A new manufacturing method has produced perovskite-silicon tandem solar cells with a conversion efficiency of 27.8%, and has “a path to the large-scale production” of the technology.
Researchers from the Fraunhofer Institute for Solar Energy Systems (Fraunhofer ISE) and the King Abdullah University for Science and Technology (KAUST), based in Germany and Saudi Arabia, respectively, developed the “hybrid route” and announced it today.
Try Premium for just $1
- Full premium access for the first month at only $1
- Converts to an annual rate after 30 days unless cancelled
- Cancel anytime during the trial period
Premium Benefits
- Expert industry analysis and interviews
- Digital access to PV Tech Power journal
- Exclusive event discounts
Or get the full Premium subscription right away
Or continue reading this article for free
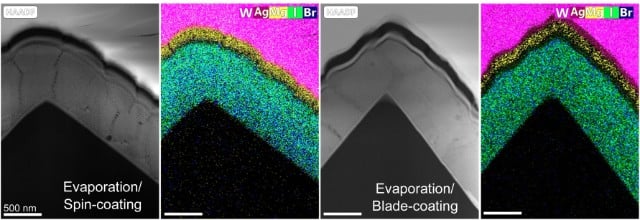
The system involves two steps: the evaporation of the inorganic components of the perovskite absorber, then the blade-coating of the organic perovskite components onto a silicon bottom cell, which the researchers said does not interfere with the thickness of the perovskite layer, a key component in maximising conversion efficiency.
The method builds on existing perovskite production processes, including the spin-coating method and the blade-coating method. In laboratory testing, the spin-coating method sees perovskite layers deposited on a rotating silicon base, but the process is thought to be unfeasible for scaling up to industrial production.
“Spin-coating is great as a lab technique as it is very flexible and allows for rapid testing of new materials, additives and process parameters. For large scale production it is however not suitable”, said Dr Juliane Borchert, group lead on perovskite materials and interfaces at Fraunhofer ISE. “We also expect that the learnings about the dynamics during blade-coating can be transferred to slot-die-coating, which is even more suitable for scaling.”
Towards commercial-scale perovskites
Scaling up perovskite production is the primary challenge for proponents of the technology. While perovskite cells are often shown to have a higher conversion efficiency than conventional silicon cells, the lack of industrial-scale perovskite production has raised questions about the future of the technology.
Last year, ISC Kostanz co-founder Radovan Kopecec dismissed the so-called “perovskite populists”, who had put, in his opinion, undue faith in a technology without sufficient commercial-scale deployment.
However, others in the industry have sought to invest in perovskite research and deployment. Earlier this year, UK perovskite solar company Oxford PV and Chinese solar manufacturer Trinasolar entered into a patent licensing agreement for perovskite-based technologies, after the former completed the world’s first commercial scale of perovskite-silicon tandem modules.
The latest Fraunhofer ISE-KAUST research follows the latter’s development of a synthetic molecule that can improve a perovskite cell’s energy efficiency and longevity. Last month also saw perovskite-silicon tandem cells belonging to Korean module manufacturer Qcells pass a number of stress tests, verified by quality assurance body TÜV Rheinland.






