Tariff and policy uncertainty saw installations decline across US utility and non-residential PV last year even as the residential segment bounced back, according to the Solar Energy Industries Association (SEIA) and Wood Mackenzie.
The latest update from the trade body and the consultancy found a 7% year-on-year dip for US utility-scale PV installations in 2018.
Unlock unlimited access for 12 whole months of distinctive global analysis
Photovoltaics International is now included.
- Regular insight and analysis of the industry’s biggest developments
- In-depth interviews with the industry’s leading figures
- Unlimited digital access to the PV Tech Power journal catalogue
- Unlimited digital access to the Photovoltaics International journal catalogue
- Access to more than 1,000 technical papers
- Discounts on Solar Media’s portfolio of events, in-person and virtual
The segment, the analysis found, produced the bulk (6.2GW) of PV-wide capacity additions (10.6GW) in the country last year but faltered under “disruption, delay and even cancellation” due to Section 201 tariffs.
Adopted last year, the US levies on module and cell imports prompted sponsors to postpone 2018 commercial launches to 2019, according to the SEIA and Wood Mackenzie. In the Carolinas, delays were compounded by a hold-up with interconnections under the PURPA programme.
For utility-scale PV, the flip side to the Section 201 tariffs was that module prices are falling faster than expected. This, the analysis pointed out, boosted competitiveness and helped drive the signing of 13.2GW of utility solar PPAs in 2018; the resulting, current contracted pipeline of 25.3GW marks an all-time record for US solar.
PV in US power addition top two for sixth year running
According to the SEIA and Wood Mackenzie, the 10.6GW added across all PV subcategories in 2018 marks the sixth consecutive year where solar is amongst the US top two for power additions, together with natural gas.
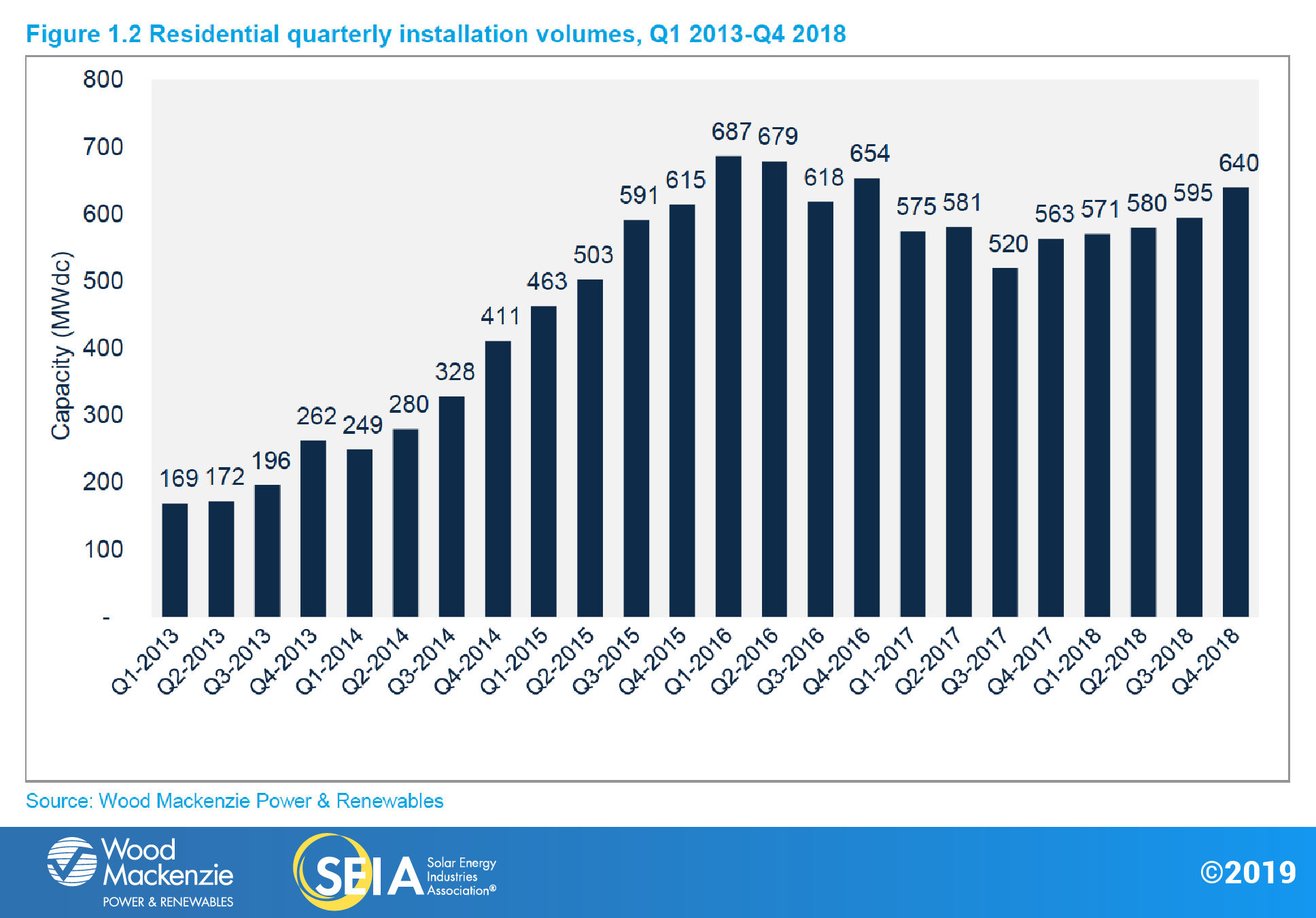
Unlike utility solar, the residential segment reversed its decline throughout 2017 by recording in 2018 year-on-year installation growth of 7%. The steady pace of addition indicates the market is nearing its maturity point, the new analysis indicates.
According to the document, installations across California, Massachusetts and the other typical residential heavyweights are being fast overtaken by new-entrants including Texas and Florida.
Future residential growth can be fuelled by incentives and net metering – Nevada saw a 261% jump in 2018 after reinstating the policy – but could be hindered by high customer acquisition costs, the SEIA and Wood Mackenzie noted.
Their analysis found a slight decline – 8% – in non-residential installations of US PV in 2018. Massachusetts and California alone saw a joint 450MW dip last year, although the former (64% drop) bore the brunt to a greater extent than the latter (17%).
See here for more information on the US Solar Market Insight by the SEIA and Wood Mackenzie