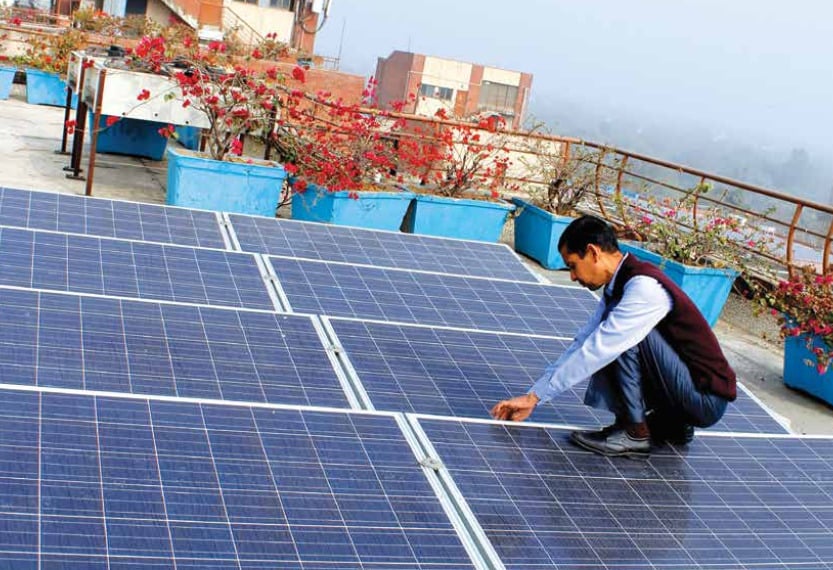
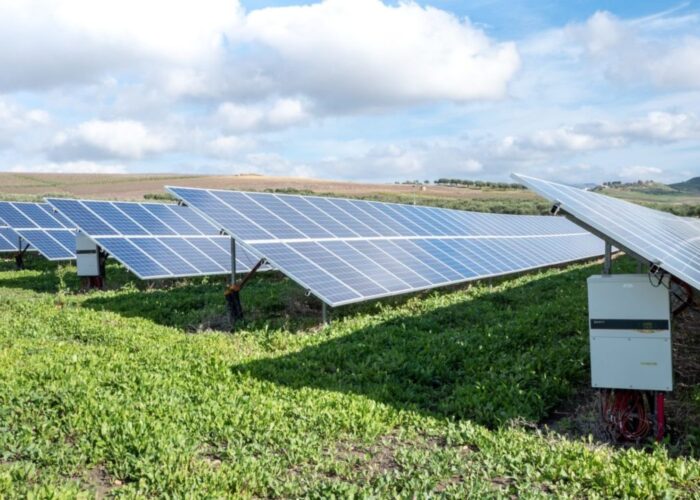
The government of the Indian state of Madhya Pradesh has introduced its 2016 policy for decentralized renewable energy systems with a particular focus on rooftop solar PV.
The aim is to reduce the burden on conventional sources of energy and lower distribution losses. Meanwhile, consumer electricity bills can be lowered and energy independence increased.
Unlock unlimited access for 12 whole months of distinctive global analysis
Photovoltaics International is now included.
- Regular insight and analysis of the industry’s biggest developments
- In-depth interviews with the industry’s leading figures
- Unlimited digital access to the PV Tech Power journal catalogue
- Unlimited digital access to the Photovoltaics International journal catalogue
- Access to more than 1,000 technical papers
- Discounts on Solar Media’s portfolio of events, in-person and virtual
The technology neutral policy still has the major focus on distributed solar PV rooftop systems as they have “the largest potential for mass replication amongst consumers and small independent power producers”, according to the state policy makers.
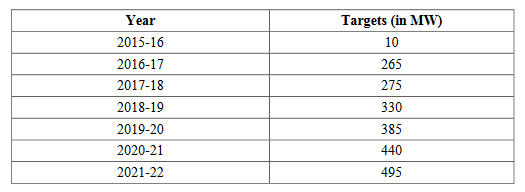
Out of the target of 40GW of solar rooftop targeted by India’s Ministry of New and Renewable Energy by 2022, Madhya Pradesh has been allotted a target of 2.2GW. The annual capacity of targets for grid-connected solar rooftop projects is as follows:
The grid-connected systems included involve net metering, gross metering with wheeling and banking, as well as self-consumption. Off-grid systems are also encouraged.







