.5GW, up from about 81.5GW in Q1 2023. The capacity of solar that is under construction increased by 14GW year-on-year, while the advanced development pipeline shrank by only over 1GW. Until the end of Q1 2024, 72.1GW of renewables were under construction, consisting of 553 projects across 45 states.
Geographically, Texas and California were the top two states with the most projects under construction, having a total capacity of 18.9GW and 8.6GW, respectively. These two states were followed by New Mexico (5.2GW), Wyoming (5.1GW) and Arizona (4.7GW).
With regard to projects in the advanced stages of development at the end of Q1 2024, utility-scale solar accounted for 50% of the advanced development pipeline, followed by offshore wind (22%), battery storage (17%) and onshore wind (11%).
Over 6GW of PPAs
In Q1 2024, 6.05GW of power purchase agreements (PPAs) were announced, increasing by 103% year-on-year. A total of 905MW of BESS PPAs were announced in the same quarter as well, rising by 201% year-on-year.
The ACP said the significant increase in PPAs for solar and BESS can be partially attributed due to the price differences in PPAs between technologies. Since 2019, the number of PPA announcements for solar has supported a dramatic rise in solar deployments, resulting in a record-breaking 21.1GW of solar added to the grid in 2023.