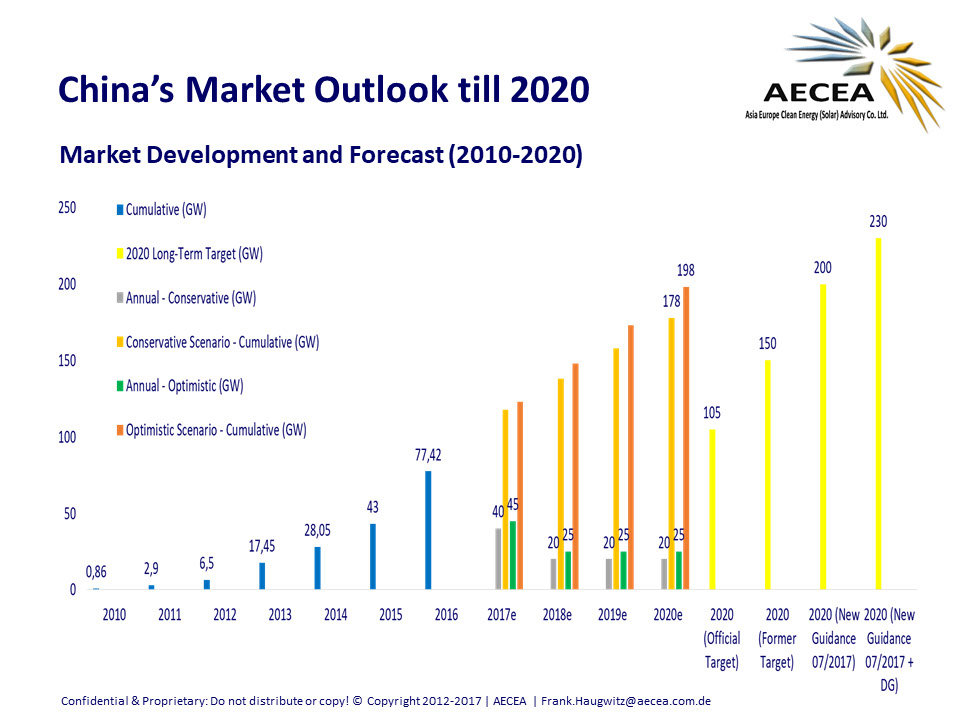
According to independent solar industry advisory firm AECEA, China has already exceeded its 13th Five-Year-Plan (2016-2020) target of 105GW by installing around 10.52GW of solar in July, after record first half 2017 installations of 24.4GW.
China’s National Energy Administration (NEA) had previously stated that in the first half of 2017 a total 24.4GW of solar was grid connected. Demand growth in the second half of the year is being fuelled by an expected 5.5GW of ‘Top Runner’ project deadlines at the end of September, 2017 and a government target of 8GW of ‘Poverty Alleviation’ schemes through the year.
Try Premium for just $1
- Full premium access for the first month at only $1
- Converts to an annual rate after 30 days unless cancelled
- Cancel anytime during the trial period
Premium Benefits
- Expert industry analysis and interviews
- Digital access to PV Tech Power journal
- Exclusive event discounts
Or get the full Premium subscription right away
Or continue reading this article for free
With 10.52GW of solar installations in July, AECEA has raised its 2017 forecast and estimates that China might be able to install between 40GW and up to 45GW by the end of the year. This could equate to a 16% year-on-year growth rate but could reach as much as a 30% increase over record installs in 2016.
Growth of solar was said to be far outstripping other energy sources in 2017. AECEA noted that 1.09GW of new nuclear energy was added in China between January and July, while hydro added 6.69GW and wind added 7.3GW.
China added a total of 18.84GW of thermal power, yet solar easily surpassed that figure at around 34.92GW in the January to July timeframe.






