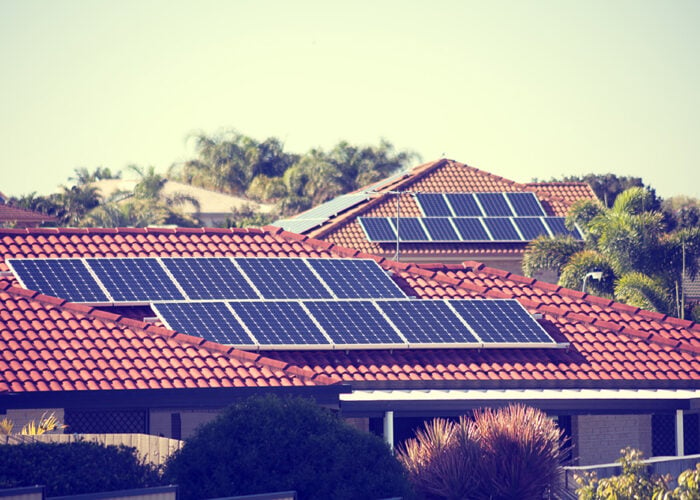
Perovskite solar cells are susceptible to severe reverse bias challenges beyond those of traditional silicon cells, which may represent further impediments to the technology’s commercialisation, according to new research.
A recent paper in the journal Joule by researchers Dongchen Lan and Martin Green from UNSW Sydney found that perovskite cells in the module that become shaded can be driven into reverse-bias operation by cells with higher current output.
Unlock unlimited access for 12 whole months of distinctive global analysis
Photovoltaics International is now included.
- Regular insight and analysis of the industry’s biggest developments
- In-depth interviews with the industry’s leading figures
- Unlimited digital access to the PV Tech Power journal catalogue
- Unlimited digital access to the Photovoltaics International journal catalogue
- Access to more than 1,000 technical papers
- Discounts on Solar Media’s portfolio of events, in-person and virtual
This, they said, demonstrated how perovskite cells “can face additional challenges beyond those of silicon cells”, which could hamper their potential commercialisation.
Reverse bias is where the electrons generated in the solar cell flow in the wrong direction, from the anode to the cathode, resulting in a significantly reduced current and output.
The scientists pointed to a lack of research on the subject of reverse bias challenges facing perovskite solar cells. “Improved understanding and resolution of these reverse-bias effect are necessary for perovskites to become a commercial reality,” they said.
Experience shows that the most demanding durability issues for fielded modules arise when cells become reverse biased, said Lan and Green.
Following their findings, the researchers proposed a number of strategies to mitigate the reverse bias they discovered. These include “subdividing a long-thin cell module into series/parallel connection of smaller cells”, which thin film manufacturer First Solar has already done for its modules after it was shown they were susceptible to transient shadows, the researchers said.
Additionally, another strategy involves providing bypass protection across each perovskite cell, rather than bypass diode for every 20 – 24 cells as is the case with most silicon modules, which Lan and Green said would be possible at lower cost.
It has been a busy year for perovskite research. In the last two months alone researchers have said perovskite-on-silicon PV modules are more environmentally advantageous than conventional silicon heterojunction (HJT) modules over a 25-year lifetime, while others have claimed two world records by achieving an efficiency of over 30% for perovskite-on-silicon-tandem solar cells.
And in June the US Department of Energy’s (DOE) National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL) revealed that a tin-lead perovskite cell can overcome problems with stability and improve efficiency, with their latest experiment yielding a 25.5% conversion efficiency.







