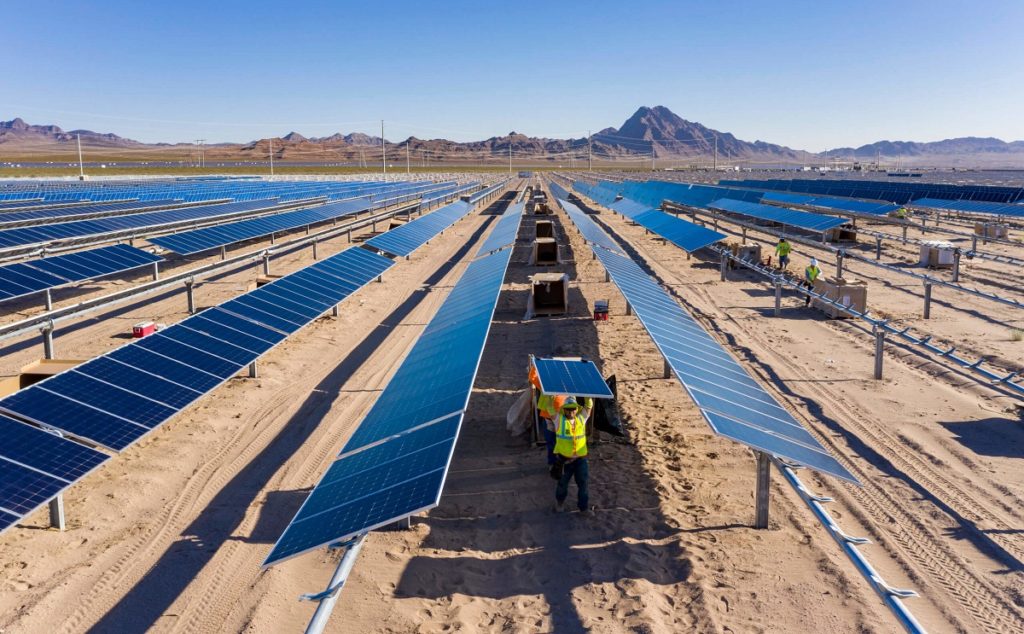
Utility-scale solar PV in the US could be as a cheap as US$16.89/MWh by the end of the decade, new analysis published by the National Renewable Energy Lab (NREL) has shown.
Research institute NREL has published its 2021 Annual Technology Baseline (ATB) report which provides electricity generation technology cost and performance data to inform the US electricity sector.
Try Premium for just $1
- Full premium access for the first month at only $1
- Converts to an annual rate after 30 days unless cancelled
- Cancel anytime during the trial period
Premium Benefits
- Expert industry analysis and interviews
- Digital access to PV Tech Power journal
- Exclusive event discounts
Or get the full Premium subscription right away
Or continue reading this article for free
It has highlighted how the levelised cost of energy (LCOE) in 2019 for utility-scale PV ranged from US$31.32/MWh for ‘class 1’ solar PV, effectively NREL’s most cost-effective class, to US$50.23/MWh for ‘class 10’.
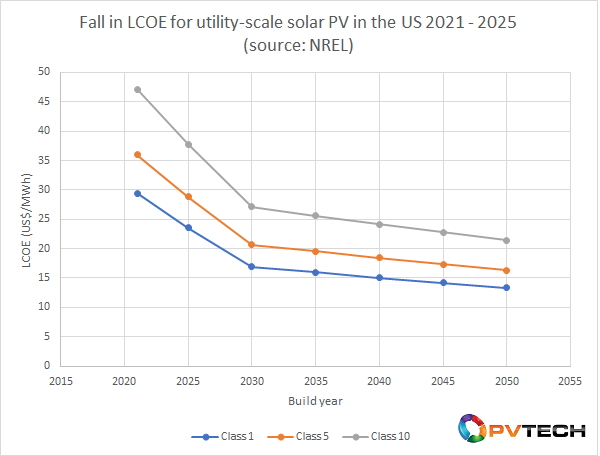
It expects LCOEs to fall to between US$29.39/MWh and US$47.14/MWh for class 1 and class 10 projects this year, with a central ‘class 5’ estimate of US$35.98/MWh, before tumbling to between US$16.89/MWh and US$27.10/MWh by 2030.
While costs will continue to fall out to 2050, NREL’s analysis shows a levelling off of cost reductions. According to this year’s ATB, class 1 solar PV will be able to generate at US$15.06/MWh in 2040 and US$13.35/MWh by 2050. The below graph shows NREL’s cost trajectory for solar out to 2050, while also highlighting the narrowing of the differences in LCOE between class 1 and class 10 utility-scale solar PV over those years.
The ATB collates current and projected data into one format for energy analysts, modelers and system planners. It is based on original projections for the renewable and storage technologies and scenarios for technologically-based innovation for fossil fuels.
“Comparisons of possible future power systems depend on assumptions and scenarios,” said Laura Vimmerstedt, NREL energy analyst and ATB project lead. “The ATB provides critical cost and performance assumptions for energy analysis, including studies at national labs and beyond.”






