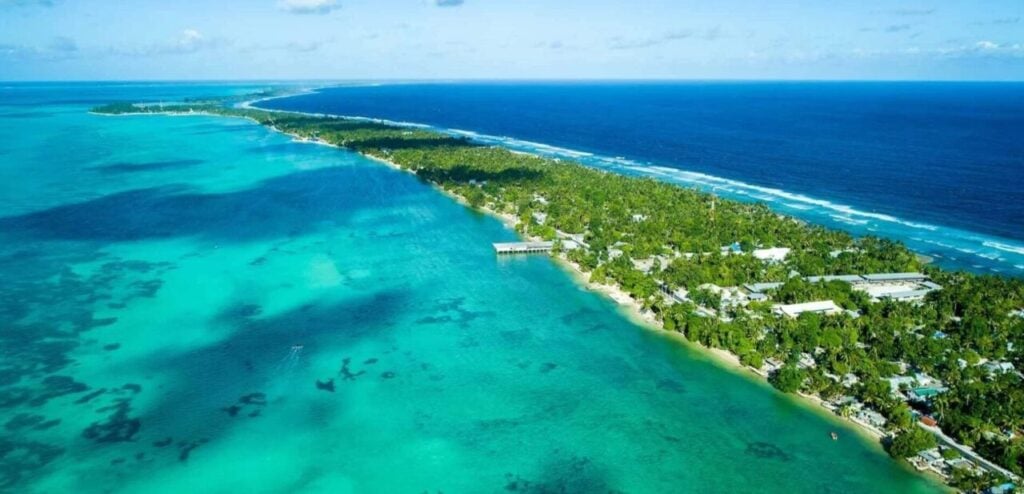
Australian module manufacturer Tindo Solar has supplied 70 of its 430W N-Type bifacial Walara solar modules to power data cable landing stations for the East Micronesia Cable System (EMCS) project in the Pacific nations of Nauru and Kiribati.
The EMCS project, jointly funded by Australia, the United States and Japan at a cost of approximately US$95 million, comprises 2,250km of undersea data cable linking Tarawa in Kiribati to Nauru and to Kosrae and Pohnpei in the Federated States of Micronesia.
Try Premium for just $1
- Full premium access for the first month at only $1
- Converts to an annual rate after 30 days unless cancelled
- Cancel anytime during the trial period
Premium Benefits
- Expert industry analysis and interviews
- Digital access to PV Tech Power journal
- Exclusive event discounts
Or get the full Premium subscription right away
Or continue reading this article for free
When completed in late 2025, the infrastructure will deliver high-speed data connectivity to approximately 100,000 people across these Pacific Island nations.
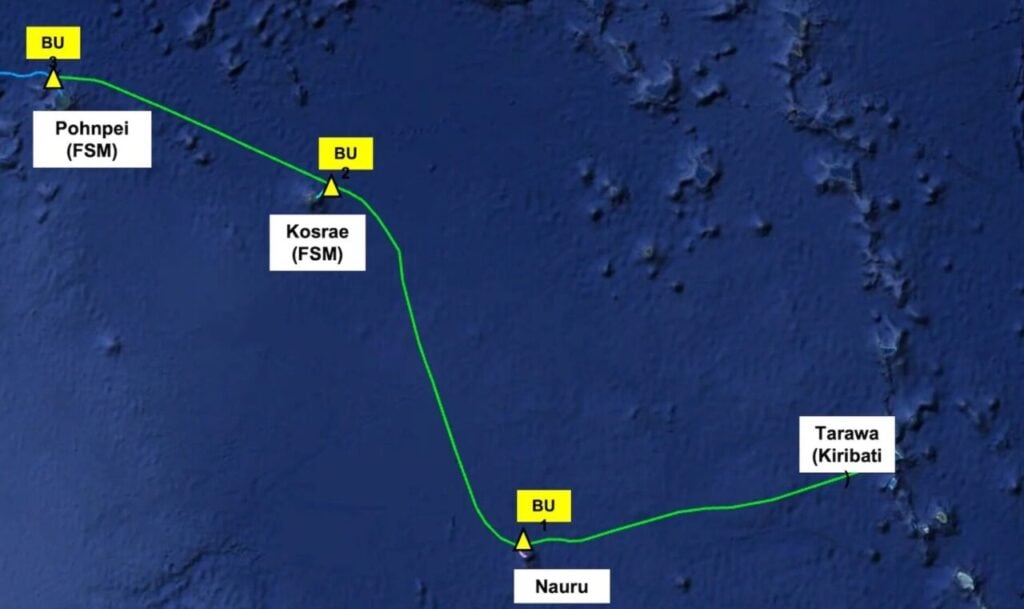
Tindo’s solar modules will power the cable landing stations that house critical optical transmission and power feed equipment for the submarine cable system.
These stations, positioned at the water’s edge in highly humid environments, require reliable and durable power solutions that can withstand challenging coastal conditions.
The procurement partner to the East Micronesia Cable, P.R.A. Electrical Pty Ltd (PRA), which has expertise in South Pacific projects, evaluated the undersea cable project as requiring high-quality solar panels with guaranteed performance and durability.
Chris Atkinson, project manager from PRA, noted that Tindo’s Walara modules are designed to withstand extreme conditions, such as the humidity at these landing stations.
“The landing stations are on the water’s edge, and it’s very humid in these countries. Tindo has a proven lamination process that doesn’t allow condensation under the glass, and the panels are also cyclone-rated, which makes them well-suited to this type of infrastructure,” Atkinson said.
Tindo Solar’s Walara solar PV modules
The modules supplied for the EMCS project are Tindo’s 430W Walara G3P modules, which feature N-Type bifacial technology with 108 half-cut cells.
The bifacial design allows the module to capture sunlight from both sides, significantly boosting overall power output – a critical feature for maximising energy generation in space-constrained infrastructure applications.
The Walara series includes 3.2mm fully tempered double ARC glass and is housed in an anodised aluminium alloy frame with an IP68-rated junction box.
Tindo has independently tested these modules for cyclone resistance, hail impact, damp heat tolerance, and thermal performance across a range of -40°C to 85°C, making them particularly suitable for the challenging environmental conditions of Pacific Island nations.
All modules shipped by Tindo come with a 25-year product and a 25-year performance warranty, guaranteeing power output will be at least 87.4% of the nominal output power at the end of the warranty period.
Manufacturing capabilities and expansion plans
This Pacific project represents another export agreement for the Adelaide-based manufacturer, which has been expanding its international footprint. Earlier this year, Tindo secured a 15MW export agreement with Vietnam, worth AU$8.4 million (US$5.47 million) over five years.
The company also inked a 30MW module supply agreement earlier this year for Australia’s first “net zero pipeline” project in North Queensland, with deliveries scheduled for 2026 and 2027.
Tindo currently manufactures its modules at its facility in Mawson Lakes in Adelaide’s northern suburbs. The facility has the capacity to produce 360,000 modules annually, equivalent to approximately 150MW.
However, the company’s manufacturing capabilities are set to expand following its success in the Solar Sunshot Program, where it secured an AU$34.5 million federal government funding award.
This funding will support upgrading Tindo’s Adelaide manufacturing facility, boosting solar module production from 20MW to 180MW per year and introducing advanced automation processes.
The company has also outlined more ambitious plans to construct an AU$100 million factory that could increase its output by 1GW per year.
Tindo has also been advancing its technological capabilities through strategic partnerships, such as its collaboration with the University of New South Wales to develop tunnel oxide passivated contact (TOPCon) technology.
This partnership has enabled Tindo to enhance the efficiency and performance of its N-type solar modules. The company recently launched its Walara G4P series featuring TOPCon technology.






