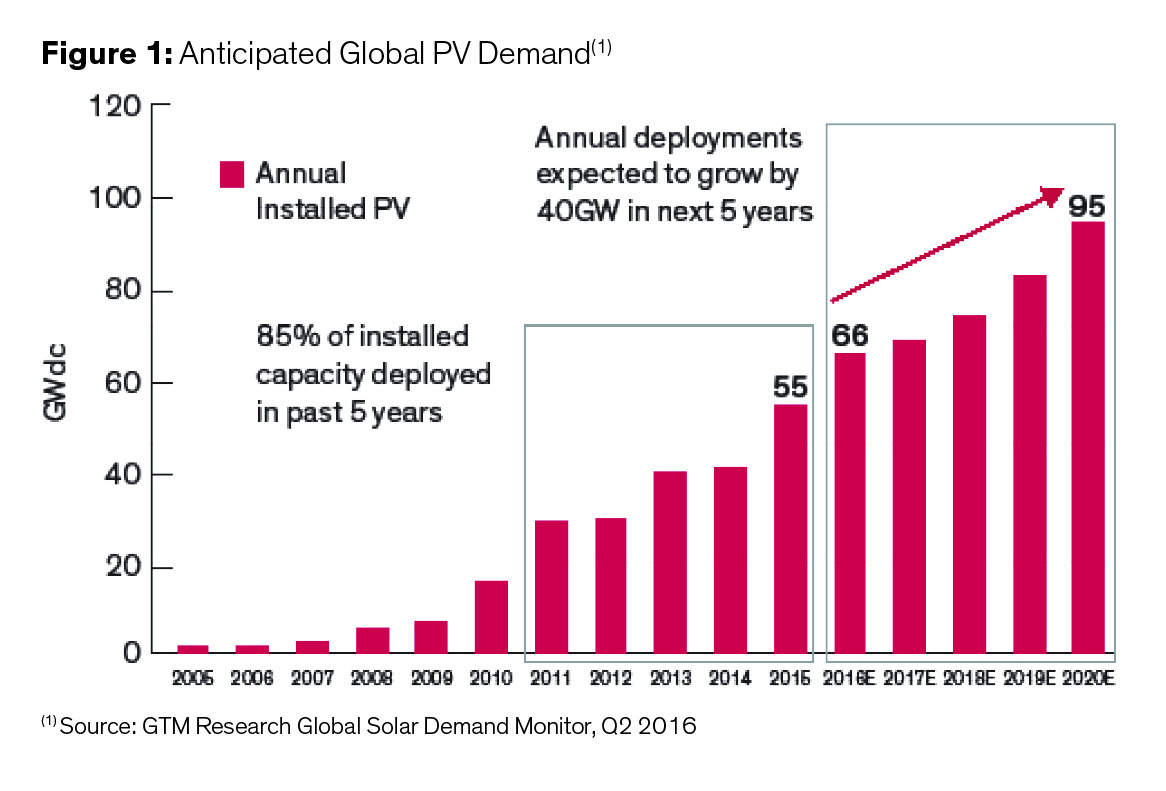
Renewable energy demand continues to grow globally, with solar leading alternative energy technologies. According to GTM Research, growth for solar in 2016 was expected to be about 21% in 2016, translating to 66GW of solar power output globally; see Figure 1. More recent updates from GTM show actual growth in 2016 to 74GW and projections of 109GW by 2021. Innovation impacting the longevity and durability of PV solar systems is paramount to a sustainable solar energy future.
Unlock unlimited access for 12 whole months of distinctive global analysis
Photovoltaics International is now included.
- Regular insight and analysis of the industry’s biggest developments
- In-depth interviews with the industry’s leading figures
- Unlimited digital access to the PV Tech Power journal catalogue
- Unlimited digital access to the Photovoltaics International journal catalogue
- Access to more than 1,000 technical papers
- Discounts on Solar Media’s portfolio of events, in-person and virtual
Benefits of PV encapsulant films – Material choice matters
PV encapsulant films are crucial in the protection and long-term functionality of solar collection cells in PV modules. Weather, moisture incursion/corrosion and long-term UV exposure negatively impact PV modules. Advances in PV film technology can significantly mitigate these issues, resulting in a more durable, long-lasting module.
Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) has long been used in PV encapsulant films, offering good light transmittance, elasticity and adhesion properties. However, its moisture, heat and UV-aging resistance, along with yellowing that can cause lower power outputs, are a challenge.
Dow’s R&D developed revolutionary metallocene catalysts for POE, applying world-leading technical capabilities to the challenge of optimizing PV encapsulant film materials that provide:
- Increased power generation, electrical efficiency, reliability and extended module life
- Improved Potential Induced Degradation (PID) resistance, reducing premature module failure and replacement
- Lower Levelized Cost of Energy (LCOE) – better project economics for solar developers, utilities and their customers
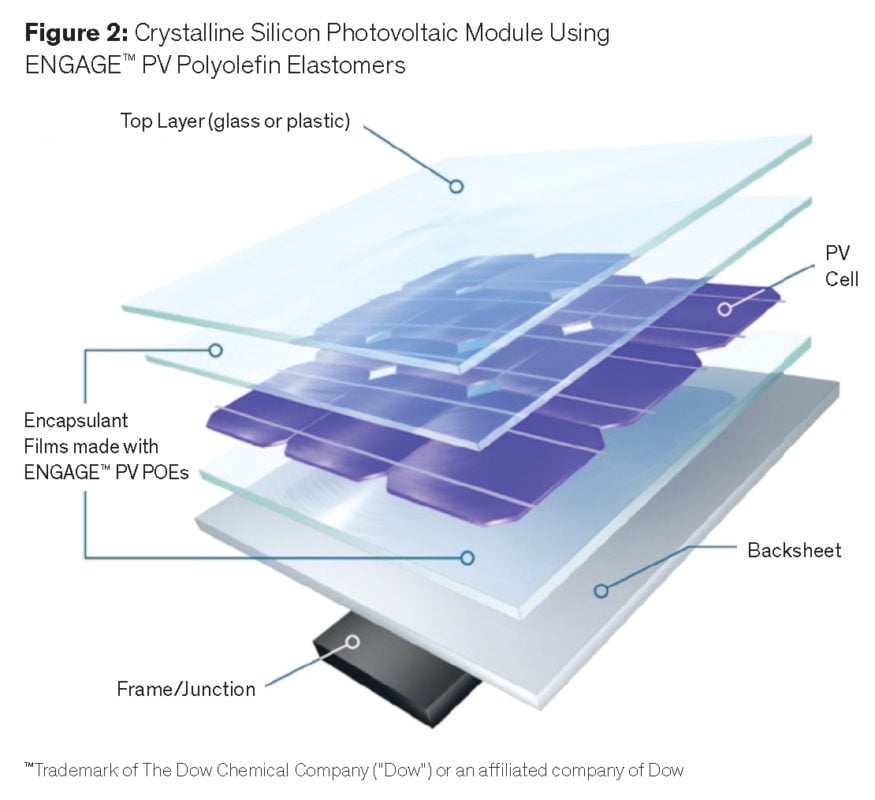
POE films, like ENGAGE™ PV Polyolefin Elastomers from Dow, can be used on many module types: high power output, rigid (c-Si, N-type, P-type, thin film), flexible and glass/glass for commercial, residential and utility applications (Figure 2).
POE performance advantages
Innovation in encapsulant film materials helps film and module producers manufacture advantaged products offering exceptional protection for the PV cell, with improved performance and lower system lifetime costs for the end user.
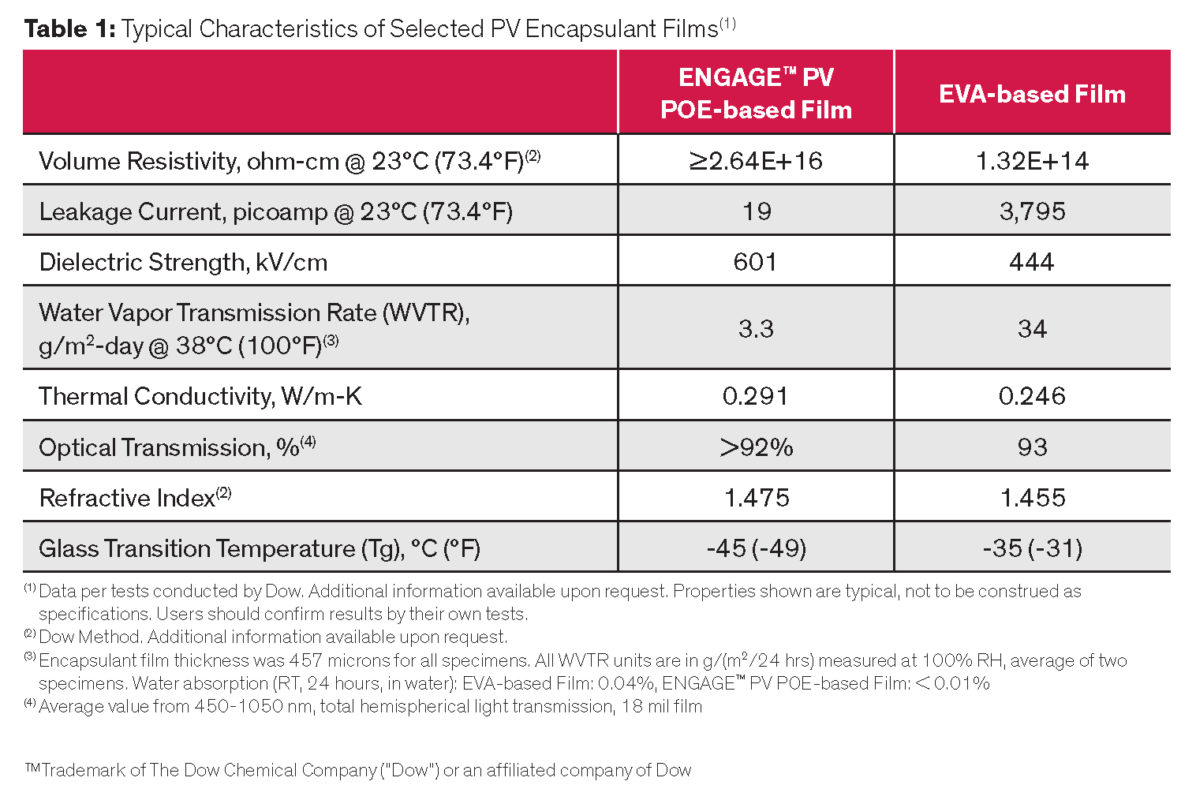
Modules made with POE-based encapsulant films outperform those made with EVA in these critical areas (Table 1):
- Volume resistivity and leakage current
- Water vapor transmission rate (WVTR)
- Dielectric strength
- Optical transmission/yellowing
- Generation of acetic acid (none with POE)
- UV and weather resistance
- PID performance
- Energy output, operating efficiency, reliability
- Service life (including LCOE/total lifetime system costs)
Other testing of POE materials versus EVA compared:
- Power degradation rates/projected power output
- Leakage current
- PID resistance
Power degradation rates/projected power output
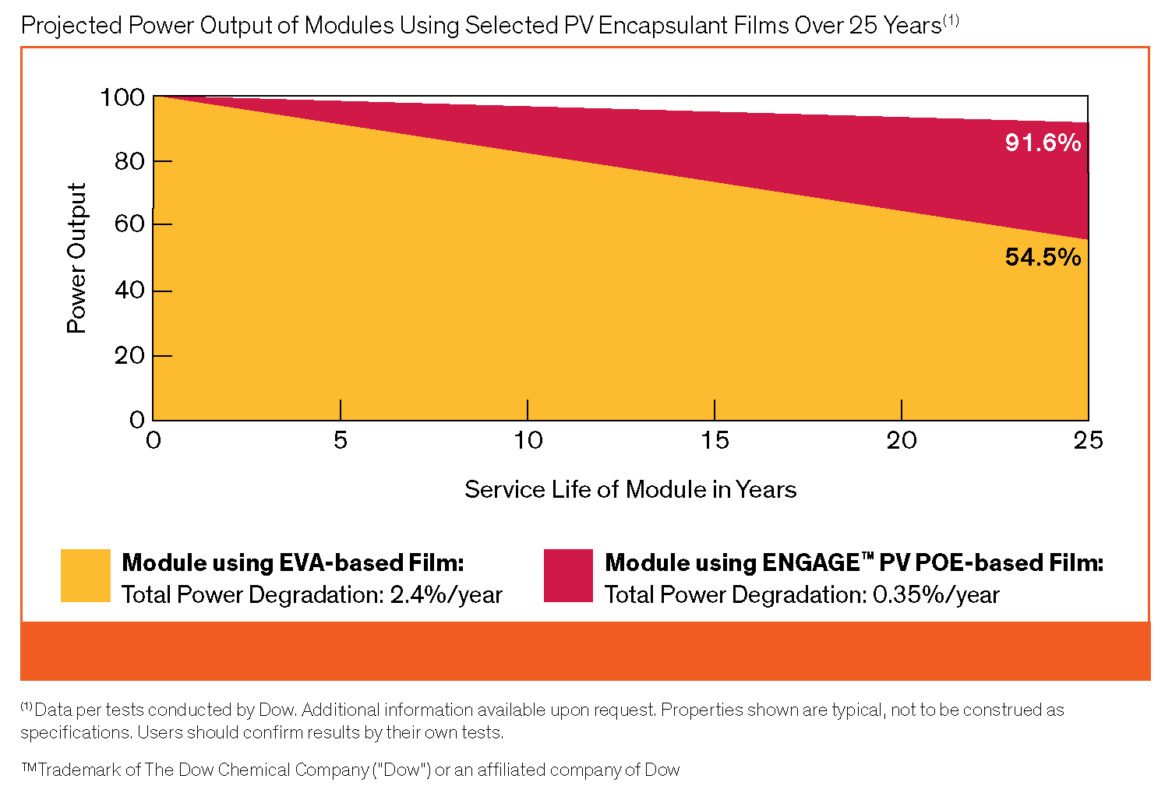
Dow worked with Florida Solar Energy Center to compare EVA- and POE-based film modules over a three-year period. The EVA-based film modules lost three times more total power output (based on a combination of degradation rate plus PID for total degradation rate) during the study than those modules made with POE-based film. Calculations based on this study along with further testing, translate to an estimated 54.5% retained power output after a 25-year service life for EVA-based modules, versus nearly 92% retained power output for POE over the same time period (Figure 3).
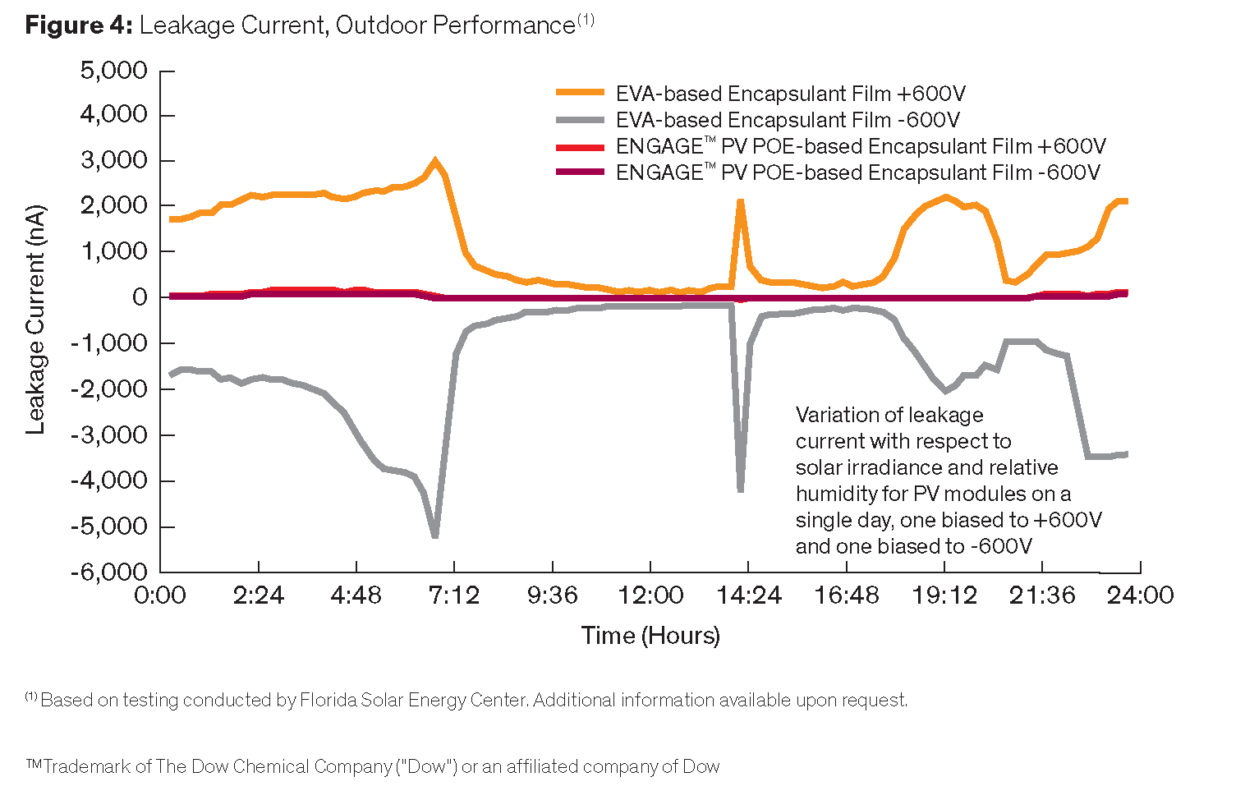
Leakage current
PV modules’ ability to perform in any type of outdoor environment is crucial. Leakage current can occur as part of the module degradation process, compromising reliability. EVA-based modules (Figure 4) are more susceptible to high temperatures and humidity. POE-based modules maintain low leakage current, enhancing electrical performance and module reliability.
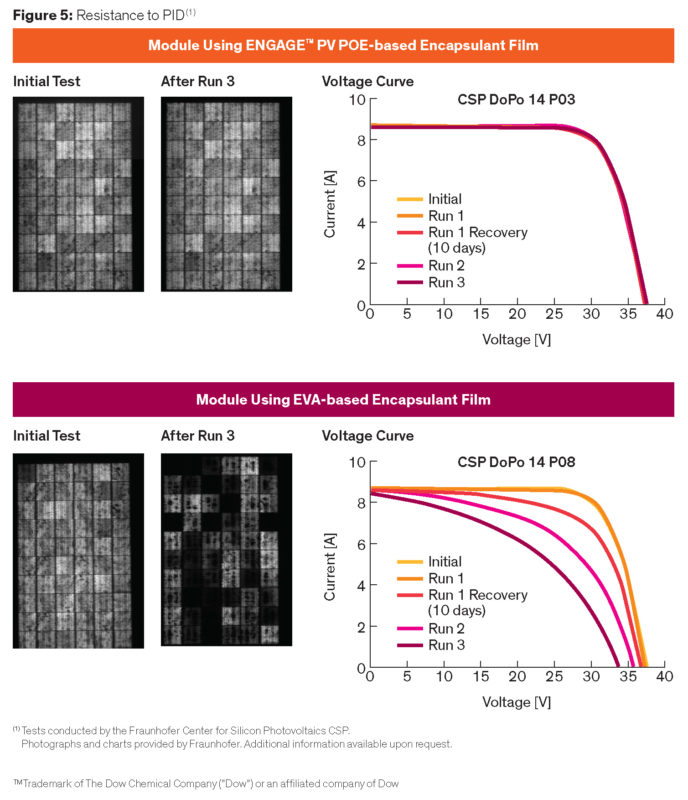
PID resistance
PV modules’ ability to resist potential induced degradation (PID) from high voltage stress results in improved power output performance and long-term reliability. Dow and the Fraunhofer Center for Silicon Photovoltaics tested both POE- and EVA-based modules. All were exposed to three test cycles of 50% RH at -1000V at 50⁰C over two days. Run 1 was followed by a recovery period of ten days in a dark room at room temperature. Figure 5 shows representative findings of PID. EVA-based film exhibited significant and rapid power loss versus POE-based film.
Consider a Smart Choice
As PV demand grows, developers, municipal and investor-owned utilities and alternative-energy savvy consumers will require systems reliably offering long service life with wider timeframes between module replacement. Materials innovators play a prominent role in sustainable solar power infrastructure. POE-based films are the smart choice for PV film and module producers, offering system reliability and a strong ROI for all players in the solar energy value chain. Learn more.

Andrew began his career with h-UCC Singapore in 1996. In 2001, he joined h-Dow/UCC Singapore. Since then, he’s held various positions such as Chemist, Account Manager, Technical Service & Development (TS&D) from Specialty Polymers to Specialty Chemicals businesses within Dow at its Midland, Michigan; Shanghai, PRC and Singapore locations. In 2011, Andrew returned to Dow Singapore to assume the Regional Marketing Manager role for Dow Elastomers. He was recently named Marketing Manager, Asia Pacific for Dow Elastomers, Electrical & Telecommunications. Andrew holds a Degree in Analytical Chemistry from The National University of Singapore and Postgraduate Diploma in Marketing from The Chartered Institute of Marketing, UK.








