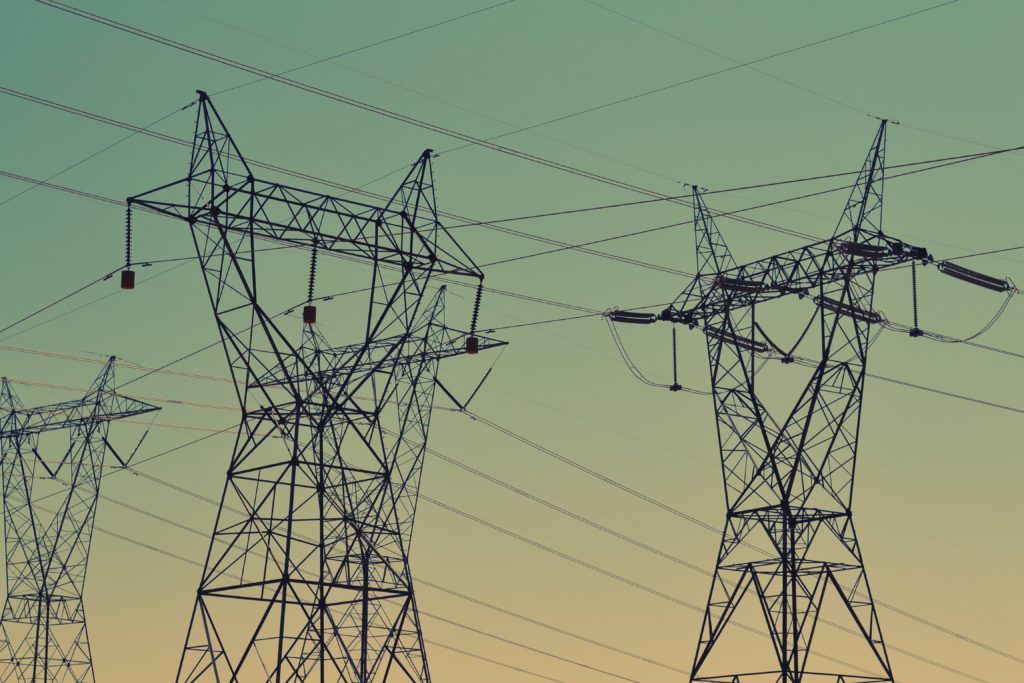
California’s energy transition will need 53GW of solar PV by 2045, with the state’s transmission system requiring a US$30.5 billion investment alongside major increases in energy storage to accommodate the extra power.
A draft version of California ISO’s (CAISO) 20-Year Transmission Outlook report providing a roadmap for the next two decades and a draft 2021-2022 Transmission Plan covering the next 10 years, was issued today.
Try Premium for just $1
- Full premium access for the first month at only $1
- Converts to an annual rate after 30 days unless cancelled
- Cancel anytime during the trial period
Premium Benefits
- Expert industry analysis and interviews
- Digital access to PV Tech Power journal
- Exclusive event discounts
Or get the full Premium subscription right away
Or continue reading this article for free
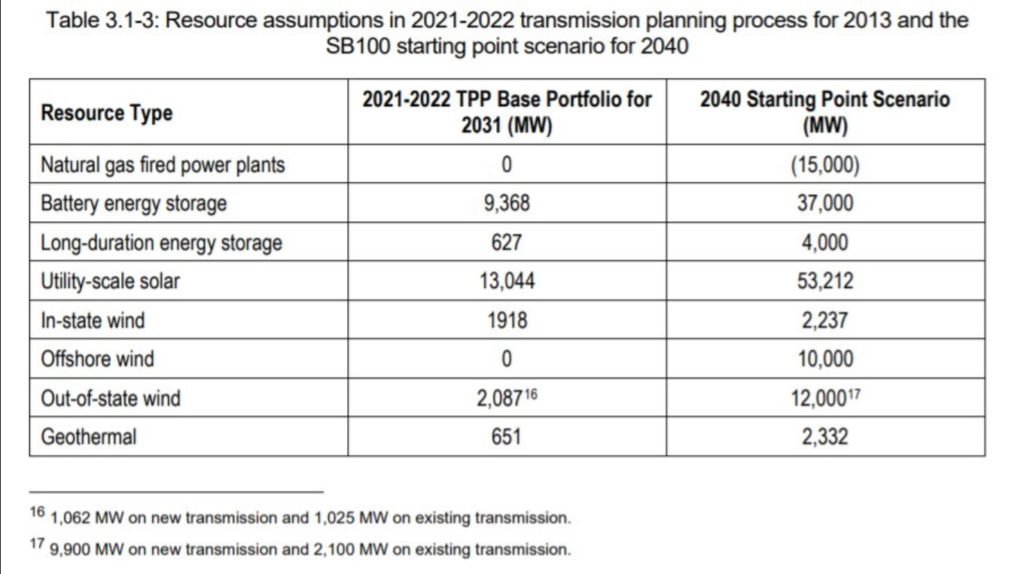
It outlined that by 2045, the state would require 53GW of utility-scale solar, 37GW of battery energy storage systems (BESS), 4GW of long-duration storage and more than 2GW of geothermal, alongside 24GW of wind power reserves, all of which need to be connected to the grid.
Created in collaboration with the regulatory California Public Utilities Commission (CPUC) and the state government’s California Energy Commission, the draft plan will be voted on in March by CAISO’s Board of Governors.
California’s grid and wholesale markets operator based its solar predictions on “known commercial interest to allocate solar development to transmission zones”.
The planned investment will be a boon for solar deployment in California and elsewhere, Rob Gramlich, founder and president of Grid Strategies LLC and a frequently testifier to the US congress on transmission related issues, told PV Tech. “I think it can help solar development in other areas across the desert Southwest serve California. Solar developers can use the lower cost of land outside California, and the earlier daily sun patterns to provide energy at different times.”
The report said, “transmission needs will range from high-voltage lines that traverse significant distances to access out-of-state resources”, with lead times for such upgrades ranging from eight to 10 years being “reasonable or optimistic”.
“This highlights the need for longer-term decisions to be made and development activities to be initiated in the annual transmission planning processes,” it said as it looked past typical 10-year-ahead timeframes.

“This is exactly the type of planning for the future that all grid authorities should be doing,” said Gramlich. “California needs clean energy that produces at different times in a day, and this plan integrates offshore wind, Nevada geothermal, solar from other time zones, and wind from Wyoming and Idaho,” said Gramlich.
“All regions should be looking at the resources available to them this way and seeking geographic diversification through transmission.”
Last month, the US Department of Energy (DOE) launched a “Building a Better Grid” initiative to catalyse the development of “new and upgraded high-capacity electric transmission lines” across the US under President Joe Biden’s US$1 trillion Bipartisan Infrastructure Bill.
The CAISO report forecast that the state’s peak load in 2040 would be 82.3GW, up from an estimated 64.1GW in 2030. It said CAISO would need to accommodate 73.9GW of this through its network.
CAISO, which currently has almost 80GW of solar and 148GW of storage in its interconnection queue, said California was facing “an unprecedented need for new renewable resources over the next 10 to 20 years”.
Renewables supplied 33% of California’s electricity needs in 2020, including power imported from neighbouring states, according to the California Energy Commission.
In 2018, Senate Bill 100 was passed that increased the renewables requirement for electric utilities to 50% by 2026, 60% by 2030, and 100% by 2045.
In order to create its roadmap, CAISO identified transmission network needs “by mapping resources to the appropriate regions, identifying the transmission additions necessary to add those resources to the grid, and then examining the need to deliver those resources over the bulk transmission system.”
At the end of last year, PV Tech Premium looked at what the global grid system might look like in 2030 through conversations with analysts, experts and transmission companies. The analysis touched on themes identified in CAISO’s report and you can read it in full here.






