Recently billed by solar industry experts as another degradation crisis that could be worse than the impact on PV module performance than PID (potential Induced Degradation), ‘Silicon Module Super League’ (SMSL) member, Hanwha Q CELLS has highlighted that both its mono and multicrystalline products have performed exceptionally well in LeTID (Light and elevated Temperature Induced Degradation) tests undertaken by Fraunhofer CSP.
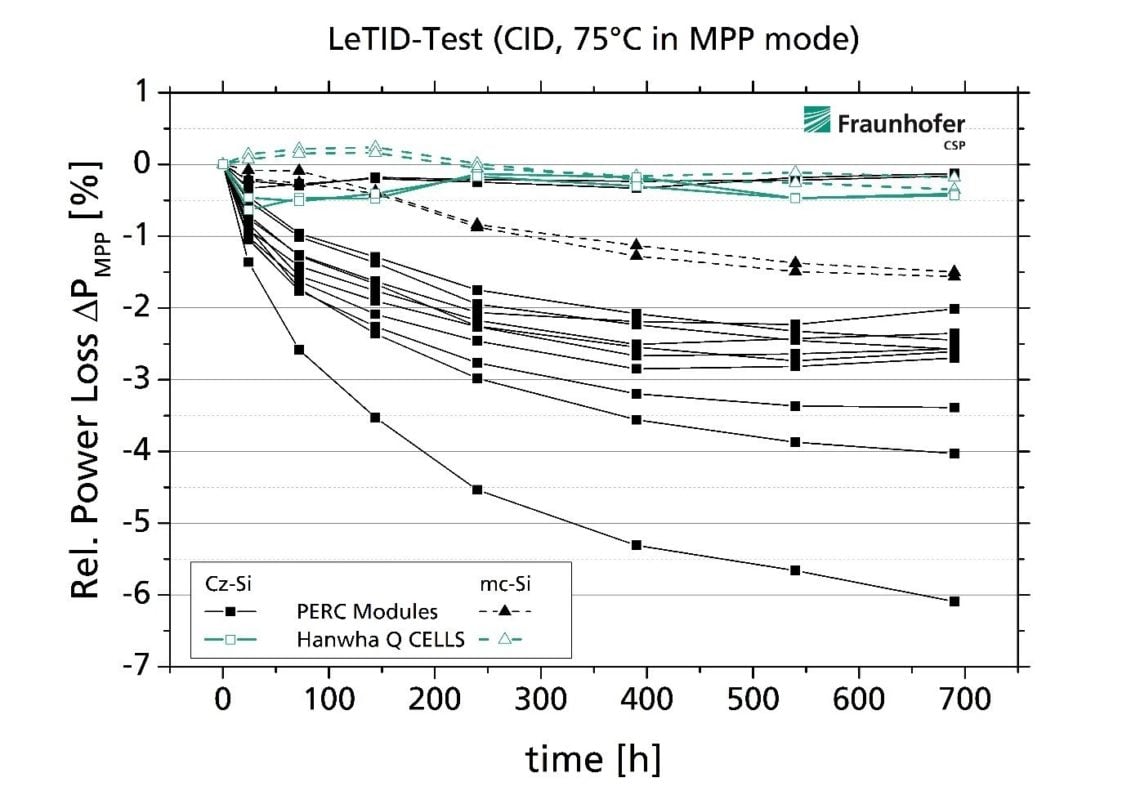
Both Hanwha Q CELLS' half-cell monocrystalline ‘Q.PEAK DUO’ modules and multicrystalline ‘Q.PLUS’ modules were reported to have exhibited little impact due to LeTID, this among nine module types tested by Fraunhofer CSP.
Try Premium for just $1
- Full premium access for the first month at only $1
- Converts to an annual rate after 30 days unless cancelled
- Cancel anytime during the trial period
Premium Benefits
- Expert industry analysis and interviews
- Digital access to PV Tech Power journal
- Exclusive event discounts
Or get the full Premium subscription right away
Or continue reading this article for free
Hanwha Q CELLS' two different module types exhibited <1% power loss during Fraunhofer CSP's testing procedure.
Hanwha Q CELLS Co., Ltd. CTO Daniel Jeong said: “The performance of our Q.PEAK DUO and Q.PLUS modules demonstrates Hanwha Q CELLS' continued commitment to tackling the toughest challenges in the industry and highlights the importance of focusing our R&D efforts in areas where we can deliver the most added value to our customers.”
“Hanwha Q CELLS is proud to be at the forefront of anti-LeTID technology and will continue to shape and support the solar industry by developing new photovoltaic technologies and tackling head-on the technical hurdles that arise. We do this to ensure that our products are the go-to option for discerning developers who want to install quality that lasts and performs reliably, regardless of the conditions,” assed Jeong.
Recently, PV Tech posted a technical blog from Radovan Kopecek, Joris Libal and Lejo J. Koduvelikulathu from ISC-Konstanz on LeTID, which can be found here.






