A transatlantic interconnection between Europe and North America could provide both grids more security and efficiency, according to a report from think tank Ember.
Grid flexibility will be required in both directions to stabilise prices (security) and, more importantly, avoid curtailment of renewable energy (efficiency).
Try Premium for just $1
- Full premium access for the first month at only $1
- Converts to an annual rate after 30 days unless cancelled
- Cancel anytime during the trial period
Premium Benefits
- Expert industry analysis and interviews
- Digital access to PV Tech Power journal
- Exclusive event discounts
Or get the full Premium subscription right away
Or continue reading this article for free
Connecting both regions could also open new opportunities for further investment in renewable energy, although this would be a secondary benefit, not a prerequisite, says Ember’s report.
The primary benefit relies on integrating the energy markets, improving grid resilience and having electricity prices reflect real-time supply and demand in both regions, thus reducing volatility.
Ember underscores two upcoming trends that will give significance to building a transatlantic interconnection, the first being the power grids to be mostly decarbonized, while the second is related to the increased electricity demand in the coming decades.
Grids on both sides of the Atlantic will be predominantly decarbonized—primarily using solar PV, wind and hydro—making them more vulnerable to changing weather conditions. This will, in turn, require more grid flexibility to match hour-by-hour electricity supply and demand.
The distance between a transatlantic interconnection project with the Xlinks project—connecting Morocco with the UK, able to export 3.6GW of capacity—and the AAPowerLink project—between Australia and Singapore through a 2GW high-voltage direct current subsea cable—would be quite similar. One major difference would be that connecting Europe with North America would be via a two-way interconnector rather than one-way transmission, allowing renewable energy capacity to go both ways.
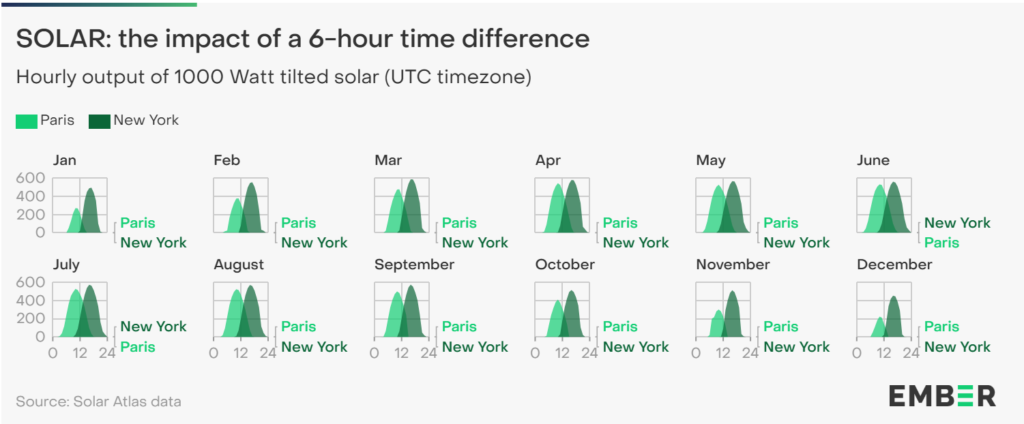
Solar PV’s key role in a 6-hour time zone difference
In the report, an example of an interconnection between France and New York explains how the excess of solar PV generation during the early afternoon in Europe could be transmitted to New York as the morning demand picks up, while the opposite would happen when France’s evening peak time receives the excess solar generation from New York.
The 6-hour difference between both sides would allow for solar PV to play a key role in providing “substantial arbitrage opportunities”.
Moreover, in order to ensure both the security and efficiency of a transatlantic interconnection, multiple cables to different landing points would be beneficial.
According to Ember, despite a high capital cost, transatlantic interconnection could prove cheaper than other alternatives, such as nuclear or hydrogen. Although the report does not analyse the financial viability of a transatlantic interconnection project, it does highlight two predominant factors: the cost of building the cables and how much government support it would get.






