India’s rapidly progressing solar sector is heavily exposed to water risks, with around 94% of installed capacity deployed in water-stressed areas, according to a new report from consultancy firm Bridge to India.
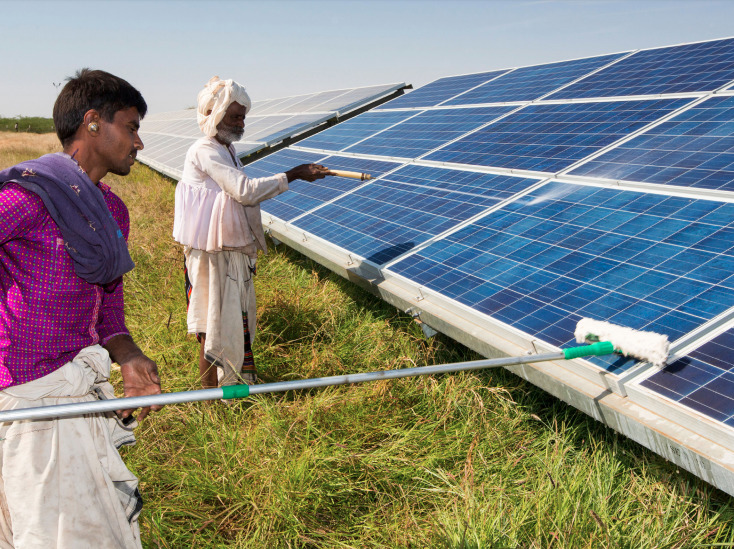
The ‘Water use in solar power sector’ report said that cleaning PV modules is critical for optimising the operation of solar plants, since soiling from the accumulation of dust, dirt, pollution, bird-droppings etc. can cause generation losses of 3-6%. Often the necessary cleaning is dependent on water use.
Try Premium for just $1
- Full premium access for the first month at only $1
- Converts to an annual rate after 30 days unless cancelled
- Cancel anytime during the trial period
Premium Benefits
- Expert industry analysis and interviews
- Digital access to PV Tech Power journal
- Exclusive event discounts
Or get the full Premium subscription right away
Or continue reading this article for free
In India, the majority of the water used in cleaning solar projects (60%) comes from bore-wells in the ground, with the remaining 40% coming from surface water sources, such as rivers, canals and lakes. The sourcing method can significantly affect water costs.
Moreover, the cost of water has doubled in many parts of the country over the last three years and Bridge to India forecasts that any further increase would start to “substantially impact” project economics.
However, Bridge to India also noted that certain technologies are available that can reduce the necessity of water use, such as robotic cleaning and anti-soiling coating.
Indeed PV Tech has reported on the use of robotic dry cleaning solutions from Isreal-based firm Ecoppia at much of the Bhadla Solar Park in Rajasthan, an extremely arid state in northwest India, as well as at Rewa Solar Park in Madhya Pradesh. Indeed Bridge to India reported that Rajasthan and neighbouring state Gujarat are the most exposed states to water-risk in India.
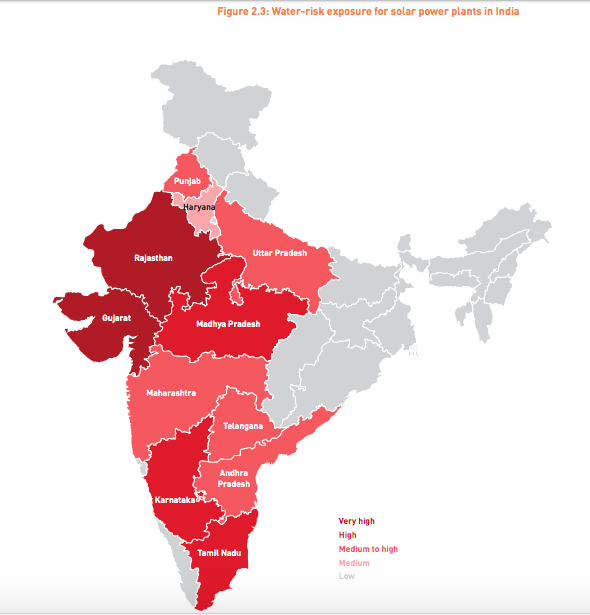
Bridge to India added that it is “imperative” that policymakers, project developers and investors start to adopt suitable mitigation technologies and bring more attention to the water usage situation.
The report covers areas such as variability of water use across projects in India, estimated consumption by state, costs of using surface water sources versus groundwater sources, as well as the technologies available to reduce water consumption. Around 3GW of power plants are currently considering various types of robotic solutions in India.
Vinay Rustagi, managing director, Bridge to India, said: “India’s solar sector is growing rapidly – total installed capacity has risen from just 1GW in 2012 to over 25GW at present and is expected to go up by over 50GW in the next five years. Rapid growth and concentration in water-stressed areas exposes solar projects to a growing water risk – scarcity, rising cost, conflict with other social and economic uses and environmental degradation.”
Bridge to India noted the irony that solar is often promoted for its efficiency in water usage compared to thermal power plants that require huge ponds of water to operate, but the locations of solar plants in India are not conducive to a plentiful water supply.
Thermal power ponds are even touted as having major potential for floating solar projects.






