Australia’s Energy Corporation of New South Wales (EnergyCo) has formally increased the amount of renewable energy generation and energy storage projects that can connect to the Central-West Orana Renewable Energy Zone (REZ) to 7.7GW.
As revealed by the state-owned energy company yesterday (16 January), the increase has been enabled by increasing the intended network capacity for the REZ from 3GW to 6GW. This was achieved following a headroom assessment that started in early August 2024.
Unlock unlimited access for 12 whole months of distinctive global analysis
Photovoltaics International is now included.
- Regular insight and analysis of the industry’s biggest developments
- In-depth interviews with the industry’s leading figures
- Unlimited digital access to the PV Tech Power journal catalogue
- Unlimited digital access to the Photovoltaics International journal catalogue
- Access to more than 1,000 technical papers
- Discounts on Solar Media’s portfolio of events, in-person and virtual
The New South Wales government initially announced an increase in the REZ’s intended network capacity in December 2023. Still, EnergyCo had yet to formally confirm an increase in projects able to connect.
The network capacity of the Central-West Orana West REZ will initially operate at 4.5GW. This network capacity enables up to 7.7GW of solar PV, wind and battery energy storage system (BESS) projects to inject power into the grid, as they will be doing so at different times of the day and not all exporting energy simultaneously, EnergyCo said.
One of the perks of this increased capacity means that projects listed within the Central-West Orana REZ Environmental Impact Statement (EIS), submitted in October 2023, which included measures to avoid, minimise, or mitigate potential environmental and community impacts, could add additional co-located BESS to capture renewable energy generated from solar PV and wind to be exported at times of low output.
EnergyCo also confirmed that the increase in capacity means that the company would increase the Community and Employment Benefit funding from access fees, which is currently at an initial AU$128 million (US$79 million).
The Central-West Orana REZ will be built on roughly 20,000 km2 near Dunedoo, Mudgee, and Dubbo, a rural area about 330km northwest of Sydney. It will potentially unlock an estimated AUS$20 billion in private investment in solar PV, wind, and energy storage. Below is a map of the REZ.
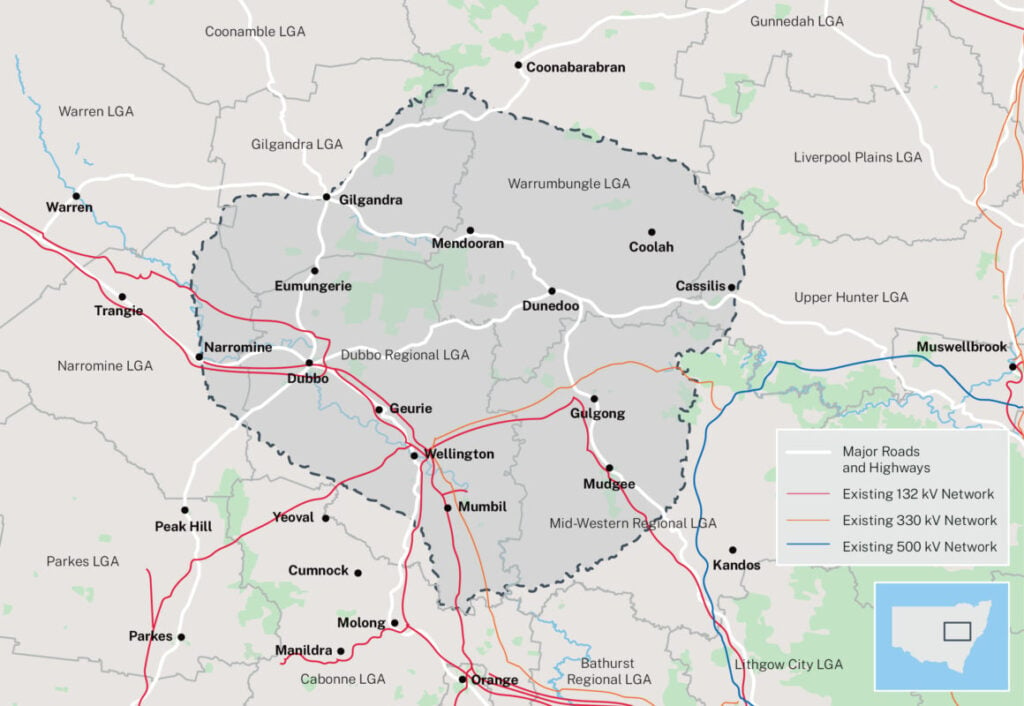
Australia’s REZ initiatives critical to the withdrawal of coal-fired power
REZs are each deemed critical infrastructure projects. They combine transmission infrastructure with large-scale energy generation, such as solar PV and wind, alongside energy storage capabilities. EnergyCo describes them as the “modern-day equivalent of power stations.”
Australia’s various REZs will be a critical juncture for its energy transition, mainly as it looks to wean itself off of fossil fuels, particularly with the withdrawal of its coal-fired power plants.
The Central-West Orana REZ is unique in that it is the first in the country to have transitioned into the delivery phase after receiving Commonwealth planning approval in August 2024. Following a competitive tender, EnergyCo selected a consortium of Acciona Concesiones, Cobra, and Endeavour Energy called ‘ACEREZ’ as the preferred network operator to deliver the Central-West Orana REZ transmission system.
The NSW government is developing at least five separate multi-gigawatt REZ facilities connected to the grid and partially using long-duration energy storage (LDES) to replace traditional centralised power plants. The five REZs include the Hunter-Central Coast, the South-West, New England, Central-West Orana, and Illawarra.
However, it is worth noting that REZ is not exclusive to New South Wales, with additional zones being explored in multiple states. Queensland, for instance, recently published a roadmap detailing how it would develop its 12 REZs. Victoria, on the other hand, has identified six REZ locations.
The potential of ‘inland REZ’
A report released by Australian transmission system operator Transgrid last year signalled that remote inland REZ areas could provide an additional boost to the country’s decarbonisation efforts. Western New South Wales was noted as a region with “excellent potential.”
According to Transgrid, the western portion of the state has “excellent” solar and wind resources on underutilised, low-density land. Should these developments be pursued, these inland REZ areas could provide critical grid-balancing services for the National Electricity Market (NEM).
Remote inland REZs could be developed across several locations in New South Wales, including Broken Hill, Noona, and the Northwest Horizon regions. Transgrid said these regions have “some of the best” solar and wind resources readily available anywhere on the NEM.
Developing diverse renewable energy generation in inland REZs could also facilitate cost-effective asset buildout. According to Transgrid, the Levelised Cost of Transmission (LCOT) may be lower due to longer transmission asset life, with potential cost reductions from smaller generators and reduced storage needs.
It added that the organisation was actively exploring the viability of the inland REZs and developing multiple corridors from existing networks to connect them to the NEM.







