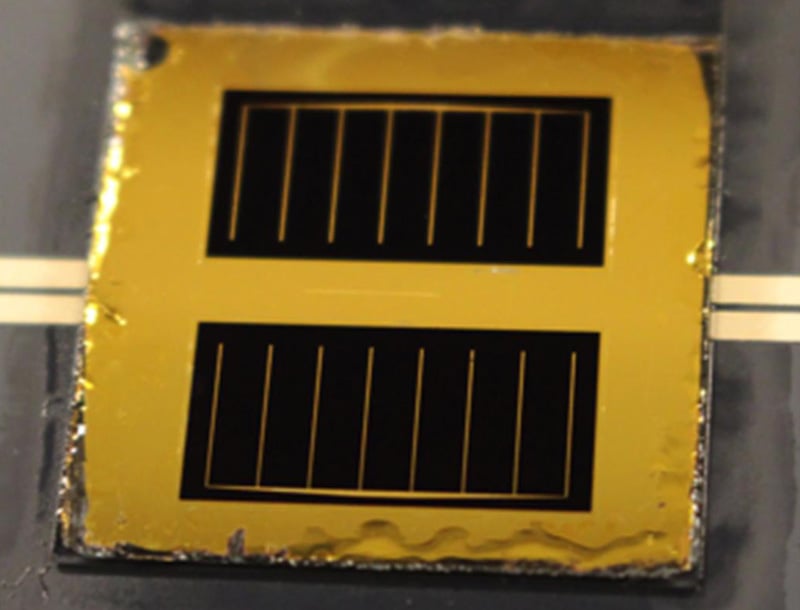
Collaboration by the U.S. Energy Department's National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL) and at the Swiss Center for Electronics and Microtechnology (CSEM) has set a certified record conversion efficiency of 29.8% for a III-V/Si solar cell.
The mechanically stacked and separately made solar cell was comprised of a silicon heterojunction base cell with a gallium indium phosphide cell on top, giving it a dual-junction formation that “exceeded the theoretical limit of 29.4 percent for crystalline silicon solar cells,” according to senior researcher at NREL, David Young.
Try Premium for just $1
- Full premium access for the first month at only $1
- Converts to an annual rate after 30 days unless cancelled
- Cancel anytime during the trial period
Premium Benefits
- Expert industry analysis and interviews
- Digital access to PV Tech Power journal
- Exclusive event discounts
Or get the full Premium subscription right away
Or continue reading this article for free
“We believe that the silicon heterojunction technology is today the most efficient silicon technology for application in tandem solar cells” said, Christophe Ballif, head of PV activities at CSEM.
“CSEM partnered with the NREL scientists with the objective to demonstrate that 30 percent efficient tandem cells can be realized using silicon heterojunction bottom cells, thanks to the combination with high performance top cells such as those developed by NREL,” said Matthieu Despeisse, the manager of crystalline silicon activities at CSEM.
A new design for the dual-junction solar cell and contributions from CSEM were said to be key to setting the new record, yet greater efficiencies are possible with closer collaboration, according to the research centres.
Multi-junction cells hold the promise of significantly higher efficiencies than that of conventional silicon cells but have remained extremely expensive to fabricate and confined to niche space markets.
Ultimately, at some future point in time, sequential high-volume thin-film deposition techniques could produce lower-cost cells.





