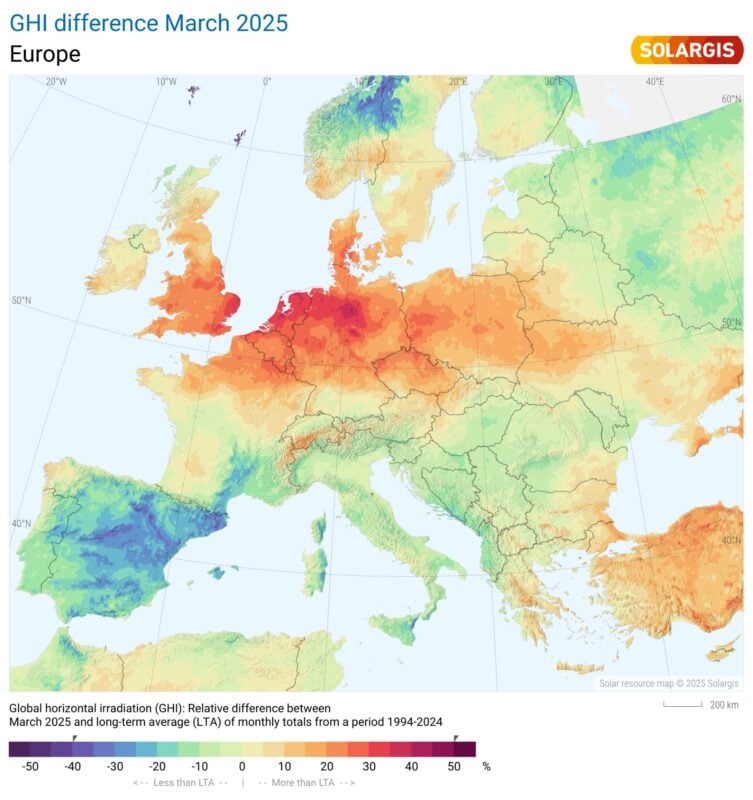
Solar irradiation in Western Europe has increased by 50% above-average during Spring, according to an analysis by weather data and software provider Solargis.
During the months of March, April and May, the region has seen solar irradiance levels higher than historical long-term (over the past 30 years) averages, which created favourable conditions for solar energy generation, according to the company.
Try Premium for just $1
- Full premium access for the first month at only $1
- Converts to an annual rate after 30 days unless cancelled
- Cancel anytime during the trial period
Premium Benefits
- Expert industry analysis and interviews
- Digital access to PV Tech Power journal
- Exclusive event discounts
Or get the full Premium subscription right away
Or continue reading this article for free
In March 2025, parts of Belgium, Germany, and the UK saw levels of Global Horizontal Irradiation (GHI) increase up to 50% above long-term averages, according to data from Solargis. In April, most of North-Western Europe registered levels 35% above average, while Southern Europe countries—Spain, Portugal, and Italy—experienced the opposite, with up to 25% lower irradiance. Scotland registered a 35% increase in GHI compared to average figures.
Helped by the surge in solar irradiance between March and May, the UK has seen its power output rise by 42% from the same period in 2024, with solar PV generating 7.6TWh of electricity in the first five months of 2025. For the first time, the country also saw solar PV account for more than 10% of its electricity generation in April and May.
Moreover, the increased availability of solar resources has created opportunities for higher-than-expected energy yields and “underscores the growing need for precise forecasting and project evaluation solutions”, according to Solargis.
Due to the difference between regions – with Western Europe irradiance above average this Spring and Southern Europe below – Solargis said that high-resolution time series data is becoming essential for PV developers and operators. “As solar stakeholders increasingly prioritise precision, adopting time series as the industry standard will support more resilient and optimised energy generation,” added Solargis.






