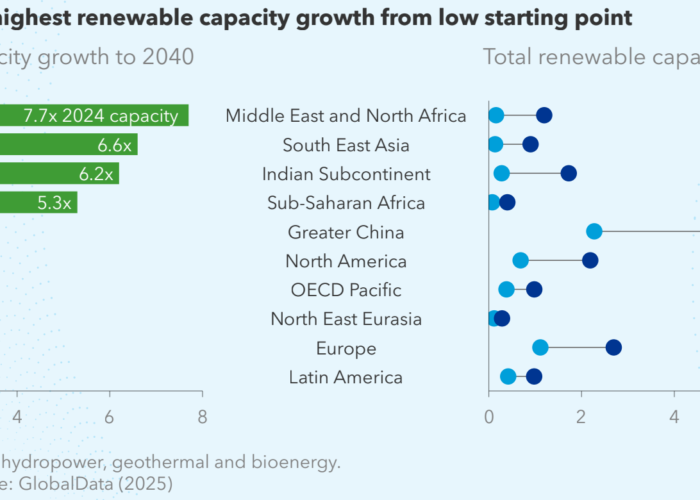
The European Commission (EC) has published an action plan to accelerate the rollout of electricity grids and increase grid efficiency.
The EC said in the plan that renewable generation projects face long wait times to obtain connection rights in many countries. Currently, the waiting time for permits for grid reinforcements is between four and ten years, and eight and ten years for high-voltage deployments.
Try Premium for just $1
- Full premium access for the first month at only $1
- Converts to an annual rate after 30 days unless cancelled
- Cancel anytime during the trial period
Premium Benefits
- Expert industry analysis and interviews
- Digital access to PV Tech Power journal
- Exclusive event discounts
Or get the full Premium subscription right away
Or continue reading this article for free
The plan aims to address the main challenges in expanding, digitalising and better using EU electricity transmission and distribution grids.
The EC identified 14 actions under seven categories for accelerating the pace of grid development in Europe, with the first one being accelerating the implementation of Projects of Common Interest (PCI) and developing new projects through political steering, reinforced monitoring and encouraging more proposals for new projects.
To accelerate the completion of PCIs, the EC, member states and project promoters will prioritise the implementation of PCIs and Projects with Mutual Interests (PMIs) already identified from 2024 onwards. Based on reinforced monitoring of project implementation, project promoters need to update member states and the EC on the progress and to identify issues to be solved, including permitting.
Second, the action plan will improve the long-term planning of grids to accommodate more renewables and electrified demand, including hydrogen, in the energy system by steering the work of system operators as well as national regulators.
Starting from the first quarter of 2024, the European Network of Transmission System Operators (ENTSO-E) will enhance top-down planning towards 2050 by integrating the identification of offshore and onshore system needs and further considering hydrogen.
“This action plan for grids requires strong governance”
“The EC’s EU action plan for grids clearly brings into focus the critical role of electricity grids in achieving the European energy transition. We believe that this action plan for grids requires strong governance to track the delivery of the targets, ensuring milestones are achieved, and challenges are addressed in a timely manner,” said Damian Cortinas, chair of the board of ENTSO-E.
In the introducing regulatory incentives for forward-looking grid build-out category, the EU DSO Entity – the association for all sizes of Distribution System Operators (DSOs) in Europe – will support DSO grid planning by mapping the existence and characteristics of distribution development plans by mid-2024.
The EC will also propose guiding principles to identify conditions under which anticipatory investments in grid projects should be granted by Q1 2025.
Starting from mid-2024, the EC will issue guidance on cross-border cost sharing for offshore projects.
The EC will incentivise better usage of the grids with three actions. First, ENTSO-E and the EU DSO Entity will agree on shared definitions for available grid hosting capacity for system operators and establish a pan-EU overview. Both organisations will promote the uptake of smart grid, network efficiency and innovative technologies starting from Q4 2024.
The Agency for the Cooperation of Energy Regulators (ACER), in its next tariff report, will recommend best practices in relation to the promotion of smart grids and network efficiency technologies through tariff design, focusing on consideration of operating expenses in addition to capital expenditure and benefit sharing.
Other areas in the action plan include improving access to finance, accelerating deployment through faster permitting and public engagement and strengthening grid supply chains.
“Our action plan will ensure better support to infrastructure planning, development and operation, central steps to connect Europe’s growing renewable energy sources to the end-users that need them – from households to hydrogen producers,” said Maroš Šefčovič, EC vice-president for institutional relations.
More provisions needed
Naomi Chevillard, head of regulatory affairs at SolarPower Europe, commented: “The grids action plan is an excellent and necessary initiative from the European Commission. This will help solar project developers efficiently locate their projects, and unlock the massive grid queues in the EU.”
But she added that the action plan lacks “concrete, regulatory provisions to support the easy win of growth and integration of flexibility at all voltage levels”.
“Flexibility is immediately available at the consumer’s house, where elements of grid infrastructure need up to ten years to be deployed. Today’s plan falls short of clarifying the EU regulatory framework for storage with regard to taxation or treatment of stored renewable electricity, and risks endangering flexibility growth with its ambiguous regulatory framework,” she commented.
According to the EC, electricity consumption in the EU is expected to increase by about 60% between now and 2030. With rooftop solar and more offshore renewables coming online, the EU energy network needs to accommodate a more digitalised, decentralised and flexible electricity system.
Overall, the EC estimates that €584 billion in investments are necessary for the electricity grids this decade, as 40% of distribution grids are more than 40 years old, and cross-border transmission capacity is due to double by 2030. Wind and solar generation capacity must increase from 400GW in 2022 to at least 1,000GW by 2030, including a large build-up of offshore renewables of up to 317GW, to be connected to existing grid infrastructure.
More details on the action plan can be read here.