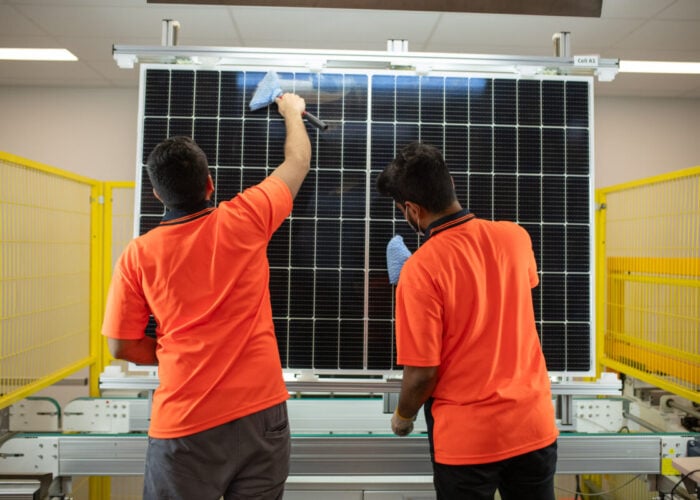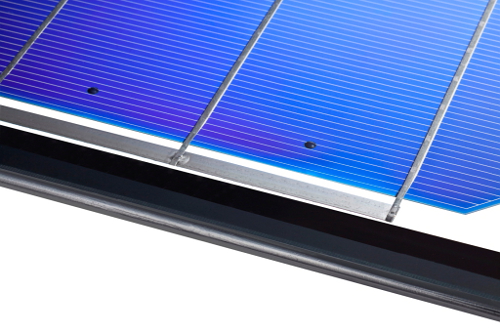
The development program initially sparked from a Fraunhofer ISE patent has been honed to industrial-scale production opportunities both in durability and cost advantage of conventional PV modules using top side glass, encapsulants and backsheets.
With the ‘TPedge’ assembly approach, solar cells are fixed in a gas-filled space between the two glass panes with special adhesive pins, eliminating encapsulants and backsheets as well as the aluminium frame and sealing.
Unlock unlimited access for 12 whole months of distinctive global analysis
Photovoltaics International is now included.
- Regular insight and analysis of the industry’s biggest developments
- In-depth interviews with the industry’s leading figures
- Unlimited digital access to the PV Tech Power journal catalogue
- Unlimited digital access to the Photovoltaics International journal catalogue
- Access to more than 1,000 technical papers
- Discounts on Solar Media’s portfolio of events, in-person and virtual
Fraunhofer ISE said it had developed a special cost of ownership (COO) model on SEMI industry standards to accurately cost the TPedge assembly approach as well as a cell-to-module power analysis (CTM), and measurements from the CalLab PV Modules.
“The results show that the specific module costs of the TPedge concept are approximately 2 percent less than the conventional glass-foil-laminate concept,” noted long-standing project head at Fraunhofer ISE, Max Mittag. “The cost reduction is mostly due to lower material costs. Material costs are crucial since they are responsible for ca. 90 percent of the total module production costs, including cells.”
Fraunhofer ISE also noted that the TPedge concept also lowers material costs compared to the glass-glass-laminate concept.
Previous production cost reduction claims for the technology also highlighted faster throughput cycle times that aimed at 45 seconds per module. Complete module assembly would have been less than a minute, compared to a standard module assembly cycle time of 16 minutes.
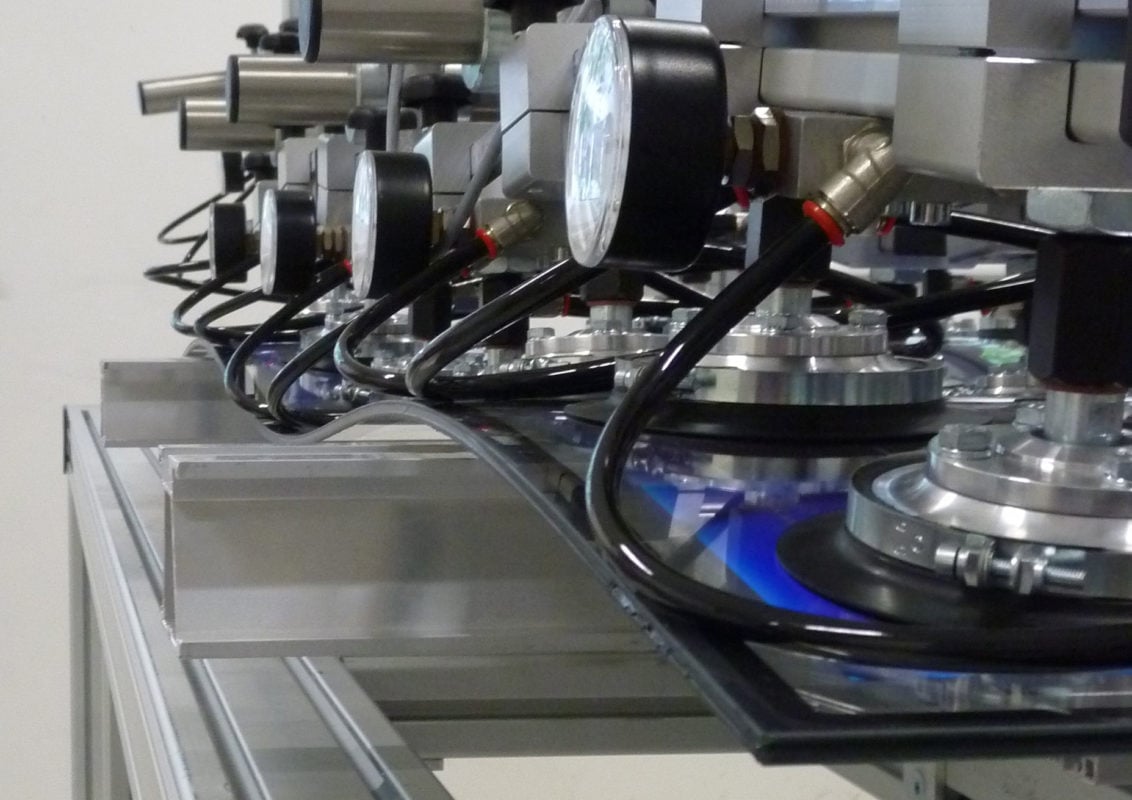

The module prototypes jointly produced with Bystronic glass underwent many typical tests based on the standards IEC 61730 and 61215 at the PV Module-TEC (Module Technology Center) at Fraunhofer ISE, which verified the durability of the modules by exposing them to 400 temperature cycles (-40 °C … + 85 °C) in the testing process. Durability tests for mechanical loads (see above image) and hail were also carried out successfully, according to Fraunhofer ISE.
The culmination of the program has been the ability to transfer the once lab prototype to an industrial-scale module using the standard 60-cell configuration.