Several European countries have underestimated the deployment of solar PV by 205GW by 2030, according to energy think tank Ember’s latest report.
The report, Putting the mission in transmission: Grids for Europe’s energy transition, looked at 35 national grid development plans from European Transmission System Operators (TSOs) – including the EU, the UK and Western Balkans – with many countries “out of step with the reality of the energy transition”.
Try Premium for just $1
- Full premium access for the first month at only $1
- Converts to an annual rate after 30 days unless cancelled
- Cancel anytime during the trial period
Premium Benefits
- Expert industry analysis and interviews
- Digital access to PV Tech Power journal
- Exclusive event discounts
Or get the full Premium subscription right away
Or continue reading this article for free
Based on trade association SolarPower Europe’s business-as-usual scenario, out of 23 countries analysed, 19 had underestimated the deployment of solar PV by 205GW by 2030.
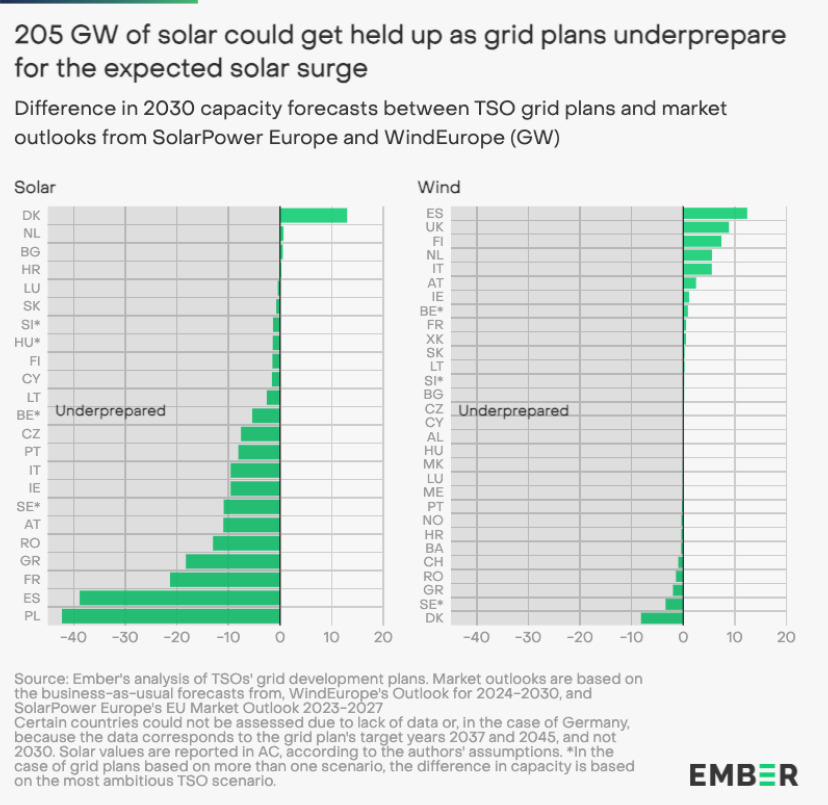
If the gap between the solar capacity that is expected and the grid expansion plans continues over time, this would cause increased grid congestion in the short term, while solar projects would end up stuck in grid connection queues.
Only four countries’ TSOs – Croatia, Denmark, Finland and the Netherlands – have anticipated more ambitious capacity scenarios for solar (and wind) than their country’s existing targets. The difference for these countries ranges from 50% higher for Denmark to 200% higher for Finland. Grid plans for these four countries combined anticipate 81GW of solar and wind capacity in excess of the national policy targets.
At a country level, France has the highest absolute difference between the energy scenario from its TSO for solar capacity (35GW) compared to its national solar capacity targets (54GW), with a difference of 19GW by 2030.
Solar misalignment more frequent than wind
Furthermore, the comparison between solar and wind technologies, showed that solar tends to be more affected by a misalignment, with 60GW of solar capacity underestimated across 11 countries against 27GW for wind.
The difference between a country’s national target and grid plans from a TSO is often due to a time lag between the two, with national plans updating their targets sooner than the TSOs, as shown below.
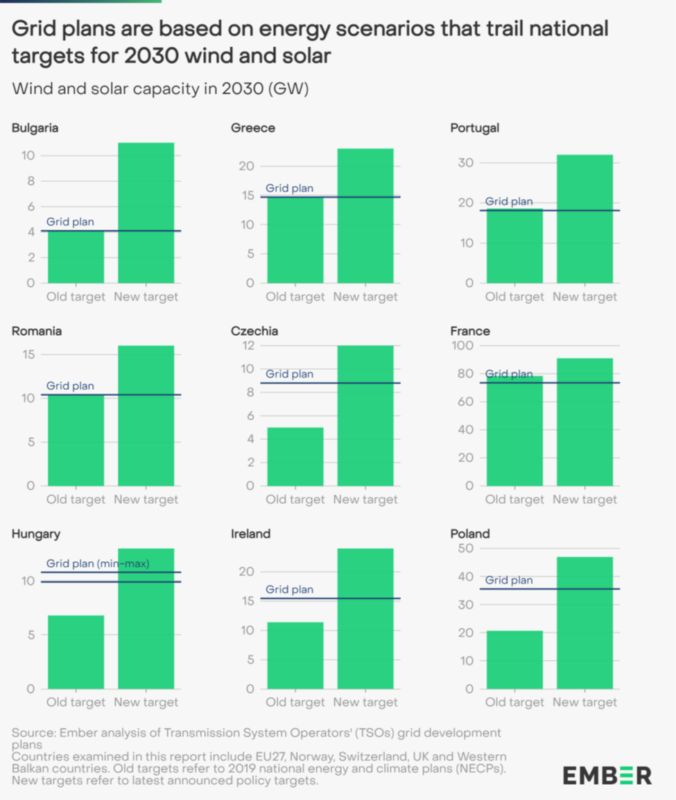
Elisabeth Cremona, energy & climate data analyst at Ember, said: “We can’t afford to overlook grids. They risk holding Europe’s supercharged energy transition back if plans aren’t updated. Making sure solar and wind can actually connect to the system is as critical as the panels and turbines themselves. There is no transition without transmission.”
“As clean technology deployment surges forward, it is increasingly coming up against the bottleneck of insufficient grid capacity, leading to connection delays, curtailment and increased costs for consumers.”
On the bright side
Despite the challenges mentioned above, positive steps have been taken by TSOs to address grid challenges. Among them, grid expansion over the coming decade, along with upgrades and several TSOs prioritising non-wire solutions – such as load flexibility – to alleviate grid congestion.
Between the 35 countries analysed by Ember, over 25,000 km of new lines are planned between now and 2026, a 5.3% increase in the total length of national transmission networks. At the top of the table is Spain with the most capacity added during that time span, with over 5,000 km. It is followed by Germany (3,600 km) and Denmark (3,300 km).
Prioritising grids in political agenda
Although the expansion of national transmission networks is accelerating, grid plans are still struggling to keep pace with the growth of renewable energy and the increased targets.
Among the key recommendations from the report would be to prioritise grids in national political agendas, strengthening its support and financing; regulatory frameworks should be revised to give enough time to plan and invest in grids; renewables should be at the forefront of grid planning, in order for TSOs to better anticipate the needs of the grid in the coming decades.






